Printer Friendly Version of the Framework
advertisement
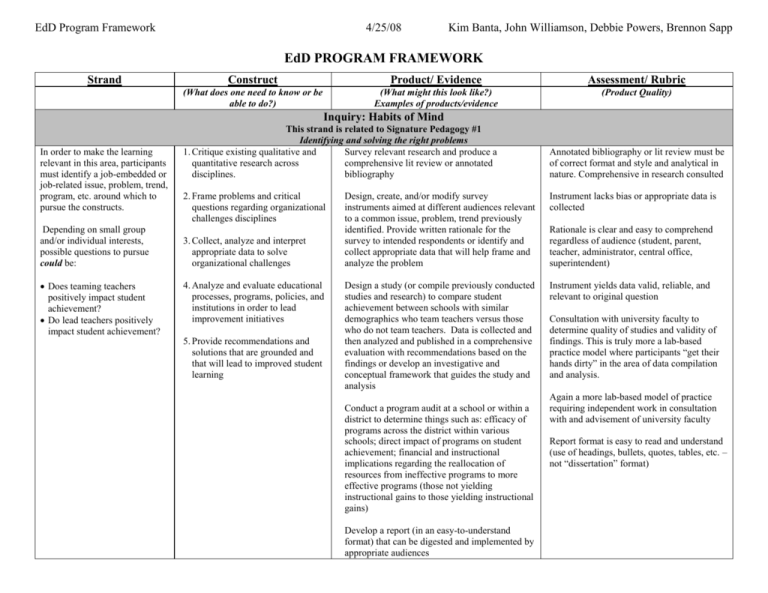
EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp EdD PROGRAM FRAMEWORK Strand Construct Product/ Evidence Assessment/ Rubric (What does one need to know or be able to do?) (What might this look like?) Examples of products/evidence (Product Quality) Inquiry: Habits of Mind In order to make the learning relevant in this area, participants must identify a job-embedded or job-related issue, problem, trend, program, etc. around which to pursue the constructs. Depending on small group and/or individual interests, possible questions to pursue could be: Does teaming teachers positively impact student achievement? Do lead teachers positively impact student achievement? This strand is related to Signature Pedagogy #1 Identifying and solving the right problems 1. Critique existing qualitative and Survey relevant research and produce a quantitative research across comprehensive lit review or annotated disciplines. bibliography 2. Frame problems and critical questions regarding organizational challenges disciplines 3. Collect, analyze and interpret appropriate data to solve organizational challenges 4. Analyze and evaluate educational processes, programs, policies, and institutions in order to lead improvement initiatives 5. Provide recommendations and solutions that are grounded and that will lead to improved student learning Annotated bibliography or lit review must be of correct format and style and analytical in nature. Comprehensive in research consulted Design, create, and/or modify survey instruments aimed at different audiences relevant to a common issue, problem, trend previously identified. Provide written rationale for the survey to intended respondents or identify and collect appropriate data that will help frame and analyze the problem Instrument lacks bias or appropriate data is collected Design a study (or compile previously conducted studies and research) to compare student achievement between schools with similar demographics who team teachers versus those who do not team teachers. Data is collected and then analyzed and published in a comprehensive evaluation with recommendations based on the findings or develop an investigative and conceptual framework that guides the study and analysis Instrument yields data valid, reliable, and relevant to original question Conduct a program audit at a school or within a district to determine things such as: efficacy of programs across the district within various schools; direct impact of programs on student achievement; financial and instructional implications regarding the reallocation of resources from ineffective programs to more effective programs (those not yielding instructional gains to those yielding instructional gains) Develop a report (in an easy-to-understand format) that can be digested and implemented by appropriate audiences Rationale is clear and easy to comprehend regardless of audience (student, parent, teacher, administrator, central office, superintendent) Consultation with university faculty to determine quality of studies and validity of findings. This is truly more a lab-based practice model where participants “get their hands dirty” in the area of data compilation and analysis. Again a more lab-based model of practice requiring independent work in consultation with and advisement of university faculty Report format is easy to read and understand (use of headings, bullets, quotes, tables, etc. – not “dissertation” format) EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Inquiry: Habits of Mind This strand is related to Signature Pedagogy #1 Identifying and solving the right problems Justification/ Literature Support Black, P., & William, D. (1998). Inside the black box: Raising standards through classroom assessment. Phi Delta Kappan, 80(2), 139-148. Retrieved March 2, 2007, from http://www.ccsso.org/projects/SCASS/Projects/Formative_Assessment_for_Students_and_Teachers/Meetings/Oct06/webpages/readnresrc.htm Friedman, T. (2006). The World is Flat: a Brief History of the Twenty-First Century. New York: Farrar, Strus, and Giroux. Pink, D. (2006). A Whole New Mind: Why Right Brainers Will Rule the World. New York: Riverhead Books. Pollock, Jane (2007) Improving student learning: One teacher at a time. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Wagner, T. & Kegan, R. (2006), Change Leadership: A Practical Guide to Transforming Our Schools. