Japan_testreview
advertisement

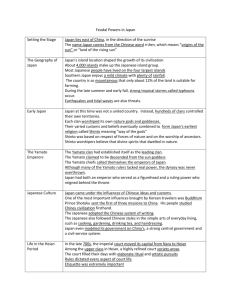
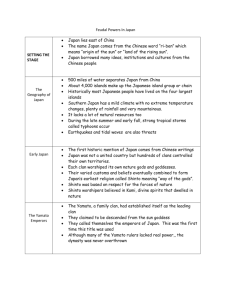
Name Date # 7.5 Feudal Japan – Test Review Directions: Use your notes 8.1 to answer the following questions. 1. Japanese people lived on coastal plains because Japan . 2. Japan’s island location kept it 3. Japanese diet consists mostly of 4. The native religion of Japan that stresses simplicity and respect for nature is 5. The main influences of China and Korea on Japanese culture were and from China and Korea. because of its geography. . , . 6. A regent is: . 7. The spread of Buddhism from China to Japan was due to the efforts of a regent named . Directions: Use your notes 8.2 to answer the following questions. 8. Because their lives were easy and removed from the rest of Japan, Japanese nobles living in the city of Heian called themselves . 9. Nobles who live near and advise the emperor are called: 10. Heian became a center for and in Japan. 11. Most Japanese literature and prose was written by . 12. Describe Heian paintings: 13. Who was Lady Murasaki Shikibu? . 14. Why was the Tale of Genji so influential? 15. What is Noh drama? 16. Zen Buddhism appealed to the samurai because it stressed and . Directions: Use your notes 8.3 to answer the following questions. 17. Who took control of Japan after the royal court became a center for art and learning? 18. The word samurai means: . 19. A general who rules in the name of the emperor is called a . 20. Wealthy landowners that contolled large amounts of land are called: . 21. A samurai warrior’s main duty was . Name Date # 22. Create a pyramid of Feudal Japanese society: 23. In exchange for loyalty to his lord (daimyo), a samurai received . 24. Because the emperor was busy with courtly life in Heian, he lost control of Japan to . 25. Minamoto made the emperor a which means . 26. The code of honor and rules of daily behavior followed by samurai was called . 27. A samurai could lose his honor by , , . 28. To improve their discipline, samurai: 29. What are the ways samurai tradition survives in Japan today? 30. In 1274, Japanese nobles united to fight the 31. . helped save Japan from the Mongols. 32. Oda Nobunaga is remembered for 33. The samurai period lasted until the 1800s because: . Name Date # 7.5 Feudal Japan – Test Review Directions: Use your notes 8.1 to answer the following questions. (beginning – c.800) is difficult to farm due to the mountains and the sea is a source of food. Japan’s island location kept it isolated from China and Korea. Japanese diet consists mostly of seafood because of its geography. The native religion of Japan that stresses simplicity and respect for nature is Shinto. The main influences of China and Korea on Japanese culture were written language, philosophy, and religion. A regent is: someone who rules for someone who is unable to rule alone. The spread of Buddhism from China to Japan was due to the efforts of a regent named Prince Shotoku. 1. Japanese people lived on coastal plains because Japan 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Directions: Use your notes 8.2 to answer the following questions. (c. 800-c. 1100s) 8. Because their lives were easy and removed from the rest of Japan, Japanese nobles living in the city of Heian called themselves dwellers among the clouds. 9. Nobles who live near and advise the emperor are called: the court 10. Heian became a center for learning and culture/art in Japan. 11. Most Japanese literature and prose was written by noble women. 12. Describe Heian paintings: bright, bold colors of scenes from literature, nature, or court life 13. Who was Lady Murasaki Shikibu? a Japanese noble woman who wrote the Tale of Genji. 14. Why was the Tale of Genji so influential? It was the world’s first novel which portrayed court life in Japan between the 800s-1100s 15. What is Noh drama? Plays/drama about Japan’s past heroes 16. Zen Buddhism appealed to the samurai because it stressed meditation and selfdiscipline. Directions: Use your notes 8.3 to answer the following questions. (c. 1192-c. 1850s) 17. Who took control of Japan after the royal court became a center for art and learning? shogun 18. The word samurai means: one who serves. 19. A general who rules in the name of the emperor is called a shogun. Name Date # 20. Wealthy landowners that controlled large amounts of land are called: daimyo. 21. A samurai warrior’s main duty was defend the daimyo (lord) and his land. 22. Create a pyramid of Feudal Japanese society: emperor shogun daimyo samurai peasants (artisans) & merchants Peasants (farmers) 23. In exchange for loyalty to his lord (daimyo), a samurai received land/food. 24. Because the emperor was busy with courtly life in Heian, he lost control of Japan to Minamoto (the first shogun). 25. Minamoto made the emperor a figurehead which means a person who appears to rule even though the real power rests with someone else. 26. The code of honor and rules of daily behavior followed by samurai was called bushido. 27. A samurai could lose his honor by losing a fight, failing to protect his daimyo, disobeying a daimyo. 28. To improve their discipline, samurai: Tea ceremony Wrote poetry Shaped bonsai trees/Flower arrangement Meditation 29. What are the ways samurai tradition survives in Japan today? Showing loyalty Practicing self-discipline Working hard Mongols. 30. In 1274, Japanese nobles united to fight the 31. Kamikaze (divine winds) helped save Japan from the Mongols. Oda Nobunaga is remembered for unifying Japan in 1500s. 32. 33. The samurai period lasted until the 1800s because: Tokugawa formed a shogunate (when a son inherits the position of shogun from father) Tokugawa shoguns isolated Japan Guns were banned Technology was limited