Double circulation Text Resource
advertisement

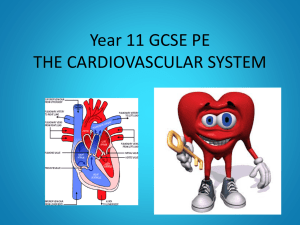
Labels for drama activity Lungs Liver Stomach Leg muscles Arm muscles Back muscles © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 Sc Animals, including humans Session B We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Kidneys Intestine Skin Brain Bladder Pancreas Heart © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 Sc Animals, including humans Session B We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Heart labels Right atrium (top left chamber when looking at heart) Left atrium (top right chamber) Right ventricle (bottom left chamber) Left ventricle (bottom right chamber) © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 Sc Animals, including humans Session B We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Heart Cloze The heart is made of _________tissue and it pumps blood around the body to deliver ___________ and _________ to all the cells in the body. The nutrients enter the blood from the ___________ system to be carried to all parts of the body. The oxygen is collected from the _________where it is exchanged for _________ dioxide. The heart is divided into four sections called ____________, the left and right atria (singular atrium) at the top and the left and ________ ventricles at the bottom. Blood is pumped from the right _______ through an _________ to the lungs. Oxygen is ____________ for carbon dioxide in the capillaries in the lungs. The blood that now contains oxygen (oxygenated) is then carried back to the heart via a ______ to the left atrium. This oxygenated blood then passes into the left ventricle through a _______ and is pumped to all parts of the body. The oxygen and nutrients pass to the body cells from the ____________ and carbon dioxide is collected. The blood is now called deoxygenated blood. This ______________ blood is carried back to the right ________ of the heart. It then passes to the right ventricle through another heart valve ready to be ___________ to the lungs again to collect more oxygen. The blood circulation is like a figure of _________. capillaries oxygen muscle chambers eight vein valve lungs ventricle nutrients digestive artery pumped deoxygenated right atrium carbon exchanged © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 Sc Animals, including humans Session B We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Teacher sheet Heart Cloze The heart is made of muscle tissue and it pumps blood around the body to deliver nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body. The nutrients enter the blood from the digestive system to be carried to all parts of the body. The oxygen is collected from the lungs where it is exchanged for carbon dioxide. The heart is divided into four sections called chambers, the left and right atria (singular atrium) at the top and the left and right ventricles at the bottom. Blood is pumped from the right ventricle through an artery to the lungs. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide in the capillaries in the lungs. The blood that now contains oxygen (oxygenated) is then carried back to the heart via a vein to the left atrium. This oxygenated blood then passes into the left ventricle through a valve and is pumped to all parts of the body. The oxygen and nutrients pass to the body cells from the capillaries and carbon dioxide is collected. The blood is now called deoxygenated blood. This deoxygenated blood is carried back to the right atrium of the heart. It then passes to the right ventricle through another heart valve ready to be pumped to the lungs again to collect more oxygen. The blood circulation is like a figure of eight. © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 Sc Animals, including humans Session B We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Websites for research on Galen and William Harvey http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/historic_figures/harvey_william.shtml short biography of William Harvey http://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/broughttolife/people/williamharvey.aspx short biography of William Harvey http://biology.about.com/library/organs/blcircsystem2.htm compares Harvey’s ideas with Galen’s theories http://www.wellcomecollection.org/explore/mind-body/topics/dissection/video.aspx?view=william-harvey or http://archive.org/details/WilliamHarveycirculationoftheblood2-wellcome great video for adults – there may be sections you’d like to show children http://physiologyonline.physiology.org/content/17/5/175.full detailed information for adults http://www.zephyrus.co.uk/williamharvey.html short biography of William Harvey http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Harvey useful information about William Harvey http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galen useful information about Galen http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/historic_figures/galen.shtml short biography about Galen http://www.pbs.org/wnet/redgold/history/timeline1.html timeline of the history of blood circulation http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/william_harvey.htm another biography of William Harvey http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEC/CC/heart_background.php history of our understanding of the circulatory system © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 Sc Animals, including humans Session B We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites