mole4
advertisement

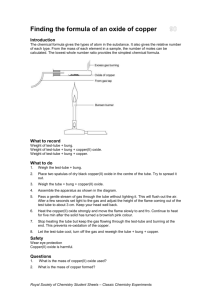
F.6/7 Chemistry Manual: Empirical Formula of Black Copper Oxide Objective: To determine the empirical formula of black copper oxide by weighing method Size of group: Two students Introduction: In this experiment, a certain quantity of black copper oxide is weighed. Town gas is allowed to pass the heated copper oxide in a boiling tube. Copper oxide undergoes reduction and the oxygen is removed and copper is left in the tube. Mass of the product, Cu is measured and mass of oxygen in the compound is calculated. Hence number of moles of copper and oxygen are determined and the mole ratio of the elements can be determined. By using this ratio the empirical formula of copper is estimated. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Theory: Give principle/reason to explain how is the formula of copper oxide determined in this experiment. The following questions should be useful to you. 1. Compare the reactivity of copper with other metals in the metal reactivity series. 2. What is the method employed in this experiment to find the masses of copper and oxygen for the copper oxide in the boiling tube? 3. Suppose the mass of copper oxide strip is m1, mass of the product is m2, show, how do you find out the mole ratio of copper and oxygen in the copper oxide? 4. How can you find out the empirical formula from the mole ratio? ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Chemicals: Black copper oxide Additional Materials: Boiling tube fitted with a two-hole stopper. The stopper should be fitted to town gas supply, balance readable 2 decimal places, stand and clamp, long wooden splint Safety Precaution Use of Town gas: It is explosive if town gas mixes with air/oxygen. Consult with your teacher whenever necessary. Procedure Record your results immediately after you get the readings. Wear goggle in the course of the practical excess town gas burning tube A clamp boiling tube black copper oxide town gas supply rubber tubing heat 1. Weigh the dry boiling tube accurately (without the stopper and tubings.). Record the mass 2. Put 4 spatula measures (about 2 g) of pure, dry copper oxide into the boiling tube. Weigh the boiling tube and the copper oxide. Record the mass. 3. Refer to the set-up diagram, shake the boiling tube to spread the copper oxide into a thin layer (not too near the mouth of tube). Put the stopper (with tubings) in place and clamp the boiling tube horizontally. Connect the rubber tubing to the town gas supply. Check that tube A is pointing upwards. Mole2: Formula of magnesium oxide /p.1 4. Light a long wooden splint and hold it in one hand. With the other hand, turn on the gas supply to a gentle flow (with the gas tap only half-open). Let the gas pass for about 4 seconds. Then carefully light the gas coming out of tube A. Adjust the gas tap until the flame is about 5 cm high. Keep this flame on throughout the experiment. If it goes out, light the escaping gas again at once. DON’T LEAVE THE SET-UP WITHOUT ATTENTION! 5. Light a Bunsen burner. Adjust the flame to a medium non-luminous one. Place the flame under the boiling tube at the position of the copper oxide. 6. To heat all the solid powder, keep moving the Bunsen flame to and fro along the tube for a few minutes, until there is no further colour change in the solid. 7. Turn off the Bunsen flame used for heating. Do not shut off the town gas passing through the boiling tube. 8. Wait for about 10 minutes. When the boiling tube is quite cool (below 70oC), shut off the gas supply. Remove the stopper and the tubings. (Caution: End of tube A may be still quite hot.) Weigh the tube and copper. Data and Results Mass of boiling tube + black copper oxide Mass of boiling tube + copper Mass of boiling tube Mass of boiling tube + copper Mass of oxygen = = = = = Calculation 1. 2. Calculate number of moles of copper and oxygen in black copper oxide. Calculate relative number of moles of copper and oxygen in the copper oxide. Hence find out the empirical formula of black copper oxide. Questions for discussion 1. List safety precautions for this practical. 2. Knowing that the empirical formula of black copper oxide is CuO, calculate percentage error for your results. Do you accept your results? 3. List all sources of experimental error. 4. If there is copper oxide unreacted in the crucible, suggest a method to confirm the presence of this unreacted reactant. 5. Explain step 7. The Report: Hand in your report to Mr. Lai (The Preparation Room) before 5:00 p.m. Mole2: Formula of magnesium oxide /p.2