Primary Succession
advertisement
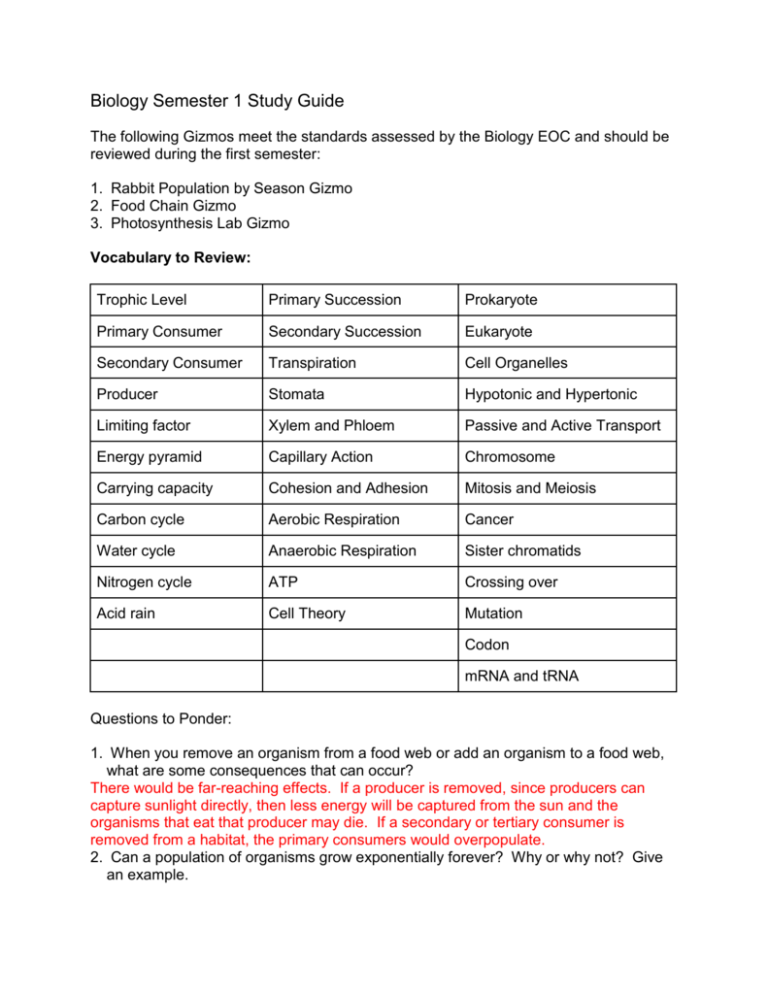
Biology Semester 1 Study Guide The following Gizmos meet the standards assessed by the Biology EOC and should be reviewed during the first semester: 1. Rabbit Population by Season Gizmo 2. Food Chain Gizmo 3. Photosynthesis Lab Gizmo Vocabulary to Review: Trophic Level Primary Succession Prokaryote Primary Consumer Secondary Succession Eukaryote Secondary Consumer Transpiration Cell Organelles Producer Stomata Hypotonic and Hypertonic Limiting factor Xylem and Phloem Passive and Active Transport Energy pyramid Capillary Action Chromosome Carrying capacity Cohesion and Adhesion Mitosis and Meiosis Carbon cycle Aerobic Respiration Cancer Water cycle Anaerobic Respiration Sister chromatids Nitrogen cycle ATP Crossing over Acid rain Cell Theory Mutation Codon mRNA and tRNA Questions to Ponder: 1. When you remove an organism from a food web or add an organism to a food web, what are some consequences that can occur? There would be far-reaching effects. If a producer is removed, since producers can capture sunlight directly, then less energy will be captured from the sun and the organisms that eat that producer may die. If a secondary or tertiary consumer is removed from a habitat, the primary consumers would overpopulate. 2. Can a population of organisms grow exponentially forever? Why or why not? Give an example. No, because eventually a limiting factor would cause the population to stabilize. An example of a limiting factor that would limit the size of a population is the amount of food available. Other examples could be amount of land, number of predators, competition….. 3. Explain this energy pyramid. At each tropic level in a food chain, energy is used by the organisms at that level to maintain their own life processes. Because of the 2nd law of energy, some energy is lost to the surroundings as heat. It is estimated that in going from one tropic level to the next, about 90 % of the energy is lost. In moving to the next tropic level, only 10 % of the original energy is available. By the third tropic level only 1% of the energy is available. 4. Matter cycles and energy flows in one direction. Explain this statement. Matter must be recycled because there is no new matter created; therefore, carbon, nitrogen, and water must be recycled so that they can be reused. Energy comes from the sun and flows in one direction, changing form. However, each time energy changes from one form to another (ex. Chemical to mechanical) some of it is transferred as heat. Therefore, we depend on the sun to continually supply us with more energy. 5. Explain what is happening to the population in this graph. What is one reason why this could be occurring? This graph is showing a population in exponential growth for the first fifty years and then due to some limiting factor, the population reaches its carrying capacity and levels off at about 1.5 million organisms. 6. Carbon must be recycled because new carbon is never made. List the processes shown in the diagram that can change carbon from one form to another. #1 Photosynthesis (carbon fixation) #2 Cellular respiration #3 Decomposers return carbon dioxide back into atmosphere #4 Burning of fossil fuels #5 Cellular respiration 7. Nitrogen is essential in building proteins and nucleic acids in organisms and nitrogen must be recycled because new nitrogen is never created. Study this diagram and describe where most of the nitrogen cycle occurs and why. Since bacteria are the only organisms that can capture atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into an organic compound, most of the nitrogen cycle happens in the soil. 8. What are some human actions that have caused many animals to become endangered on our planet? What can we do to counteract