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. EdD Program Framework Strand 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Construct Product/ Evidence Assessment/ Rubric (What does one need to know or be able to do?) (What might this look like?) Examples of products/evidence (Product Quality) Action: Habits of Hands Using skills and processes honed in the Habits of Mind module the Habits of Hands module requires the cohort to move their research from theory to practice by taking the newly acquired knowledge and designing implementation plans then actually conducting “action research” based on those plans. Again, in order to make the learning relevant in this area, participants must identify a job-embedded or jobrelated issue, problem, trend, program, etc. around which to pursue the constructs. This strand is related to Signature Pedagogy #2 Being able to get work done within a variety of communities 1. Understand theories and Compilation of relevant theories related to research of student contexts student contexts and/or lit review. Cohort (psychological, family, experiences common readings and engage in cultural) and implement them discussions relevant to those readings. to impact student achievement. Action plan developed based on readings to address the job-embedded issue selected by 2. Understand theories and students. (construct 2,3) research in teaching and learning and implement them Cohort experiences common readings and to impact student engage in discussions relevant to those readings, achievement. as well. (construct 2,3) 3. Understand theories and research of leadership and organizational culture and behavior (vision, instruction, management, leadership) and implement them to impact student achievement. 4. Employ strategies of engagement, supportbuilding, communication, psychology, motivation, and marketing to explain issues to others and garner support Action plan developed based on readings to address the job-embedded issue selected by students.(construct 2,3) Cohort experiences common readings and engage in discussions relevant to those readings, as well. A book study from a different discipline with implications for education could be undertaken as a common read for the cohort. (construct 3,4) Action plan developed based on readings to address the job-embedded issue selected by students.(construct 1,2 and 3) Action plan developed after consultation with university faculty. Key to the plan would be clearly articulated goals, ongoing evaluation, and end of year comprehensive (construct 1,2,3) Reflection papers and/or “exit slips” could be a way of assessing individual knowledge and/or understanding of group discussion. (construct 1,2,3) Book study groups would meet in roundtables. If multiple books are used the cohort could “jigsaw” so that all cohort members were exposed to the basic premise of all books. (construct 3,4) Presentation of findings to a group or audience employing technology, marketing, writing, presentation and speaking skills with an interactive component leading to a formative assessment of the work to date EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Action: Habits of Hands This strand is related to Signature Pedagogy #2 Being able to get work done within a variety of communities Justification/ Literature Support Avolia, Bruce J. (1997). The great leadership migration to a full range leadership development system. Kellogg Leadership Studies Project, Transformational Leadership Working Papers, The James MacGregor Burns Academy of Leadership. Bass, Bernard M. (1997). The ethics of transformational leadership. Kellogg Leadership Studies Project, Transformational Leadership Working Papers, The James MacGregor Burns Academy of Leadership. Bass, B.M., Waldman, D.A., Avolio, B.J. & Bebb, M. (1987). Transformational leadership and the falling dominoes effect. Group and Organizational Management, 12, 73-87. Boje, D.(2000, December 25). Transform into super leaders: Transformational leadership. Retrieved February 15, 2008, from cbea.nmsu.edu Web site: http://chae.nmsu.edu/~dboje/teaching/338/transformational_leadership.htm Bolman, L.G., & Deal, T.E. (2001). Leading with soul. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass. Changing Minds. Bass’ transformational leadership theory [Electronic Version]. Retrieved January 11, 2008 from http://changingminds.org/disciplines/leadership/styles/transformational_leadership.hm. Brand, S., Felner, R., Shim, M., Seitsinger, A., & Dumas, T. (2003) Middle School Improvement and Reform: Development and Validation of a School-level Assessment of Climate, Cultural Pluralism, and School Safety. Journal of Educational Psychology. 95 (3). Collins, J. (2001). Good to Great. New York: Harper-Collins. Changingminds.org (n.d.). Transformational leadership. Retrieved January 27, 2008, from http://changingminds.org/disciplines/leadership/styles/transformational_leadership.hm. Copland, M.A., & Knapp, M.S. (2006). Essential ideas and tasks for learning-focused leaders. Connecting leadership with learning: A framework for reflection, planning and action. Retrieved January 9, 2008 from www.ascd.org/portal/site/ascd/template.chapter. Cox, Richard, 2007-12-15, Mister Article, Where Transformation Leadership and Authenticity Meet, from http://.isterarticle.clom/articledetainl.php?artid=17650&catid=171&title=where-Tran Day, C. (2000). Beyond transformational leadership. Educational Leadership, 57 (7), 56-59. Epitropaki, O. (2001). What is? Transformational Leadership [Electronic Version]. Retrieved January 11, 2008, from http://esrccoi.group.shef.ac.uk/pdf/whatis/transformational.pdf Felner, R., Seitsinger, A., Brand, S., Burns, A., & Bolton, N. Creating a Statewide Educational Data System for Accountability and Improvement: A Comprehensive Information and Assessment System for Making Evidence-Based Change at School, District, and Policy Levels: Increasing Psychology’s Contribution to Education. Psychology in the Schools. 