Outline
advertisement

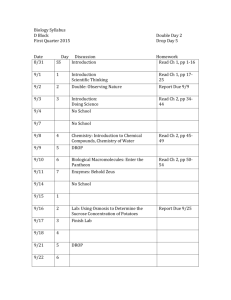
ENVS 554: Environmental Ecology INSTRUCTOR: DR. ASSAD A. AL-THUKAIR Course description: This course will provide comprehensive understanding to the complex interrelationships in nature and mechanisms of interaction among living organisms and their environments. It will introduce the ecosystem concept, interactions between organisms and the biotic environment; and investigates the structure and functioning of ecological systems and balance between terrestrial and marine/aquatic systems. In addition it t examines response of ecological systems to changes of environmental conditions caused by human activities. OFFICE: # (Building 4, Office 140, Tel. # 3827) Office Hours could be scheduled by appointment TEXTBOOK: Ecology, Concepts and applications. Manuel C. Molles , Jr. McGraw-Hill, ISBN 0-07-042716-xHandout and references from various sources (Text books, technical publications, documents and tools from credible internet sites). Course objectives: Give students introductory prospective on basic components of ecology and appreciate its importance. Identify various concepts of life on land and water and adaptations of organisms to live in various environments. Understand major relationships in ecology and effect of physical conditions in environments, water relations, energy and nutrients. Learn the importance of population dynamics, population growth, population distribution and abundance on ecology and resources. Identify various types of interactions between individuals in a populations including; competition, exploitation and mutualism. Recognize the concepts of communities and ecosystems where species abundance and diversity will be explained. Understand the basic concepts of nutrient cycling, succession, and food webs. Recognize various types of ecology including; landscape ecology, geographic ecology and global ecology. 1 SCHEDULE OF LECTURES Lecture title Lecture Number Outline Course Outline Introduction Chapter 1: What is ecology? 1 Natural History Chapter 2: Chapter 3: 2 Life on Land Life in Water 3 Individuals Chapter 4: Temperature relations Chapter 5: Water Relations Chapter 6: Energy and nutrient relations 5 6 Chapter 9: Population Growth 7 Interactions Chapter 10: Competition Chapter 11: Exploitation Chapter 12: Mutualism 8 Exam 2 Recent Scientific paper 4 Exam 1 Populations Chapter 7: Population Distribution and abundance Chapter 8: Population Dynamics Submission Assignment Communities and Ecosystems Chapter 13: Species abundance and diversity Chapter 14: Food webs 9 Chapter 15: Primary production and energy flow Chapter 16: Nutrient cycling and retention 10 Chapter 17: Chapter 18: Succession and stability Landscape Ecology 11 Chapter 19: Chapter 20: Geographic Ecology Global Ecology 12 Final Exam 2 Recent Scientific paper Course Grading: Activities Points Attendance and Participation in class discussions 10 Exam 1 20 Exam 2 20 Final 30 2 Assignment & Presentation 20 On the Net: Ocean Planet –Smithsonian (http://seawifs.gsfe.nasa.gov/ocean_planet.html). Monterey Bay Aquarium on. Line (http://www.mbayaq.org/) Australian Institute of Marine science, Coral Reefs and Mangroves (http://ibm590.aims.gov.au/ ) Coral Reef Research Institute (http://www.bio.usyd.edu.au/CRRI/crri-ind.html) Cairns On Line Environment Guide: Mangroves (http://www.cairns.aust.com/environ/mangroves.htm) GCC Report in Protecting the Environment and Preserving their Natural Resources.2004. Secretariat General of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf. http://library.gcc-sg.org/Arabic/APicshow.asp?mycover=31 The World Conservation Union (IUCN) www.IUCN.org . National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). www.noaa.gov Massachusetts Office of Coastal Zone Management. www.mass.gov/czm/czm.htm. National Protection Area www.mpa.gov 3