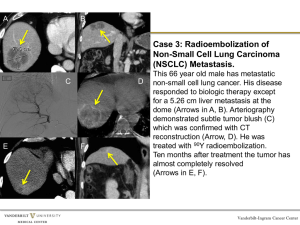
Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
advertisement

Rectal Cancer Treatment Guideline Staging: AJCC 7th edition (2010) Primary Tumor (T) TX Primary tumor cannot be assessed T0 No evidence of primary tumor Tis Carcinoma in situ: intraepithelial or invasion of lamina propria T1 Tumor invades submucosa T2 Tumor invades muscularis propria T3 Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into the pericolorectal tissues T4a Tumor pentrates to the surface of the visceral peritoneum T4b Tumor directly invades or is adherent to other organ of structures Regional Lymph Nodes (N) (at least 10~14 nodes dissection) NX Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed N0 No regional lymph nodemetastasis N1 Metastasis in 1~3 regional lymph nodes N1a Metastasisi in 1 regional lymph node N1b Metastasis in 2~3 regional lymph nodes N1c Tumor deposits in the subserosa, mesentery or nonperitonealized pericolic or perirectal tissues without regional node metatstasis. N2 Metastasis in 4 or more regional lympho nodes N2a Metastasis in 4~6 regional lymph nodes N2b Metastasis in 7 or more regional lymph nodes Distant Metastasis (M) MX Metastasis cannot be assessed M0 No distant metastasis M1 Distant metastasis M1a Metastasis confined to one organ or site (eg. liver, lung, ovary, nonregional node) M1b Metastasis in more than one organ/site or the peritoneum Staging T N M Stage 0 Tis N0 M0 Stage I T1~2 N0 M0 Stage IIA T3 N0 M0 Stage IIB T4a N0 M0 Stage IIC T4b N0 M0 T1~2 N1/N1c M0 T1 N2a M0 T3~T4a N1/N1c M0 T2~3 N2a M0 T1~T2 N2b M0 T4a N2a M0 T3~T4a N2b M0 T4b Any M0 Stage IVA Any Any M1a Stage IVB Any Any M1b Stage IIIA Stage IIIB Stage IIIC Treatment Guideline References: NCCN rectal cancer guidelines 2011 V.2 Appropriate for resection ‧Transabdominal resection a) pT1~2N0M0 => observe b) pT3N0 or pT1~3, N1~2 => postoperative ChRT cT1~2N0 cT3N0 cTanyN1~2 ‧Transanal excision (cT1N0) a) T1NXR0 => observe b) T1NX with high risk feature or T2NX => Transabdominal resection => back to above *high risk feature include positive margin, LVSI and poorly differentiated tumors 1) Preop. CCRT (preferred) (cate. 1 for node positive disease) Transabdominal resection => adjuvant C/T** 2) Transabdominal resection => a) pT1~2N0 => observe b) *pT3N0* or pT1~3N1~2 => postoperative ChRT ‧If medical contraindication to combined modality therapy => Transabdominal resection a) pT1~2N0 => observe b) *pT3N0* or pT1~3N1~2 => postoperative ChRT cT4 and unresectable CCRT (preop. setting)=> resection if possible => any T: adjuvant C/T ‧Combination chemotherapy 2~3 months => a) Staged or synchronous resection => adjuvant CCRT b) adjuvant CCRT=> Staged or synchronous resection Resectable M1 ‧Staged or synchronous resection => a) pT1~2N0M1 => advanced chemotherapy(category 2B) b) pT3~4NanyM1 or TanyN1~2M1 => postoperative ChRT ‧CCRT (preop setting) => Staged or synchronous resection => advanced chemotherapy(category 2B) *proximal pT3N0R0 with favorable prognostic features, the incremental benefit of RT is likely to be small. Consider chemotherapy alone. TanyNanyM1, unresectable synchronous metastasis or medically inoperable Advanced chemotherapy (AC) AC 5-FU/RT or capecitabine/RT(category 2B) or UFUR+LV/RT AC Resection of involved rectal segment AC Symtomatic Laser recanalization AC Diverting colostomy AC Stenting AC Asymptomatic Advanced chemotherapy determine respectability *proximal pT3N0R0 with favorable prognostic features, the incremental benefit of RT is likely to be small. Consider chemotherapy alone. Recurrence Isolated Resectable metachronous metastases 1) Resectable op then ChRT or pre-op 5FU + RT then op +/IORT 2) Unresectable C/T +/- RT No previous C/T op then AC or Neoadjuvant C/T then op, if response then repeat neoadjuvant C/T or FOLFOX; if no response then AC or OBS 2) Previous C/T as above 1) Unresectable metachronous metastases 1) Previous adjuvant FOLFOX within past 12 months FOLFIRI +/- beva. or FOLFIRI +/- cetuximab or panitumumab (KRAS wild-type gene only) 2) Previous adjuvant FOLFOX >12 months, previous 5FU/LV or capecitabine, no previous C/T AC evaluate every 2 months for respectability a) op then AC b) AC if unresectable Postoperative ChRT (Op. as primary Tx) 1, 2 exchange 1) continuous 5-FU/RT or bolus 5-FU+leucovorin/RT or capecitabine/RT , or UFUR+LV/RT => 5-FU ± leucovorin or FOLFOX or capecitabine +/- oxaliplatin or UFUR+LV Or 2) 5-FU ± leucovorin or FOLFOX or capecitabine +/- oxaliplatin=> continuous 5-FU/RT or bolus 5-FU+leucovorin/RT or capecitabine/RT or UFUR+LV/RT => 5-FU ± leucovorin or FOLFOX or capecitabine +/- oxaliplatin or UFUR+LV Preoperative CCRT 1) Continuous 5-FU/RT (category 1 for node positive disease) or 2) bolus 5-FU+leucovorin/RT or 3) capecitabine/RT or 4) UFUR+LV/RT Adjuvant CCRT continuous 5-FU/RT or bolus 5-FU+leucovorin/RT or capecitabine/RT or UFUR+LV/RT **Adjuvant Chemotherapy 5-FU ± leucovorin or FOLFOX or capecitabine +/- oxaliplatin or UFUR+LV Combination Chemotherapy a) FOLFIRI or FOLFOX or CapeOX ± bevacizumb or b) KRAS wide-type gene only FOLFIRI or FOLFOX or ± cetuximab or panitumumab Radiation Dose References: NCCN rectal cancer guidelines 2011 V.2 Definitive CTV1 = 50-60Gy CTV2 = 50Gy Preoperative CTV1 = 45 Gy (TCOG 45Gy then local boost 5.4Gy for T4 or perirectal LAP) CTV2 = 45Gy Postoperative CTV1 = 50-54Gy CTV2 = 50Gy Patient Set-up References: 1) RTOG 0822 2) ASTRO 2008 (colorectal and anal cancer, EDU session) CT simulation A custom immobilization device Arms up position Supine or prone Bowel compression if prone Full bladder (intake 500cc of water within 1Hr) Oral and IV contrast Anal marker <=5mm slices (3mm at MMH) Multiple fields Target Delineation References: 1) RTOG 0822 2) RTOG anorectal contouring ATLAS 3) DEFINITION AND DELINEATION OF THE CLINICAL TARGET VOLUME FOR RECTAL CANCER, Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 4, pp. 1129–1142, 2006 . Definitive or pre-operative CTV1 = Tumor + 2.5 cm craniocaudally (CC) and 1.5 cm radially (cover mesorectum), nodal GTV + 1 cm symmetrical expansion CTV2 = a) Superior extent of the peri-rectal component: the rectosigmoid junction or 2 cm proximal to the superior extent of macroscopic disease in the rectum/peri-rectal nodes b) The most cephalad aspect of CTVA should be where the common iliac vessels bifurcate into external/internal iliacs (approximate boney landmark: sacral promontory) c) The caudad extent should be a minimum of 2 cm caudad to gross disease, including coverage of the entire mesorectum to the pelvic floor even for upper rectal cancers d) Coverage of distal common ilac LN, int. iliac LN, obturator LN, presacral area (mid S1-S5), uninvolved iliac vessels + 0.7 cm = CTV e) The mesorectum and perirectal lymphatics CTV is generated by utilizing anatomic landmarks: Posterior Border: anterior border of the sacrum and gluteus maximus Lateral Border: ileum, piriformis and obturator muscles Anteriorly extending CTV to ~0.3 cm into the posterior bladder f) External iliac nodes should be included for tumor involving GYN and/or GU structures. g) Cover IRF (ischiorectal fossa) for lower rectal tumor: when tumor is within 6cm from the anal verge or s/p APR. PTV = ~0.5 to 1.0 cm, except at skin Postoperative CTV1 = Tumor bed + mesorectum a) Upper limit: either of the below criteria - 5cm above the anastomosis, or - recto-sigmoid junction, or - the bifurcation of the IMA into the SRA. b) Lower limit: either of the below criteria - 5cm below the anastomosis, or - the border of the levator ani muscle, which makes a funnel around the distal rectum. c) Anterior: with 3mm-margin to the adjacent organ - male: posterior wall of the prostate/seminal vesicles/ bladder - female: posterior vaginal wall/uterus d) Posterior: ant. sacral border CTV2 = as definitive contouring PTV = ~0.5 to 1.0 cm, except at skin a) Ischiorectal fossa (IRF) b) c) Inguinal lymph nodes Cover the internal and external anal sphincter, with the penile bulb/ vestibular bulb. The deeper part of the ischiorectal fossa, located above the transversen septum and bounded laterally by the internal obturator muscle and the ischium, is entirely at risk. Lower limit: ischial tuberosity. a) May consider electively irradiate the inguinal nodal region for rectal adenocarcinomas that extend to the anal verge or peri-anal skin b) The caudad extent of the inguinal region should be 2 cm caudad to the saphenous/femoral junction c) The transition between inguinal and external iliac regions is at the level of the bottom of the internal obturator vessels (approximate boney landmark: upper edge of the superior pubic rami) IMRT plan criteria References: RTOG 0822 PTV planning dose-volume constraints: 1) ≥ 98% of the PTV receives ≥ 93% of the prescribed dose 2) ≤ 10% of the PTV receives ≥ 105% of the prescribed dose 3) ≤ 5% of the PTV receives ≥ 110% of the prescribed dose 4) None of the PTV is to receive ≥ 115% of the prescribed dose Normal Organ Constraints References: QUANTEC (Radiation constraint and related toxicities) Bladder (whole organ) Small bowel Rectum (whole organ) Bladder ca. Gr. ≧3 late RTOG, Dmax<65, rate<6% Prostate ca. Gr. ≧3 late RTOG, V65≤50%, V70≤35%, V75≤25%, V80≤15% (RTOG 0415) Individual Loops Gr. ≧3 acute toxicity, V15<120cc, <10% Entire potential space Gr. ≧3 acute toxicity, V45<195cc, <10% Prostate ca. V50<50%, V60<35%, V65<25%, V70<20%, V75<15% (Gr.≧2 late toxicity <15%, Gr.≧3 late toxicity<10%)