45 (3). EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Felner, R., Ginter, M., & Primavera, J. (1987) Primary Prevention During School Transitions: Social Support and Environmental Structure. American Journal of Community Psychology. 10 (3). Felner, R., Kasak, D., Mulhall, P., & Flowers, N. (1997) The Project on High Performance Learning Communities: Applying the Land-Grant Model to School Reform. Phi Delta Kappan. 78 (7). Felner, R., Favazza, A., Shim, M., Brand, S., Gu, K., & Noonan, N. (2001) Whole School Improvement and Restructuring as Prevention and Promotion: Lessons from STEP and the Project on High Performance Learning Communities. Journal of School Psychology, 39 (2), 177-202. Hannah, M. (2008). “Five symbolic roles of leadership: Jack Welch’s letters to GE shareholders.” Wharton Leadership Digest (Vol 12 #6) http://leadership.wharton.upenn.edu/digest/index.shtml Hay, I. (2007). Leadership of stability and leadership of volatility: Transactional and transformational leaderships compared. Retrieved February 4, 2008, from www.academicleadership.org. Hipp, K. (1997). Documenting the Effects of Transformational Leadership Behavior on Teacher Efficacy. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Chicago, Illinois Jacobs, K.D. (2007). Utilizing “the William allen kristonis balanced teeter-totter model” as a means to cultivate a legacy of transformational leaders in schools: A national focus. Prairie View, TX: Prairie View A & M University. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED499651). Kinkhead, J.C. (2006). Transformational leadership: A practice needed for first-year success. Dalton, GA: Dalton State College. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED492009). Leighton, M.S., (1996). The Role of Leadership in Sustaining School Reform: Voices from the Field. U.S. Department of Education, EA9478001. Leithwood,K., & Jantzi, D. (1999). Transformational School Leadership Effects: A Replication. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 10 (4), 451-479. Leithwood, K., & Jantzi, D. (2000). The Effects of Transformational Leadership on Organizational Conditions and Student Engagement with School. Journal of Educational Administration. 38 (2), 112-26. Leithwood, K., & Jantzi, D. (2006). Transformational School Leadership for Large-Scale Reform: Effects on students, teachers, and their classroom practices. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 17 (2), 201-227. Liontos, L.B., (1992), Transformational Leadership. Eugene Oregon: ERIC Clearinghouse. Liontos, Lynn Balster, 1992-08-00, ERIC: ED347636, ERIC Clearinghouse on educational Management, from http://www.vtaide.com/png/ERIC/Transformational Leadership.html.Eugene, OR. Lucas, S., Valentine , J. (2002). Transformational Leadership: Principals, Leadership Teams, and School Culture. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. New Orleans, Louisiana. Lundenburg, F. (2003). Emerging Perspectives: The Usefulness of the Construct of Transformational Leadership in Educational Organizations. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the National Council of Professors of Educational Administration. MacDonald, J. (2005). Transformational leadership – a different concept of change. Retrieved January 27, 2008, from http://www.associatedcontent.com/article/14377/transformational_leadership_a_different.html. EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Marzano, R., Waters, T., McNulty, Brian A.(2005), School Leadership that Works. Alexandria VA: ASCD. Ross, J.A., & Gray, P., (2006). School Leadership and Student Achievement: The Mediating Effects of Teacher Beliefs. Canadian Journal of Education, 29, 3 789-822.Senge, P.M. (1990). The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization. New York: Doubleday. Schlechty, P. (1997). Inventing better schools. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Senge, P. (1990). The Fifth Discipline. New York: Doubleday. Verona, G., & Young, J. (2001). The influence of principal transformational leadership style on high school proficiency test results in New Jersey comprehensive and vocationaltechnical high schools. Seattle, WA: A paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association. EdD Program Framework Strand 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Construct Product/ Evidence Assessment/ Rubric (What does one need to know or be able to do?) (What might this look like?) Examples of products/evidence (Product Quality) Advocacy: Habits of Heart & Community Graduates will demonstrate a commitment to the educational profession and apply the role of educational leader by: implementing the code of ethics promoting the value of the profession Socializing new members in the aforementioned This strand is related to Signature Pedagogy #3 Being change agents for social justice 1. Use education to promote An evaluation of current school, district or state ethical decision making. programs for efficacy issues(construct 1,2) 2. Use education to promote social justice. 