FAMILY PEDIGREE CONSTRUCTION & ANALYSIS
advertisement

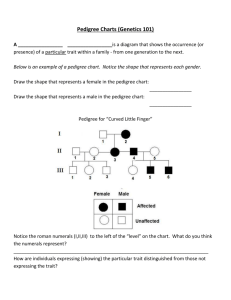
FAMILY PEDIGREE CONSTRUCTION & ANALYSIS There are many ways a genetic counselor can gather information and analyze the pattern of inheritance of a trait in a particular individual. One way is to construct a “family tree” or family pedigree. This allows the counselor and/or the individual to see the occurrence of the trait within members of his/her family and perhaps through several previous generations. By analyzing the pedigree, the mode of inheritance of that trait can be determined. This information can then be used to assist the counselor or individual in evaluating any problem(s) in question. PURPOSE: To construct a family pedigree and attempt to trace the inheritance of a particular trait. OBJECTIVES: To properly construct a family pedigree To determine the most likely mode of inheritance for a selected trait base on the constructed pedigree To determine the possible genotypes for each individual represented in the pedigree BACKGROUND INFORMATION: A Roman numeral – beginning with the oldest generation, represents each generation. The numeral is placed along the LEFT SIDE of the pedigree. Males are represented by SQUARES Females are represented by CIRCLES The genotype should be written inside the symbol. You can determine an individual’s possible genotypes by looking at the generation before and after. If one or both alleles for a particular individual are unknown a “?” should be used. A B? represents that the genotype could either be BB or Bb. A HORIZONTAL LINE between individuals represents marriage. Engagements & relationships that produce children out of wedlock are represented by a DOTTED LINE. A VERITCAL LINE represents children that result from a marriage/relationship from the relationship line. 1 A VERTICAL LINE THAT IS SPLIT AT AN ANGLE indicates fraternal twins. Identical twins are indicated as fraternal twins, but with a DOUBLE LINE BEWTEEN THE SYMBOLS. An arrow is draw to the individual whose pedigree is being constructed. A small BLACK DIAMOND represents a miscarriage. A DIAGONAL SLASH through the symbol indicates a deceased person. A DOTTED VERTICAL LINE coming from the adoptive parents indicates adopted children. If an individual remarries or re-mates, the new partner is indicated on the opposite side. If a couple has multiple children, the symbols are arranged from LEFT (oldest) to RIGHT (youngest). A CIRCLE WITHIN A SQUARE indicates an unborn child whose sex has not yet been determined. 2 MATERIALS: ½” graph paper or computer paper (min. 8.5” x 11”) Golf tee (for making circles) Ruler/straight edge METHODS: 1. You will be given a fictitious family and information about a particular dominant/recessive trait, which includes maternal & paternal grandparents on both sides of the family. You will need to CAREFULLY read the fictitious family history and create a pedigree. Helpful Hints: Read the family history several times Create a family tree with names and phenotypes (without genotypes) Then go back and figure out the correct genotypes 2. Prepare a rough draft of your fictitious family pedigree. This will be done IN CLASS Entire family (symbols) complete Names are under symbols Attempt to determine genotypes – inside symbols 3. Prepare your final fictitious family pedigree. Refer to the rubric on the following page to make sure you have met all of the following guidelines: Proper paper used Symbols are correct size Lines drawn with a ruler or computer program is used Only BLACK INK or PENCIL is used Names & genotypes are in correct locations The following heading is used a the top of the page: Name Class Name Name trait & symbols for dominant/recessive Class Pd Date 3 Pedigree Rubric NAME:_________________________________________Period:___ 1. Total point value = 50 points 2. Due date =_________________ 3. Attach this rubric to your completed pedigree! The following is a list of items that should be included on your pedigree: Your Possible Earned Points Points Required Information 3 Black pencil or black ink should be used (No broad tip markers) 5 Neatness counts! Circles and Squares Must be ½ “ (must be uniform in size) Straight lines – both horizontal and vertical (must be made with a straight edge!) 5 Individual names or question marks UNDER EVERY symbol 3 Roman numerals for EACH generation should be placed along the LEFT side of the pedigree 3 ALL members of the same generation should be on the same horizontal line 10 Proper use of pedigree symbols 3 Indicating the individual with an arrow drawn to his/her symbol 2 Pedigree should go back to the grandparents on each side 10 Correct analysis of traits/genotypes Genotype or question marks for each person INSIDE each symbol (there should be 2 in each symbol!) 3 Proper heading format. Included the trait’s pair of genes that you studied (IE: Handedness H/h) 3 Correct paper used (graph paper, etc.) 50 Total possible points 4 5