these negative actions? There are many answers to this question; here are just some examples. Negative Action Possible remedy Strengthen Endangered Species Act Overhunting Protecting and restoring habitats Habitat Loss Use of native plants and animals; Invasion of non-native species 9. Compare and contrast primary and secondary succession in a Venn diagram. Primary Slower Lichens must create soil first Starting a new community Secondary Faster Soil already present Rebuilding a community Similarities Building of a community Replaces older vegetation with larger plants (trees) 10. What process is occurring in this diagram? What properties of water make this process possible? This diagram is showing the process of transpiration. Water properties such as cohesion and adhesion allow water to be pulled up the plant. 11. What environmental factors could speed up or show down the process shown in #10? Environmental factors such as higher temperatures, wind, and increased light intensity can increase the rate of transpiration. 12. Write the two formulas for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Circle the reactants in photosynthesis and put a square about the products for cellular respiration. How do they compare? The reactants of photosynthesis are the products of cellular respiration. 13. Compare/contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Commonalities Differences Both produce ATP. Aerobic needs oxygen and anaerobic respiration occurs when no oxygen is present. Both break down glucose. Both are types of respiration. Aerobic respiration is much more efficient and produces a lot more ATP than anaerobic. Aerobic occurs in the mitochondria and anaerobic occurs in the cytoplasm. 14. Fill in the table comparing prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. Prokaryote Nucleus present? No Eukaryote Yes Prokaryote Eukaryote DNA present? Yes Yes Cytoplasm present? Yes Yes Cell membrane present? Yes Yes Cell wall present? Sometimes In plants and fungus Membrane-bound organelles No Yes 15. What type of cell is shown to the right? How do you know? This is a plant cell; it has a square shape, chloroplasts, and starch grains. Make sure that you review the parts of the cell and that you know what job each part of the cell is responsible for. 16. What is this an image of? This is a cell membrane. What is its primary role? Its primary role is to allow certain materials to come in and out of cells. What macromolecule is it made of? It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. 17. A. Label each of the three beakers as hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic. B. Explain what happens to the cell placed in each of the three beakers. Beaker 1- Isotonic; the cell stays the same size because water is entering and exiting the cell at the same rate. It is at equilibrium. Beaker 2: The solution is hypotonic. Water will enter the cell and cause it to swell. Beaker 3: The solution is hypertonic. Water will leave the cell and the cell will shrivel. 18. Use evidence from the diagram to explain the differences between passive and active transport. Passive transport is the movement of molecules in or out of a cell from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the use of energy. Examples of this are diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Active transport is the movement of molecules against the concentration gradient and therefore takes energy to do this; evidence of this is the ATP that you see needed for active transport in the diagram. 19. Why must DNA be replicated? DNA must be replicated so that the new cells generated will have the same amount of DNA as the parent cell. DNA is replicated during interphase before the cell undergoes mitosis. 