Infdis1 - Acute diarrhoea outcomes
advertisement

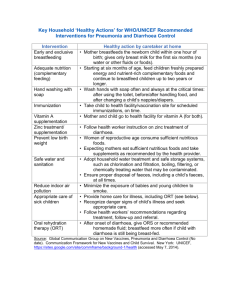
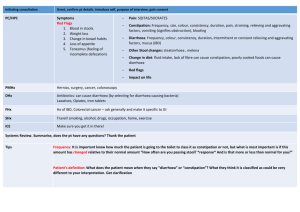
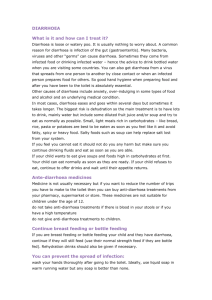
Page 1/1 Acute diarrhoea Outcomes By the end of phase III the students should be able to: * Discuss the major gastrointestinal host defence mechanisms * Explain the relative infectious doses of enteric pathogens required to cause disease * Explain the risk factors for acquiring gastroenteritis * Explain the difference between acute and chronic diarrhoea * Discuss the pathogenic mechanisms by which enteric pathogens cause GI disease * Discuss the differences with examples of each of the following: 1) Infectious diarrhoea a.) non-inflammatory or toxin mediated b.) inflammatory –invasive and non invasive 2.) Noninfectious diarrhoea * Discuss the features of gastroenteritis caused by the different pathogens o Common pathogens responsible for acute diarrhoea in children, adults, travellers, HIV/ AIDS patients (Viruses, bacteria, toxins, parasites etc.) * Epidemiology, pathogenesis, incubation period, clinical features, diagnosis and management * Discuss antibiotic associated diarrhoea Skills * Take an appropriate history from a patient suffering from acute diarrhoea * Perform an appropriate physical examination on a patient suffering from acute diarrhoea * Recognize the signs and symptoms of dehydration and initiate appropriate management * Collect and correctly send appropriate specimens to the laboratory * Correctly interpret diagnostic tests * Initiate the appropriate diagnostic workup for the patient who presents with acute diarrhoea * Prescribe the appropriate treatment for children and adults with acute diarrhoea * Communicate to patients and parents the indications and contraindications of anti-motility drugs and antibiotics * Give advise on the principles of food hygiene * Advise travellers on prophylactic measures and treatment of traveller’s diarrhoea * Advise patients on indications for hospital admission for children and adults with acute diarrhoea * Initiate prevention strategies (isolation) and notification where appropriate Find Image View Download a Copy Close