3. Demonstrate stewardship of the profession 4. Demonstrate empathy and understanding of various points of view 5. Demonstrate the capacity for lifelong learning through a natural curiosity and passion for educational issues An evaluation of alternative school placements within a district for efficacy and student achievement(construct 1,2) Develop a plan for teacher mentorship within a building or district around relevant topics including student advocacy, teacher efficacy, etc.(construct 2,3) Cohort work is cognizant of issues addressing ILPs, IEPs, SES, multiple intelligences, family situations, drug addictions, social issues, etc. (construct 1,2,4) Develop and support a specific and meaningful regional or statewide job-alike network to support relevant topics such as student advocacy, teacher efficacy, etc. (construct 2,3) Cohort agrees to common “orientations” and signs off with signatures(construct 3,4) Cohort participates in a common read regarding group dynamics such as Warren Bennis’ Organizing Genius or the DuFour work on Professional Learning Communities Work produced by the cohort reflects ethical decision making in design, implementation and evaluation.(construct 1,2,3) Participate in potentially controversial discussions related to educational issues with insight as well as tolerance for differing views.(construct 1,4,5) Participate in work teams and groups on various projects throughout the Ed. D. experience. (construct 1,4,5) Collegial atmosphere in and among cohort. Literature review related to organizational structures Book study groups would meet in roundtables. If multiple books are used the cohort could “jigsaw” so that all cohort members were exposed to the basic premise of all books.(construct 3,4) Does the work transcend time? Are you engaged in capacity building through the work? (construct 3,5) EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Advocacy: Habits of Heart & Community This strand is related to Signature Pedagogy #3 Being change agents for social justice Justification/ Literature Support Corrigan, R. (2007) Race, Poverty, and Social Justice. Sterling, VA: Stylus. Gardner, H. (2007) Five Minds for the Future. Cambridge: Harvard Business School Press. Gardner, H. (2000) Intelligence Reframed. Cambridge: Harvard Business School Press. Gay, G. (2000) Culturally Responsive Teaching. New York: Teachers College Press. Gurian, M. (2006) The Wonder of Boys. New York: Tarchaer Gurian, M. (2003) Boys and Girls LearnDdifferently. San Fransico, Jossey-Bass Howard, G. (2006) We can’t teach what we don’t know: White teachers, multiracial schools. New York: Teachers College Press. Irvine, J. (2003) Educating teachers for diversity: Seeing with a cultural eye. New York: Teachers College Press Kindlon, D. and Thompson, M. (2000) Raising Cain. New York: Ballentine Books. Kozol, J. (1992) Savage Inequalities. New York: Crown. Leadership and school results. In: Second International Handbook of Educational Leadership and Administration. Kluwer Academic, Norwell, MA, pp. 561-612. Payne, R. (2005) A framework for understanding poverty. AHA Process. Pipher, M., Ross, R. (2005) Reviving Ophelia. New York: Riverhead Trade. Reiff, H. (2007) Self-advocacy skills for students with disabilities. Dude Publishing. Roeder, Phillip W. (2002). School District Performance in Kentucky (1993-2001): Do Teaching and Financial Resources Moderate the Negative Effects of Poverty? (Report No. RC023704). Lexington, KY: University of Kentucky. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED 469 136). Sachs, L. (2006) Why Gender Matters. New York: Doubleday. School District Performance in Kentucky (1993-2001): Do Teaching and Financial Resources Moderate the Negative Effects of Poverty? Scott, T. M. (2007). Issues of personal dignity and social validity in school-wide systems of positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 9(2), 102-112. EdD Program Framework 4/25/08 Kim Banta, John Williamson, Debbie Powers, Brennon Sapp Scott, T. M., & Kamps, D. (2007). The future of functional behavior assessment in public schools: Balancing Necessity and Sufficiency. Behavioral Disorders, 32(3), 146-157. Scott, T. M., & Caron, D. (2006). Functional Behavior Assessment at the School-Wide Level: Determining Predictability and Function of Typical Problem Behaviors. Preventing School Failure 50(1), 13-20. Scott, T. M., Liaupsin, C., & Nelson, C. M. (2005). Team-based Functional Assessment and Intervention Planning: A Simplified Teaming Process. Longmont, CO: Sopris West. Strike, K., Haller, E., & Soltis, J. (2002) The Ethics of School Administration. New York: Teachers College Press.