20. This diagram shows sexual vs asexual reproduction. Explain three major differences between these two processes. Asexual reproduction can only have one parent; sexual reproduction needs two parents to make an offspring. Asexual reproduction produces offspring with exact DNA as the parent verses sexual reproduction produces offspring with genetic variations. Asexual occurs when an animal grows to a certain age and splits into 2 copies of itself. Sexual reproduction allows variation in a species while asexual is just exact copies of the parent. Sexual reproduction uses meiosis while asexual uses mitosis Asexual reproduction usually occurs in more simple-celled creatures while sexual occurs with most complex creatures (ex humans, dogs, etc) 21. How do the daughter cells compare to the parent cell after mitosis has occurred? Give an example. Daughter cells are identical copies of the parent cell. An example is a skin cell making two more skin cells exactly like it. 22. Fill in the table comparing mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis Number of divisions? 1 Meiosis 2 Mitosis Meiosis Diploid or Haploid daughter cells? Diploid Haploid Crossing over occurs? No Yes Genetically identical Identical or different daughter cells? Different 23. Environmental and genetic factors can cause cancer. What is cancer? What goes wrong in the cells? Cancer is uncontrolled cell growth. Cancer occurs when the cell cycle is no longer regulated and cells are growing without control. A tumor, or mass of cells, formed of these abnormal cells may remain within the tissue in which it, or it may begin to invade nearby tissues. An invasive tumor is said to be malignant, and cells shed into the blood or lymph from a malignant tumor are likely to establish new tumors (metastases) throughout the body. 24. The following karyotype shows the chromosomes for a person with Down Syndrome. What happened during cell division that would cause this to occur? Down syndrome is caused by a random error in cell division that results in the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. The type of error is called nondisjunction. Usually when one cell divides in two, pairs of chromosomes are split so that one of the pair goes to one cell, and the other from the pair goes to the other cell. In nondisjunction, something goes wrong and both chromosomes from one pair go into one cell and no chromosomes for that pair go into the other cell. 25. Describe what occurs during the following types of mutations: A. deletion- is a mutation in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is missing B. insertion- is the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence C. nondisjunction- is the failure of homologous chromosome or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. D. Translocation- A chromosome alteration in which a whole chromosome or segment of a chromosome becomes attached to or interchanged with another whole chromosome 26. Write the complementary strand of RNA to this DNA template strand. DNA: TAGGAATTTTTG RNA: AUCCUUAAAAAC 27. This diagram shows the process of protein synthesis. Describe what is happening at each of the major steps. A. Transcription is occurring- DNA is being copied into messenger RNA. B. mRNA is being modified before its leaves the nucleus and is transported to the ribosome. C. Translation is occurring- the mRNA is being read by the ribosome. The three letter codons are being paired up with anti-codons on the tRNA, which are bringing amino acids together to create a chain of amino acids. This chain of amino acids will then be folded into a protein. 28. The following codon chart can figure out which amino acid is represented by which codon. Use the table to figure out which amino acids would be represented by the mRNA chain. mRNA: A U G C A G G C A U U A amino acids: met pro ala leu