IG Rx percent lab
advertisement
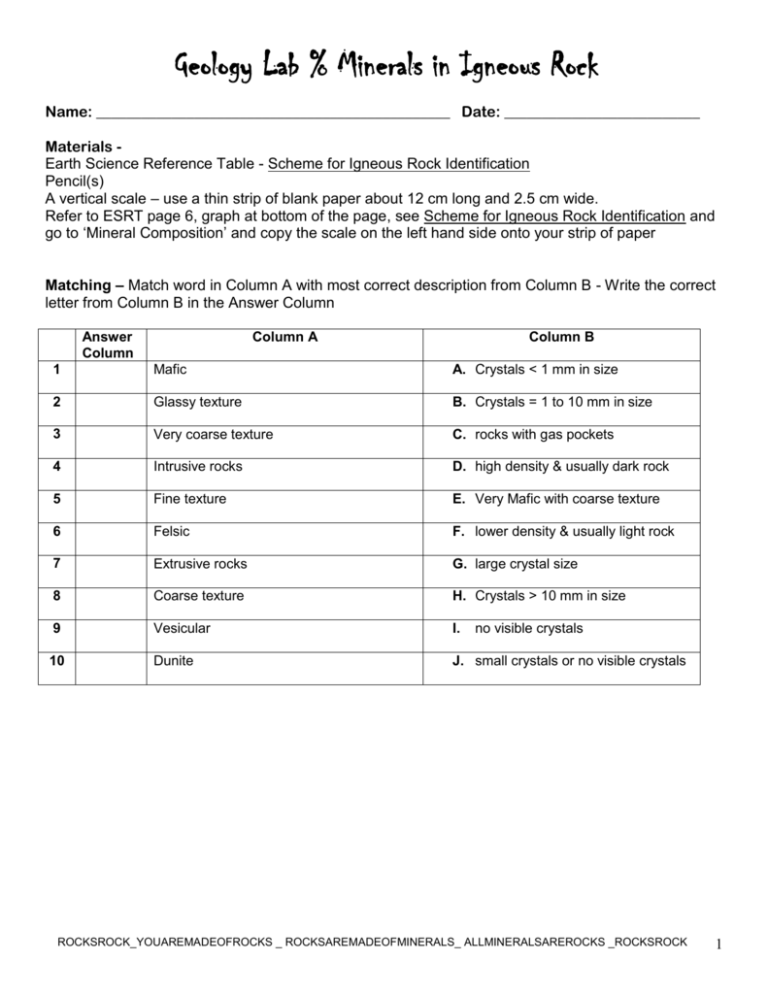
Geology Lab % Minerals in Igneous Rock Name: _______________________________________________ Date: __________________________ Materials Earth Science Reference Table - Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification Pencil(s) A vertical scale – use a thin strip of blank paper about 12 cm long and 2.5 cm wide. Refer to ESRT page 6, graph at bottom of the page, see Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification and go to ‘Mineral Composition’ and copy the scale on the left hand side onto your strip of paper Matching – Match word in Column A with most correct description from Column B - Write the correct letter from Column B in the Answer Column Answer Column Column A Column B 1 Mafic A. Crystals < 1 mm in size 2 Glassy texture B. Crystals = 1 to 10 mm in size 3 Very coarse texture C. rocks with gas pockets 4 Intrusive rocks D. high density & usually dark rock 5 Fine texture E. Very Mafic with coarse texture 6 Felsic F. lower density & usually light rock 7 Extrusive rocks G. large crystal size 8 Coarse texture H. Crystals > 10 mm in size 9 Vesicular I. 10 Dunite J. small crystals or no visible crystals no visible crystals ROCKSROCK_YOUAREMADEOFROCKS _ ROCKSAREMADEOFMINERALS_ ALLMINERALSAREROCKS _ROCKSROCK 1 Name a rock made only of QUARTZ______________________________. Name a rock made only of OLIVINE_______________________________. TO ESTIMATE the percent (%) of each mineral in these rocks 1. Find the rock that you want in the IGNEOUS ROCKS list (on the chart at the bottom of page 6) 2. Make a LIGHT pencil line straight down from the MIDDLE of the rock type through to the mineral composition chart 3. Estimate % of each mineral in the rock type using the vertical scale you just made. 4. Line it up with the light pencil line you just drew. 5. Put the 0% on the bottom edge of the range for each mineral (on the chart at the bottom of page 6) 6. READ off the % at the top edge of the mineral (on the chart at the bottom of page 6) 7. Write the % of each mineral on the igneous ID chart ROCKSROCK_YOUAREMADEOFROCKS _ ROCKSAREMADEOFMINERALS_ ALLMINERALSAREROCKS _ROCKSROCK 2 USE ESRT (page 6/16) – Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification chart Rock Extrusive or Intrusive Grain Size Andesite Texture Mineral Composition K Feldspar_____% Amphibole_____% Quartz ____% Pyroxene______% Plagioclase_____% Olivine______% Biotite____% Gabbro K Feldspar_____% Amphibole_____% Quartz ____% Pyroxene______% Plagioclase_____% Olivine______% Biotite____% Peridotite K Feldspar_____% Amphibole_____% Quartz ____% Pyroxene______% Plagioclase_____% Olivine______% Biotite____% Obsidian K Feldspar_____% Amphibole_____% Quartz ____% Pyroxene______% Plagioclase_____% Olivine______% Biotite____% Granite K Feldspar_____% Amphibole_____% Quartz ____% Pyroxene______% Plagioclase_____% Olivine______% Biotite____% Note: *All minerals are NOT in all rocks… ROCKSROCK_YOUAREMADEOFROCKS _ ROCKSAREMADEOFMINERALS_ ALLMINERALSAREROCKS _ROCKSROCK 3 Circle the correct answers: 1. Variations of mineral composition can be observed in an intrusive igneous rock called diabase. It is composed mainly of 50% pyroxene, 40% plagioclase and 5% olivine 6. Some Moon rock samples have coarse intergrown crystals composed of plagioclase feldspar, hornblende, and olivine. These Moon rock samples are most similar to Earth rock samples of Which other igneous rock is closest to diabase in mineral composition? 1. gabbro 3. breccia 1. andesite 3. rhyolite 2. marble 4. pumice 2. granite 4. gabbro 2. Different arrangements of tetrahedral in the silicate group of minerals result in differences in the minerals' 1. age, density, and smoothness 2. cleavage, color, and abundance 7. Which relative concentration of elements is found in a felsic rock? 1. high concentration of silicon and a low concentration of iron 2. high concentration of iron and a low concentration of aluminum 3. hardness, cleavage, and crystal shape 4. chemical composition, size, and origin 3. high concentration of aluminum and a low concentration of iron 4. high concentration of aluminum and a low concentration of silicon 3. Identify 3 minerals that can be found with quartz in andesite rock. 1. 2. 3. 4. potassium feldspar, olivine and biotite amphibole, olivine and biotite plagioclase amphibole and olivine plagioclase, amphibole and biotite 4. For an igneous rock to be classified as rhyolite, it must be light colored, be fine grained and contain 1. 2. 3. 4. 8. In identifying igneous rocks the feature of texture is best described as 1. 2. 3. 4. the way a rock feels the size of mineral crystals the color and clarity number of holes per square cm 9. Which mineral can be found in granite, andesite? 1. 2. 3. 4. quartz calcite pyroxene olivine quartz pyroxene olivine biotite mica 5. Which common rock is formed from the solidification of molten material? 10. Which mineral will scratch glass (hardness = 5.5), but not pyrite? 1. rock gypsum 2. slate (1) gypsum (2) fluorite 3. rhyolite 4. coal (3) orthoclase (4) quartz ROCKSROCK_YOUAREMADEOFROCKS _ ROCKSAREMADEOFMINERALS_ ALLMINERALSAREROCKS _ROCKSROCK 4 ROCKSROCK_YOUAREMADEOFROCKS _ ROCKSAREMADEOFMINERALS_ ALLMINERALSAREROCKS _ROCKSROCK 5