VCE History - Summary of Proposed Changes to the Study Design
advertisement

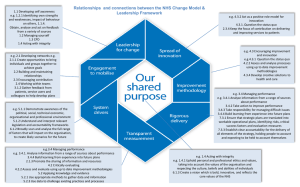
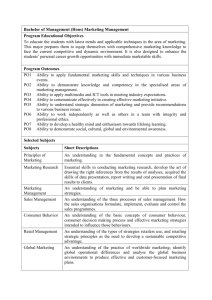
VCE HISTORY Summary of proposed changes to the study design OVERVIEW The review and development of VCE history has included the review of six units in the current study design and the development of six new units. The six units reviewed are: Twentieth Century history, Units 1 and 2 Australian history, Units 3 and 4 Revolutions, Units 3 and 4 The seven units which have been developed are: Global empires, Units 1 and 2 Ancient history, Units 1- 4 (with a choice between two Unit 2’s) This document focuses on the changes that are proposed to the current VCE histories. GENERAL CHANGES Review of VCE Histories has included: Increased specificity within areas of study especially in Units 3 and 4. The key knowledge contains a far greater degree of detail compared to the current study design. This supports teachers to develop a teaching and learning sequence and clarifies expectations for assessment. Units 1 and 2 continue to have some flexibility. Key inquiry questions which frame each area of study have also been incorporated. Updating of historical thinking based on contemporary research into the ways that students learn history. The study design contains a Characteristics of the study section in the introduction which outlines the incorporation of key aspects of historical thinking into the study. These key aspects are: ask historical questions; establish historical significance; use sources as evidence; identify continuity and change; analyse cause and consequence; consider historical perspectives; and understand ethical dimensions in history. These aspects of historical thinking have been incorporated into the key skills of all history units. The Characteristics of the study section also contains a definition of historiography. Review of assessment tasks for history. In Units 1 and 2 tasks have been more tightly specified to reflect the nature of historical rather than generic tasks. In Units 3 and 4 language of the tasks has been reviewed. Review of substantive content in each of the histories to reflect recent scholarship. SPECIFIC CHANGES Unit 1: Twentieth Century history, 1900–1945 i. ii. Area of Study 1: Ideology and conflict Area of Study 2: Social and cultural change Unit 1: Twentieth century history contains two areas of study rather than the three in the current study design. ©VCAA, August 2014 VCE HISTORY SUMMARY OF PROPOSED CHANGES In Area of Study 1, there is a focus on the period between the World Wars rather than the development of any political crisis within the first half of the twentieth century. This allows students to concentrate on the nature of ideologies which emerged as well as the events that led to World War II. Area of Study 2 combines two areas of study from the current study and allows students to investigate social and cultural life in a range of contexts. Unit 2: Twentieth Century history 1945–2000 i. ii. Area of Study 1: Competing ideologies Area of Study 2: Challenge and change Unit 2: Twentieth century history contains two areas of study rather than the three in the current study design. In Area of Study 1: Competing ideologies: there is a focus on the nature, development and course of the Cold War rather than the more general post-war conflicts contained in the current study design. This allows students to develop a deep understanding of the impact of ideological division on nations and people in a range of global contexts which characterised much of the second half of the twentieth century. In Area of Study 2: Challenge and change: students investigate a social and a political challenge in the last half of the twentieth century. Social challenged include those from the current study design (civil rights, feminism, gay liberation and so on). Political changes include some of those from the current study design and some that are more recent. They include the Middle East conflict, the anti-Apartheid movement, the Iranian revolution and the achievement of independence in Papua New Guinea. UNITS 3 and 4 AUSTRALIAN HISTORY Unit 3: Transformations: from settler society to nation i. ii. Area of Study 1: The reshaping of Port Phillip District/Victoria, 1834–1860 Area of Study 2: Making a people and a nation, 1901–1920 Area of Study 1: The reshaping of Port Phillip District/Victoria, 1834–1860 slightly modifies the period under consideration compared to 1830–1860 in the current study design. The main change in this area of study is the inclusion of increased Aboriginal content including: land management practices and ideas about land management of the Aboriginal inhabitants; the range of Aboriginal responses to the transformation of their physical and cultural environment; and the outcomes for Aboriginal communities. As with the current study design there is also an examination of European land amendment practices. The area of study also looks specifically at the demographic consequences of the gold rushes and