teachers.
advertisement

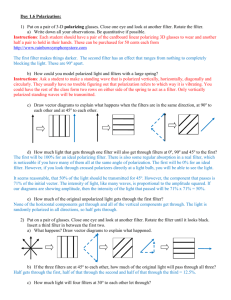
Polarized 3-D Glasses: Guided Inquiry Worksheet This worksheet is designed to be used by a small group of two to four students. They should already be able to: give examples of light behaving as a wave in refraction (i.e. apparent bending of a pencil in a glass of water), diffraction (i.e. spreading of light as it passes through a small slit between your fingers) and interference (colours in a CD and on soap film). show how the waves on a long spring can be polarized linearly and circularly. This task is quite challenging. Students should have whiteboards nearby to sketch their ideas and at least 15 minutes. It is important that the students discuss and write the reasons for their predictions. Background information: We see in 3-D because each of our eyes gets a slightly different 2-D information and our brains combine these two to form a 3-D image. To see this for yourself, hold a finger in front of your face and look at it and the background with one eye and then the other eye. 3-D movies work by projecting two images and making sure that each eye receives a different one. The 3-D glasses have polarizing filters which will only let in one of the two projected images into each eye. The filters in the glasses are usually polarized in one of the three following combinations: Plus/Minus45o vertical/horizontal or clockwise/counter-clockwise. Inquiry: You are going to figure out which of the three polarizations these glasses use. One pair of glasses will be sitting on the table as shown above. You will look at them using another pair of glasses with the right side covered. A). B) 1) Suppose the glasses are polarized +/- 45o. i) What will you see? A or B? The light passing through the two ‘lenses’ will be polarized up toward the center. at minus 45 This means that your left eye only receives light that is polarized which is also what the lens on the left will be passing. You should see A. ii) What if you look at them from the other side of the table? Looking at the other side means a rotation about a vertical axis. This does not change the polarization of the glasses, the light is still up toward the center and the answer is still A. iii) What if they are placed upside down? The polarization has now switched, it is down toward the center. now see the light on the right side – the answer is B. Your left eye will 2) Suppose the glasses are polarized horizontal/vertical? i) What will you see? A or B? Your left eye sees vertical light. This is the light that comes through the left lens of the glasses – which is one your right. You should see B. ii) What if you look at them from the other side of the table? Now when you look at the glasses, the glass’s left side is also your left side and you should see A. iii) What if they are placed upside down? This doesn’t change horizontal or vertical so you should still see B assuming you are back at your original side of the table. 3) Suppose the glasses are polarized clockwise/counter-clockwise? i) What will you see? A or B? Your left eye sees clockwise light. This is the light that comes through the glasses left side which is one your right. You should see B. ii) What if you look at them from the other side of the table? The glasses’ left eye is now on your left. You should see A. iii) What if they are placed upside down? Turning upside down switches clockwise to counter clockwise so you should see A from the original side. 4) Your answers for the three types should be different. Summarize them in the table below. Plus/Minus Horizontal/Vertical Clockwise/Counter i A B B ii A A A iii B B A 5) Ask for some glasses to test your ideas. Which polarization is it? Why would this polarization be an advantage? (Hint: What if you put your glasses on incorrectly?) It is plus/minus. The arms for these glasses can be easily folded in two different ways. This would reverse the polarization for the other two types of polarization and your left eye would get the right eye’s image which would not give the correct 3-D information. You can check that the polarization is plus/minus 45o by looking at a shiny floor or other surface with reflective glare. Reflection polarizes light parallel to the surface. If you turn your head at 45o you will see that the glare is reduced by one lens and not the other. Polarized sunglasses have both lenses polarized horizontally to reduce the glare on water and roads. 6) The newer 3-D glasses in the movie theatres are circularly polarized. Why would this be an advantage? (Hint: What happens if you tilt your head to rest on someone’s shoulder?) These glasses are made of hard plastic and so they won’t be put on backwards. If you tilt your head toward your date, you do not change the polarization with these glasses like you do with the other two types.