exp3_0903489 - Faculty of Engineering and Technology
advertisement

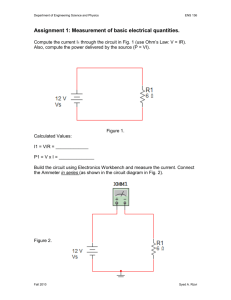
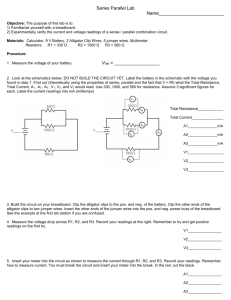
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electrical Engineering Department Power Lab. EE 489 Experiment # 3: Current, Voltage & Power Relations Across A Transmission Line ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------Objective : To determine the A, B, C & D constants of a short and medium length transmission lines and to investigate voltage, current and power relations at both ends under no load and full load conditions with and without shunt compensation. Procedure : P a r t (a) : Determination of A, B, C & D Constants of a Short Length Transmission Line. a . 1 - Open Circuit Test. 1 - Connect the circuit as shown in fig. 1. 2- Adjust the source voltage at 50V and take the readings of Vs, Is,W and VR , and determine the phase shift between Vs and VR . 3-Repeat step (2) for source voltages of 75,100, 120V. 4- From each set of readings , calculate A and C constants and determine the average values. a . 2 - Short Circuit Test. 1-Connect the circuit as shown in fig. 2. 2- Increase the source voltage very slowly adjusting IR to 1A and take the readings of VS, IS, W, IR and determine the phase shift between Vs and IR(IS). 3- Repeat step (2) for IR = 2, 3 and 4 A respectively . 4- From each set of readings , calculate B and D constants and determine the average values. -1- Part (b) : Determination of A, B, C & D Constants of a Medium Length Transmission Line. b . 1 - Open Circuit Test. 1-Connect the circuit as shown in fig. 3. 2-Adjust the source voltage at 50V and take the readings of Vs, Is, W,V R ,I c 1 , I c 2 and determine the phase shift between (Vs& VR ) ,(Vs&Is). “use phasor diagrams where it is necessary”. 3- Repeat step (2) for source voltages of 75, 100, 120 V. 4- From each set of readings , calculate A and C constants and determine their average values. b . 2 - Short Circuit Test. 1- Connect the circuit as shown in Fig. 4. 2-increase the source voltage very slowly adjusting IR t o l A and take the readings of Vs, IS; W, IR , I C1, I C2 and measure the phase shift between (Vs & I s ), ( V S & I R ). “use phasor diagrams where it is necessary” 3- Repeat step (2) for IR = 2, 3 and 4 A respectively . 4-From each set of readings , calculate B and D constants and determine the average values. - Draw the equivalent circuit of this line . -Verify the A, B, C, D constants using the relevent equations and the R, L, C values deduced from measurments. -2- Part (c) : Operation at No Load . 1 - Connect the circuit as shown in fig. 5 with switch S open. 2-Adjust Vs to 100 v ( L-N). 3- Take the readings of Vs, Is, and VR . 4- With XL adjusted to it's maximum value , close switch S . 5-Keep Vs constant and adjust XL till VR = V S =100v. 6- Take the reading of IL and calculate XL . 7-Comment on the value of IL . 8-From theory, calculate the combined A,B,C,D constants of the transmission line connected in series with the inductor and comment on the result . 9- Draw the circle diagram of the uncompensated line and deduce from it the amount of shunt compensation required at no load to make Vs = VR. How does this value correlate with the measured value?. Part (d) : Load Test. 1- Connect the circuit as shown in fig. 6. 2- Adjust I to 2A and adjust the P.F. to 0.8 lagging by adjusting individually I1 & I2 while keeping VR constant at 100v by continuous adjustment of Vs. 3- Take the readings of Vs, IR , PR , Is, VR , I1, I2, P.F. . 4- Draw the circle diagram and verify the measured results. 5- Determine from the circle diagram the amount of shunt compensation if Vs is lowered to 100v ,and VR is required to remain constant at 100 v. 6- Ensure mat Xc is kept at it's maximum value ,and close switch S. 7- Increase Ic gradually to achieve Vs = VR = 100 v , measure Ic & repeat step 3. 8- Calculate the VAR injected by Xc and check this value with the value determined in step 5. 9- Explain why ls increases after shunt compensation with reference to the P.F. at the sending end. -3- XL=3.75 Fig. 1 Short Transmission Line Open Circuit Test Fig. 2 Short Transmission Line Short Circuit Test Fig. 3 Medium Transmission Line Open Circuit Test Fig. 4 Medium Transmission Line Short Circuit Test -4- -5- -6- -7-