Igneous Rock WKS
advertisement
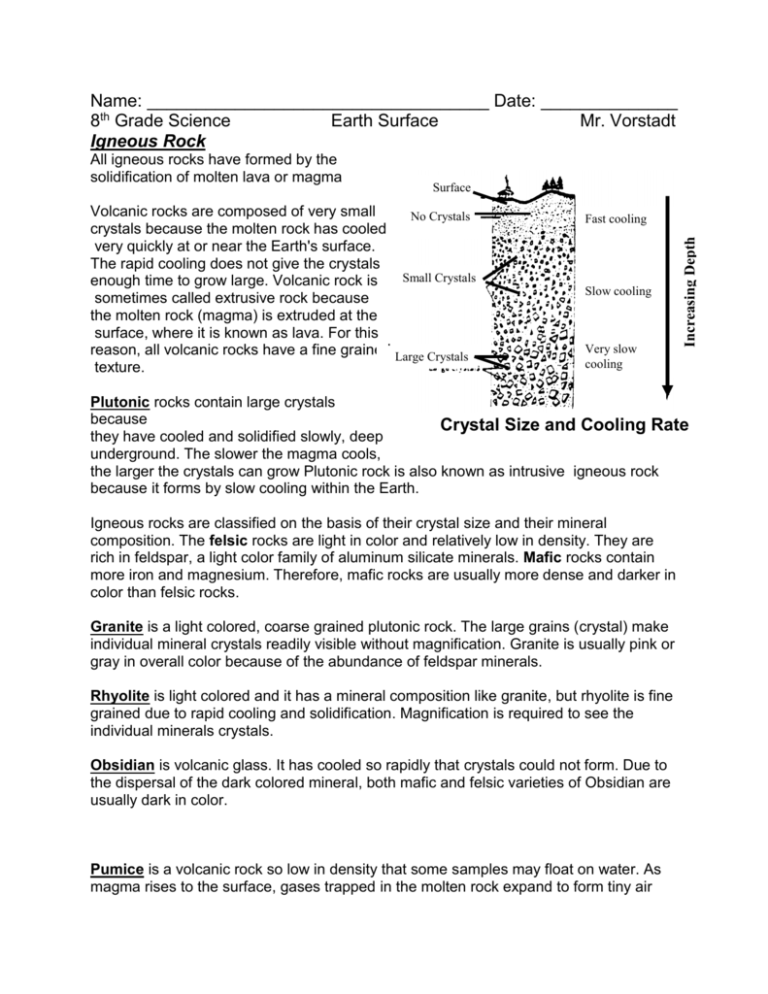
Name: ___________________________________ Date: ______________ 8th Grade Science Earth Surface Mr. Vorstadt Igneous Rock Surface Volcanic rocks are composed of very small No Crystals crystals because the molten rock has cooled very quickly at or near the Earth's surface. The rapid cooling does not give the crystals Small Crystals enough time to grow large. Volcanic rock is sometimes called extrusive rock because the molten rock (magma) is extruded at the surface, where it is known as lava. For this reason, all volcanic rocks have a fine grained Large Crystals texture. Fast cooling Slow cooling Very slow cooling Increasing Depth All igneous rocks have formed by the solidification of molten lava or magma Plutonic rocks contain large crystals because Crystal Size and Cooling Rate they have cooled and solidified slowly, deep underground. The slower the magma cools, the larger the crystals can grow Plutonic rock is also known as intrusive igneous rock because it forms by slow cooling within the Earth. Igneous rocks are classified on the basis of their crystal size and their mineral composition. The felsic rocks are light in color and relatively low in density. They are rich in feldspar, a light color family of aluminum silicate minerals. Mafic rocks contain more iron and magnesium. Therefore, mafic rocks are usually more dense and darker in color than felsic rocks. Granite is a light colored, coarse grained plutonic rock. The large grains (crystal) make individual mineral crystals readily visible without magnification. Granite is usually pink or gray in overall color because of the abundance of feldspar minerals. Rhyolite is light colored and it has a mineral composition like granite, but rhyolite is fine grained due to rapid cooling and solidification. Magnification is required to see the individual minerals crystals. Obsidian is volcanic glass. It has cooled so rapidly that crystals could not form. Due to the dispersal of the dark colored mineral, both mafic and felsic varieties of Obsidian are usually dark in color. Pumice is a volcanic rock so low in density that some samples may float on water. As magma rises to the surface, gases trapped in the molten rock expand to form tiny air pockets. .Although it doesn't look much like obsidian, pumice is actually a frothy form of volcanic glass. Scoria is a rock full of larger air pockets, formed as gases expand within the cooling lava. Scoria is more dense than pumice, and the bubbles are clearly visible. Basalt is a fine grained, dark colored volcanic rock. Because it forms near the surface, basalt is composed of very fine crystals. It is rich in iron and magnesium minerals, so it is dark in color and relatively dense, Gabbro is a dark (mafic) plutonic rock. It is coarse grained, like granite, but because it is rich in iron and magnesium, it is dark in color. Gabbro is the coarse grained equivalent of basalt. Use the chart on the other page and the descriptions on the igneous rock to answer the following questions. 1. What name is applied to a coarse grained, felsic igneous rock? ________________ 2. If granite rock was made of smaller crystals it would be called? ________________ 3. What name is applied to a coarse grained, dark colored igneous rock? __________ 4. What are the five minerals found in granite? _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the four minerals found in basalt and give the approximate percentages of each mineral? _________________________ _____% _________________________ _____% _________________________ _____% _________________________ _____% 6. Why do plutonic rocks have larger crystals than volcanic rock? ________________ __________________________________________________________________ 7. According to the chart what is the texture of Pumice? ________________________ 8. What is the fine grained rock similar in composition to rhyolite? ________________ 9. What is the difference between rhyolite and granite? ________________________ 10. In order for igneous rock to formed the _________________________ and _________________________. 11. How large are the crystals of granite? __________ 12. What five minerals are commonly found in basalt? ________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 13. How do extrusive rocks differ from intrusive rocks? ________________________ 14. What is the color of rhyolite? _________________________________________ 15. What is the approximate percentage of plagioclase in diorte? _______________ 16. What is the word (s) used to describe the grain size in pumice? ______________ 17. What two common minerals are found in granite, but not in basalt? __________________________________________________________________ 18. What igneous rock contains exceptionally large crystals? __________________________________________________________________








