Triple-Entry Vocabulary Journal Template
advertisement

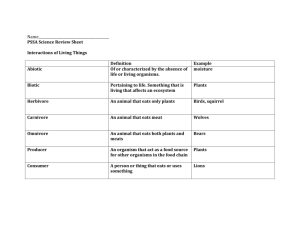
Name _____________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # ______ Ecology Triple-Entry Vocabulary for Chapter 18-20 – Bio http://quizlet.com/40167138/ch-18-20-ecology-vocabulary-flash-cards/ Word/Definition in Context Biosphere- the part of the earth where life exists (includes all living organisms Ecology- the study of the interactions between organisms and the other living and nonliving components of their environment Ecosystem- a community of organisms and their abiotic environment Community- a group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other Population- a group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific geographical area and interbreed Habitat- the place where an organism usually lives Biotic factor- an environmental factor that is associated with or results from the activities of living organisms Abiotic factor- an environmental factor that is not associated with the activities of living organisms Niche- the unique position occupied by a species Producer- an organism that can make organic molecules from inorganic molecules Consumer- an organism that eats other organisms or organic matter Definition in My Own Words Picture, Memory Aid, Phrase Earth globe “study of” relationship organisms area interacting environment same interbreeding natural environment inhabited living has cells Nonliving (without life) rocks job role autotroph photosynthetic plants heterotroph animals Herbivore- an organism that eats only plants plants vegetation Carnivore- an organism that eats meat flesh animals Omnivore- an organism that eats a variety of other organisms (plants and animals) Decomposer- an organism that feeds by breaking down organic matter from dead organisms both human bacteria fungi soil/dirt Name _____________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # ______ Word in Context Trophic level- an organism’s Definition in My Own Words Picture, Memory Aid, Phrase “feeding level” relative position of energy transfer in a food chain or food pyramid Food web- a diagram that shows the feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem Food chain- the pathway of energy transfer through various stages as a result of the feeding patterns of a series of organisms Natality- the number of births that occur in a period of time in a given area Mortality- the number of deaths occurring in a period of time Immigration- the movement of an individual or group into an area Emigration- the movement of an individual or group out of an area Carrying capacity- the largest population that an environment can support at any given time Population density- the number of individuals of the same species that live in a given unit of area Dispersion- the pattern of distribution of organisms in a population Predator- an animal that hunts, kills, and eats other animals Prey- an animal that is hunted, killed, and eaten by a predator Symbiosis- a relationship in which two different organisms live in close association with each other Parasitism- a relationship between two species in which one species benefits from the host while the host is harmed Commensalism- a relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected Mutualism- a relationship between two species in which both species benefit Ecological succession- a gradual process of change and replacement in a community arrow connected trophic level linear birth increase death decrease enter/entering increase exit/exiting decrease maximum size measurement available/availability clumped even “does the eating” fox “gets eaten” rabbit close relationship two organisms together one helped, one harmed one benefits, other unaffected both benefit series of events community