the specific political consequences of an influx of immigrants with democratic and new world aspirations. Area of Study 2: Making a people and a nation, 1901–1920 modifies the period under consideration compared to 1888–1914 in the current study design. As such, there is less emphasis on the nationalism of the 1880s and 90s and an opportunity to consider ways in which participation in World War I affected and changed the new nation. As with the current study design, students explore the legislation of the new parliament in regard to electoral law, industrial arbitration and social welfare and those that were included and excluded in the new ‘social laboratory’. ©VCAA August 2014 2 VCE HISTORY SUMMARY OF PROPOSED CHANGES Unit 4: Opening Australia to the world i. Area of Study 1: Crises that tested Australia 1930–1975 ii. Area of Study 2: Movements and changes in Australian society 1970–2000 Area of Study 1: Crises that tested Australia 1930–1975 explores crises that affected Australia and their impact. These include the Vietnam War 1962–1973, the Great Depression 1930–1939 and World War 2, covering the period 1939–1950. Consequently the date range differs from the current study design (1914–1950). Students study one of these crises in depth and explore the causes of Australia’s involvement in external crises, the social economic and political responses and the extent to which the crisis created change in Australia. Area of Study 2: Movements and changes in Australian society 1970–2000. Students examine the debates and changes in one of four movements for change: Aboriginal activism and land rights, women’s fight for equality, opening Australia’s economy to the world and Australia’s changing population and immigration policy. While two of these options: Immigration and Aboriginal rights are in the current study, the proposed course considers events and changes from later in the 20th century. The Aboriginal option focuses on changes in attitudes to land rights, including changes in legislation resulting from the Mabo and Wik decisions of the High Court. The immigration option focuses on changing attitudes to Asian immigration, refugees and the notion of Multiculturalism. Women’s fight for equality covers the demands of the women’s movement and achievements in the last part of twentieth century and the economic option looks at the changes resulting from global trends including floating the dollar, reduction of tariffs and the notion of a ‘social wage.’ All areas of study contain increased detail to make expectations of teaching and learning and assessment clear. UNITS 3 and 4 REVOLUTIONS i. ii. Area of Study 1: Causes of revolution Area of Study 2: Consequences of revolution The introduction to the Units provides the dates of the revolutions that will be the focus of the investigation: America, 1776; France, 1789; Russia, October 1917; China, 1949. This provides a clear focus for study. The dates for Area of Study 1 have been revised: American Revolution from 1754–4th July 1776 (French and Indian War to the Declaration of Independence 1776). Current study 1763–1776. French Revolution from 1763–October 1789 (End of the Seven Years War to The October Days 1789) Current study 1781–1789. Russian Revolution from 1896–October 1917 (Coronation of Tsar Nicholas to the 25th October Revolution 1917) Current study 1905–1917. Chinese Revolution from 1912–1949 (The Chinese Republic to the Communist victory in the Civil War 1st October 1949). Current study 1898–1949. The area of study continues to focus on key events contributing to revolution, key ideas which challenged the existing order, key individuals and the role of popular movements. The dates for Area of Study 2 have been maintained apart from the Russian Revolution where the period had been extended from 1917–1924 to 1917–1927 to cover the end of the New Economic Policy (NEP) . Both areas of study contain increased detail to make expectations of teaching and learning and assessment clear. ©VCAA August 2014 3 VCE HISTORY SUMMARY OF PROPOSED CHANGES ASSESSMENT Outcome statements in all areas of study across Units have been altered to reflect the new focus of the units. Twentieth Units 1 and 2 Outcome statements Current Study Outcome Statements Consultation Draft Outcome Statements Unit 1 Area of Study 1 On completion of this unit the students should be able to analyse and explain the development of a political crisis and conflict in the period 1900–1945. Unit 1 Area of Study 1 On completion of this unit, the student should be able to explain the consequences of World War I and the peace treaties, and analyse the impact of ideologies on nations and on the events that led to World War II. Area of Study 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse and discuss patterns of social life and the factors which influenced changes to social life in the first half of the twentieth century. Area of Study 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse and discuss patterns of social life and cultural change and the factors which influenced changes