Type of Reasoning
advertisement

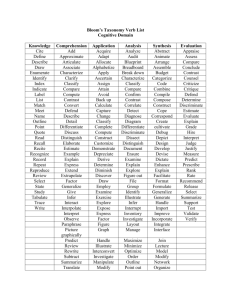
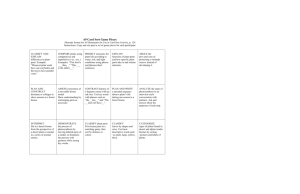
Properties of Matter Elementary Type of Reasoning Signal Words Example Questions Next Steps Considerations 1. Analyze Components Parts Ingredients Order Main idea pattern What does the addition or removal of heat do to matter? What patterns do you notice? Experiments related to the removal or addition of heat and resultant changes of state. How are the molecules in a solid, liquid, and gas alike? How are they different? Use the picture above to identify water in all 3 states of matter. 2. Compare/Contrast Discriminate Distinguish Analogy Alike Different Similar Formulate, describe, combine, blend, organize, adapt, modify, interpret How would you describe the effect of changes on the physical properties of an ice cube that has been heated to a classmate? Investigations: properties of water, changes in states of matter Example of Group Sort Category Common relationship identify How many ways can you sort this bag of items? Explain why you chose to sort the items as you did. Identify differences between properties and materials. Modeling sorting based on properties. Example: Explain why a plastic wrapper is a solid even though it is flexible. 3. Synthesize 4. Classify 5. Infer/deduce 6. Evaluate Role play Properties of Matter MIDDLE SCHOOL Type of Reasoning 1. Analyze 2. Compare/Contrast Signal Words Example Questions What is? Identify Components/Parts Determine What properties determine the placement of an element on the periodic table? Pre-assessment Basic Research Grouping ‘activity Discriminate, distinguish, different, similar, analogy, alike Distinguish between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Fermentation Lab where a gas is produced Compare and contrast chemical and physical properties of solids Mystery Powder Lab Combine, formulate, blend, adapt, modify How would you use physical properties to organize material into similar groups? Lab where students identify physical properties and they use them to classify into groups. Sort, examples of, group, classify, identify, types of, organize, categories, similar characteristics, chronological, common relationship, differentiate Identify the reactants and products in the following reactions….. Model using proficient students or yourself. Group using obvious items Simplify vocabulary and directions Predict Conclude Use evidence Imply why Infer why plastic and Styrofoam are used to make football helmets. What evidence did you use? Justify, support, defend, prove, take a position, judge, critique, appraise, dispute, give evidence, evaluate Evaluate the mystery substances, classify each according to their properties, and justify the classifications 3. Synthesize 4. Classify 5. Infer/deduce 6. Evaluate Next Steps Considerations Classify matter as an element or compound. Predict what an unknown substance might be used for and give reasons for your predictions Observe properties of various materials. Discuss uses, advantages, disadvantages based on these properties in terms of application Lab with different mystery substances using different tests to identify each substance Properties of Matter HIGH SCHOOL Type of Reasoning 1. Analyze 2. Compare/Contrast 3. Synthesize 4. Classify Signal Words Components Parts Ingredients Order Main idea pattern Next Steps Considerations Describe the logical sequence that a substance goes through at the molecular level, as it is being heated In a lab, determine the melting points of various substances Differentiate between conductors and nonconductors in terms of the resistance in the flow of electrons. Electron flow relay Test resistance of conductors and non-conductors with Ohmmeter. Distinguish between metals and nonmetals based on the patterns in the periodic table Lab experiment & generate properties of mystery materials. Using list of properties of elements, highlight on PTable –note patterns Combine Blend Modify formulate How would you describe the relationship between energy and matter? Formulate a lab to test the law of conservation of matter. Describe the law of conservation of matter. Write a lab report Sort, differentiate between, Find an example of… Classify, organize, group, identify, similar characteristics, type of, chronological, common relationship Given the following materials, sort into conductors or non-conductors. Conductivity tester (What to do with metalloids?) Predict, Imply, Why, conclude from evidence Predict behavior based on the temperature, particle number, pressure and volume using the Universal Gas Laws Change temperature and kids of gases to predict behavior. Justify whether the object is a metal or nonmetal. Have students complete lab to determine whether objects are metals or nonmetals and defend their decisions. Discriminate, differentiate, similarities, differences, analogies 5. Infer/deduce 6. Evaluate Example Questions Justify, why or why not? Critique, dispute, appraise, defend, judge Sort these materials as being an element, compound, or mixture. Apply to experiences: tires, dissolved oxygen, air pollution, hypothermia, global warming to discuss implications Properties of Matter Key Ideas about Reasoning: It is important to think about/formulate questions before instruction. Questions must be intentional and purposeful to really align to learning targets and lessons. Good questions move students to appropriate applications. The use of a particular word in and of itself doesn’t necessarily imply what we inferred. Time must be spent really understanding the vocabulary we use. Careful questioning really allows us to assess for learning , and know what students know. Formulated by SLSN September 2007