Evolutionary Explanations of group displays in human aggression
advertisement
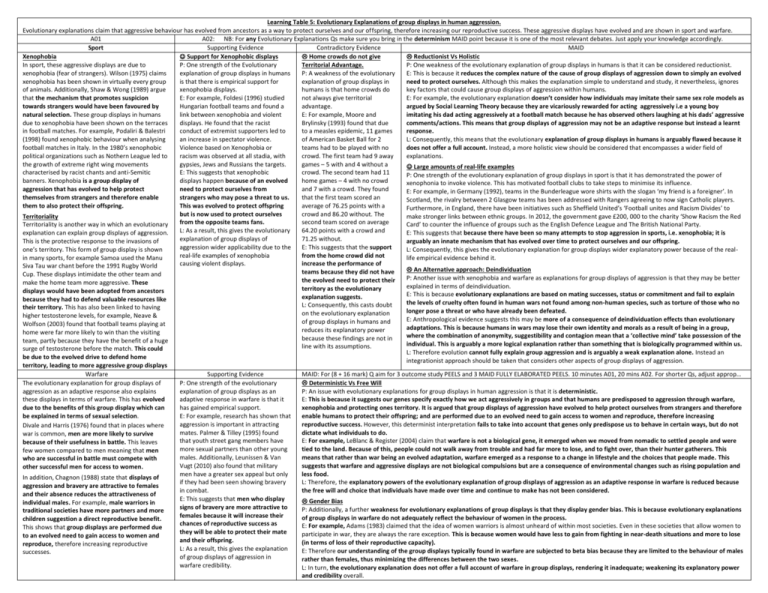
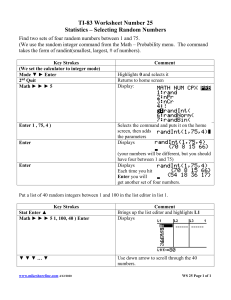
Learning Table 5: Evolutionary Explanations of group displays in human aggression. Evolutionary explanations claim that aggressive behaviour has evolved from ancestors as a way to protect ourselves and our offspring, therefore increasing our reproductive success. These aggressive displays have evolved and are shown in sport and warfare. A01 A02: NB: For any Evolutionary Explanations Qs make sure you bring in the determinism MAID point because it is one of the most relevant debates. Just apply your knowledge accordingly. Sport Supporting Evidence Contradictory Evidence MAID Xenophobia Support for Xenophobic displays Home crowds do not give Reductionist Vs Holistic In sport, these aggressive displays are due to P: One strength of the Evolutionary Territorial Advantage. P: One weakness of the evolutionary explanation of group displays in humans is that it can be considered reductionist. xenophobia (fear of strangers). Wilson (1975) claims explanation of group displays in humans P: A weakness of the evolutionary E: This is because it reduces the complex nature of the cause of group displays of aggression down to simply an evolved xenophobia has been shown in virtually every group is that there is empirical support for explanation of group displays in need to protect ourselves. Although this makes the explanation simple to understand and study, it nevertheless, ignores of animals. Additionally, Shaw & Wong (1989) argue xenophobia displays. humans is that home crowds do key factors that could cause group displays of aggression within humans. that the mechanism that promotes suspicion E: For example, Foldesi (1996) studied not always give territorial E: For example, the evolutionary explanation doesn’t consider how individuals may imitate their same sex role models as towards strangers would have been favoured by Hungarian football teams and found a advantage. argued by Social Learning Theory because they are vicariously rewarded for acting aggressively i.e a young boy natural selection. These group displays in humans link between xenophobia and violent E: For example, Moore and imitating his dad acting aggressively at a football match because he has observed others laughing at his dads’ aggressive due to xenophobia have been shown on the terraces displays. He found that the racist Brylinsky (1993) found that due comments/actions. This means that group displays of aggression may not be an adaptive response but instead a learnt in football matches. For example, Podaliri & Balestri conduct of extremist supporters led to to a measles epidemic, 11 games response. (1998) found xenophobic behaviour when analysing an increase in spectator violence. of American Basket Ball for 2 L: Consequently, this means that the evolutionary explanation of group displays in humans is arguably flawed because it football matches in Italy. In the 1980’s xenophobic Violence based on Xenophobia or teams had to be played with no does not offer a full account. Instead, a more holistic view should be considered that encompasses a wider field of political organizations such as Nothern League led to racism was observed at all stadia, with crowd. The first team had 9 away explanations. the growth of extreme right wing movements gypsies, Jews and Russians the targets. games – 5 with and 4 without a Large amounts of real-life examples characterised by racist chants and anti-Semitic E: This suggests that xenophobic crowd. The second team had 11 P: One strength of the evolutionary explanation of group displays in sport is that it has demonstrated the power of banners. Xenophobia is a group display of displays happen because of an evolved home games – 4 with no crowd xenophonia to invoke violence. This has motivated football clubs to take steps to minimise its influence. aggression that has evolved to help protect need to protect ourselves from and 7 with a crowd. They found E: For example, in Germany (1992), teams in the Bunderleague wore shirts with the slogan ‘my friend is a foreigner’. In themselves from strangers and therefore enable strangers who may pose a threat to us. that the first team scored an Scotland, the rivalry between 2 Glasgow teams has been addressed with Rangers agreeing to now sign Catholic players. them to also protect their offspring. This was evolved to protect offspring average of 76.25 points with a Furthermore, in England, there have been initiatives such as Sheffield United’s ‘Football unites and Racism Divides’ to but is now used to protect ourselves crowd and 86.20 without. The Territoriality make stronger links between ethnic groups. In 2012, the government gave £200, 000 to the charity ‘Show Racism the Red from the opposite teams fans. second team scored on average Territoriality is another way in which an evolutionary Card’ to counter the influence of groups such as the English Defence League and The British National Party. L: As a result, this gives the evolutionary 64.20 points with a crowd and explanation can explain group displays of aggression. E: This suggests that because there have been so many attempts to stop aggression in sports, i.e. xenophobia; it is explanation of group displays of 71.25 without. This is the protective response to the invasions of arguably an innate mechanism that has evolved over time to protect ourselves and our offspring. aggression wider applicability due to the E: This suggests that the support one’s territory. This form of group display is shown L: Consequently, this gives the evolutionary explanation for group displays wider explanatory power because of the realreal-life examples of xenophobia from the home crowd did not in many sports, for example Samoa used the Manu life empirical evidence behind it. causing violent displays. increase the performance of Siva Tau war chant before the 1991 Rugby World An Alternative approach: Deindividuation teams because they did not have Cup. These displays intimidate the other team and P: Another issue with xenophobia and warfare as explanations for group displays of aggression is that they may be better the evolved need to protect their make the home team more aggressive. These explained in terms of deindividuation. territory as the evolutionary displays would have been adopted from ancestors E: This is because evolutionary explanations are based on mating successes, status or commitment and fail to explain explanation suggests. because they had to defend valuable resources like the levels of cruelty often found in human wars not found among non-human species, such as torture of those who no L: Consequently, this casts doubt their territory. This has also been linked to having longer pose a threat or who have already been defeated. on the evolutionary explanation higher testosterone levels, for example, Neave & E: Anthropological evidence suggests this may be more of a consequence of deindividuation effects than evolutionary of group displays in humans and Wolfson (2003) found that football teams playing at adaptations. This is because humans in wars may lose their own identity and morals as a result of being in a group, reduces its explanatory power home were far more likely to win than the visiting where the combination of anonymity, suggestibility and contagion mean that a ‘collective mind’ take possession of the because these findings are not in team, partly because they have the benefit of a huge individual. This is arguably a more logical explanation rather than something that is biologically programmed within us. line with its assumptions. surge of testosterone before the match. This could L: Therefore evolution cannot fully explain group aggression and is arguably a weak explanation alone. Instead an be due to the evolved drive to defend home integrationist approach should be taken that considers other aspects of group displays of aggression. territory, leading to more aggressive group displays Warfare Supporting Evidence MAID: For (8 + 16 mark) Q aim for 3 outcome study PEELS and 3 MAID FULLY ELABORATED PEELS. 10 minutes A01, 20 mins A02. For shorter Qs, adjust approp… The evolutionary explanation for group displays of P: One strength of the evolutionary Deterministic Vs Free Will aggression as an adaptive response also explains explanation of group displays as an P: An issue with evolutionary explanations for group displays in human aggression is that it is deterministic. these displays in terms of warfare. This has evolved adaptive response in warfare is that it E: This is because it suggests our genes specify exactly how we act aggressively in groups and that humans are predisposed to aggression through warfare, due to the benefits of this group display which can has gained empirical support. xenophobia and protecting ones territory. It is argued that group displays of aggression have evolved to help protect ourselves from strangers and therefore be explained in terms of sexual selection. E: For example, research has shown that enable humans to protect their offspring; and are performed due to an evolved need to gain access to women and reproduce, therefore increasing aggression is important in attracting reproductive success. However, this determinist interpretation fails to take into account that genes only predispose us to behave in certain ways, but do not Divale and Harris (1976) found that in places where mates. Palmer & Tilley (1995) found dictate what individuals to do. war is common, men are more likely to survive that youth street gang members have E: For example, LeBlanc & Register (2004) claim that warfare is not a biological gene, it emerged when we moved from nomadic to settled people and were because of their usefulness in battle. This leaves more sexual partners than other young tied to the land. Because of this, people could not walk away from trouble and had far more to lose, and to fight over, than their hunter gatherers. This few women compared to men meaning that men males. Additionally, Leunissen & Van means that rather than war being an evolved adaptation, warfare emerged as a response to a change in lifestyle and the choices that people made. This who are successful in battle must compete with Vugt (2010) also found that military suggests that warfare and aggressive displays are not biological compulsions but are a consequence of environmental changes such as rising population and other successful men for access to women. men have a greater sex appeal but only less food. In addition, Chagnon (1988) state that displays of if they had been seen showing bravery L: Therefore, the explanatory powers of the evolutionary explanation of group displays of aggression as an adaptive response in warfare is reduced because aggression and bravery are attractive to females in combat. the free will and choice that individuals have made over time and continue to make has not been considered. and their absence reduces the attractiveness of E: This suggests that men who display Gender Bias individual males. For example, male warriors in signs of bravery are more attractive to P: Additionally, a further weakness for evolutionary explanations of group displays is that they display gender bias. This is because evolutionary explanations traditional societies have more partners and more females because it will increase their of group displays in warfare do not adequately reflect the behaviour of women in the process. children suggestion a direct reproductive benefit. chances of reproductive success as E: For example, Adams (1983) claimed that the idea of women warriors is almost unheard of within most societies. Even in these societies that allow women to This shows that group displays are performed due they will be able to protect their mate participate in war, they are always the rare exception. This is because women would have less to gain from fighting in near-death situations and more to lose to an evolved need to gain access to women and and their offspring. (in terms of loss of their reproductive capacity). reproduce, therefore increasing reproductive L: As a result, this gives the explanation E: Therefore our understanding of the group displays typically found in warfare are subjected to beta bias because they are limited to the behaviour of males successes. of group displays of aggression in rather than females, thus minimizing the differences between the two sexes. warfare credibility. L: In turn, the evolutionary explanation does not offer a full account of warfare in group displays, rendering it inadequate; weakening its explanatory power and credibility overall.