to social life and culture in the inter-war years. Area of Study 3 On completion of this unit the students should be able to analyse the relationship between the historical context and a cultural expression of the period from 1900–1945 Current Study Outcome Statements Consultation Draft Outcome Statements Unit 2 Area of Study 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse and discuss how post-war societies used ideologies to legitimise their worldview and portray competing systems. Unit 2 Area of Study 1 On completion of this unit, students should be able to explain the ideological divisions in the post war period and analyse the nature, development and impact of the Cold War on nations and people, in relation to one or more particular conflicts in the period. Area of Study 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to evaluate the impact of a challenge(s) to established social, political and/or economic power during the second half of the twentieth century. Area of Study 2 On completion of this unit, the student should be able to describe and analyse the motivations behind challenges and changes to existing power, and evaluate the impact of the challenges. Area of Study 3 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse issues faced by communities arising from political, economic and/or technological change. ©VCAA August 2014 4 VCE HISTORY SUMMARY OF PROPOSED CHANGES Australian History Unit 3 Outcome Statements Current Study Outcome Statements Consultation Draft Outcome Statements Outcome 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to explain the motives and hopes underlying the settlement of the Port Phillip District (later the colony of Victoria) up to 1860 and the impact on the Indigenous population. Outcome 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the nature of change in the Port Phillip District/Victoria in the period 1834–1860. Outcome 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to evaluate the extent to which changing attitudes are evident in Australian’s reactions to significant social and political issues. Outcome 2 On completion of this unit students should be able to analyse the visions and actions that shaped the new nation after Federation and the changes that resulted from participation in World War I. Total marks Marks Assessment tasks allocated 50 Each of the following four assessment tasks must be taken over Units 3 and 4: An historical investigation An analysis of primary sources An analysis of historians’ interpretations An essay 50 Teachers may choose the order of the assessment tasks 100 Australian History Unit 4 Outcome Statements Current Study Outcome Statements Consultation Draft Outcome Statements Outcome 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the ways in which Australians acted in response to a significant crisis faced by the country during the period 1914 to 1950. Outcome 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the extent to which Australia was reshaped by a significant crisis during the period 1930 to 1975. Outcome 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to evaluate the extent to which changing attitudes are evident in Australian’s reactions to significant social and political issues. Outcome 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the transformation in the late twentieth century of a significant aspect of Australian life. Total marks Marks Assessment tasks allocated 50 Each of the following four assessment tasks must be taken over Units 3 and 4: An historical investigation An analysis of primary sources 50 An analysis of historians’ interpretations An essay Teachers may choose the order of the assessment tasks 100 *School-assessed Coursework for Unit 3 contributes 25 per cent. ©VCAA August 2014 5 VCE HISTORY SUMMARY OF PROPOSED CHANGES Revolutions Units 3 and 4 Outcome Statements Current Study Outcome Statements Consultation Draft Outcome Statements Outcome 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to evaluate the role of ideas, leaders, movements and events in the development of the revolution. Outcome 1 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the causes of revolution, and assess the contribution of significant ideas, events, individuals and popular movements. Outcome 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the challenges facing the emerging new order, and the way in which attempts were made to create a new society, and evaluate the nature of the society created by the revolution. Outcome 2 On completion of this unit the student should be able to analyse the consequences of revolution and evaluate the extent of change brought to society. Total marks Marks Assessment tasks allocated 50 Each of the following four assessment tasks must be taken over Units 3 and 4: An historical investigation An analysis of primary sources 50 An analysis of historians’ interpretations An essay Teachers may choose the order of the assessment tasks 100 *School-assessed Coursework for Unit 4 contributes 25 per cent. ©VCAA August 2014 6