performance indicators - Aurora Public Schools
advertisement

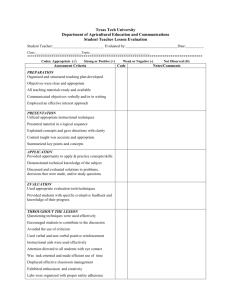
Aurora Public Schools Teacher Evaluation Draft March 9, 2010 Planning and Preparation Specific Indicators Component Teachers demonstrate Comprehensive knowledge of content, Understanding of standards, and pedagogy. the Content 1 2 3 4 Teacher displays little understanding of the subject or structure of the discipline, content standards or of content-related pedagogy. Teacher's knowledge of content, content standards and pedagogy represent developing understanding but do not extend to connections with skills outside the classroom. Teacher demonstrates solid understanding of content, content standards, and pedagogy. Teacher actively builds on knowledge of prerequisites and misconceptions when describing instruction or seeking causes for student misunderstanding. Teacher's instructional practices reflect current pedagological knowledge. Teacher demonstrates thorough knowledge of students' backgrounds, skills, and interests, and uses this knowledge to differentiate and shelter instruction for groups of students. Teacher's knowledge of the content, content standards and pedagogy are extensive. Teacher's knowledge of content extends to how the content affects and is affected by other disciplines and events in the world at large. Knowledge of Students Teachers demonstrate knowledge of students in order to plan, group, differentiate, and/or shelter instruction. Teacher makes little or no attempt to acquire knowledge of students' backgrounds, skills, or interests, and does not use such information in planning. Teacher demonstrates partial knowledge of students' backgrounds, skills, and interests and attempts to use this knowledge in planning for whole class instruction and some small group instruction. Designing Instruction Teachers demonstrate the ability to design standardsbased instruction by developing learning objectives, utilizing resources, selecting instructional strategies/approaches for effective student learning. The instructional design is not based on standards. The design does not align planning elements nor does it engage students in meaningful learning. Teacher's lesson or unit lacks defined structure. The instructional design uses some standards. The design aligns some of the planning elements and engages some students in meaningful learning. Teacher's lesson or unit has a recognizable structure. The instructional design is based on standards. The design aligns most of the planning elements and engages most students in meaningful learning. Teacher's lesson or unit has a clearly defined structure. Assessment Teachers effectively assess student learning to plan for instruction. Teacher's approach to assessing student learning contains no clear criteria or standards, and lacks congruence with instructional goals. Teacher has no plans to use assessment results in designing future instruction. Teacher's plan for student assessment is partially aligned with the instructional goals and includes criteria and standards that are not entirely clear or understood by students. Teacher uses the assessment to plan for future instruction for the class as a whole. Teacher's plan for student assessment is aligned with the instructional goals with clear assessment criteria and standards that have been communicated to students. Teacher designs instruction and assessment which allows for student self reflection and self assessment. Teacher uses the assessment for designing instruction and for sheltering and differentiating for groups of students. Teacher demonstrates thorough knowledge of students' backgrounds, skills, and interests, and uses this knowledge to differentiate and shelter for groups of students as well as for individual student learning. The instructional design is based on standards. The design aligns the planning elements and shows evidence of student input and effective engagement. Teacher's lesson or unit is highly coherent and has a clear structure. Teacher's plan for student assessment is fully aligned with instructional goals, containing clear assessment criteria and standards that are not only understood by students but also requires evidence of student self reflection and self assessment. Classroom Environment Component Specific Indicators Expectations for learning Creating an and achievement Environment of Respect and Rapport that Establishes a Culture for Learning Management of Managing instructional groups or Classroom individual students Procedures and Student Behavior Organizing Physical Space 1 2 3 4 Instructional goals and activities, interactions, and the classroom environment convey only modest expectations for student achievement. Instructional goals and activities, interactions, and the classroom environment convey inconsistent expectations for student achievement. Instructional goals and activities, interactions, and the classroom environment convey high expectations for student achievement. Both student and teacher establish and maintain high expectations for student achievement. Students are not productively engaged and the teacher is not responding to the situation. Tasks for individuals or groups are partially organized and explicit. Students are mostly engaged with some off-task behavior. Transitions or noninstructional duties are fairly efficient resulting in little loss of instructional time. Standards of conduct appear to have been established for most situations, and most students seem to understand them. Teacher is generally aware of student behavior and attempts to respond to misbehavior with uneven results. Tasks for individual or groups are organized and explicit. Students are engaged. Tasks for individual or groups are organized and explicit. Students are actively engaged Transitions or noninstructional duties are efficient resulting in minimal loss of instructional time. Transitions are efficient with students assuming responsibility. Standards are established and clear to most students. Standards of conduct are clear to students. Teacher is consistently alert to student behavior and response to student behavior is appropriate. Teacher initiate preventative measures and students monitor their own and peer behaviors The classroom is safe, and classroom furniture is adjusted for a lesson, or if necessary, a lesson is adjusted to the furniture, but with effectiveness. Teacher uses physical resources effectively, and learning is accessible to students. The classroom is safe, and the furniture arrangement is a resource for learning activities. Management of transitions and non-instructional duties Considerable time is lost due to non-instructional duties or transitions. Expectations No standards of conduct appear to have been established, or students are confused as to what the standards are. Monitoring and response to student behavior Student behavior is rarely monitored, and teacher is unaware of what students are doing. Safety and arrangement of furniture The classroom, within teacher’s control, is unsafe and the furniture arrangement is not suited to the lesson, or both. The classroom, within teacher’s control, is unsafe or the furniture arrangement is not suited to the lesson,. Accessibility to learning and use of physical resources Teacher uses physical resources poorly, or learning is not accessible to some students. Teacher uses physical resources adequately, and essential learning is accessible to most students. Teacher uses physical resources effectively, and learning is accessible to all students. Instruction Component Communicating Clearly and Accurately Specific Indicators 1 2 3 4 Directions and procedures Oral and written language Teacher spoken and written directions and procedures are confusing to most students. Teacher spoken and written directions and procedures are clarified after initial student confusion. Teacher spoken and written directions and procedures are clear to students and contain an appropriate amount of detail. Using Questioning Quality of questions Teacher‘s questions are of low quality. Teacher’s questions are a combination of low and high quality. Engaging Students in Learning Engagement of students Grouping of students Structure and pacing Few students engaged in active learning. Instructional groups are not productive. The lesson has no clearly defined structure. The pacing is too slow or rushed, or both. At least half of the students engaged in active learning. Instructional groups are partially productive. The lesson has a recognizable structure. Pacing of the lesson is inconsistent. Most of the teacher’s questions are of high quality and help the teacher assess student learning. Most students engaged in active learning. Instructional groups are productive. The lesson has a clearly defined structure. Pacing of the lesson is consistent. Providing Feedback to Students Quality of feedback Timeliness of feedback Feedback is either not provided and/or it is of low quality. Feedback is inconsistent in quality and not provided in a timely manner. Feedback is of high quality and provided in a timely manner. Teacher spoken and written directions and procedures are clear to students and teacher is prepared to anticipate possible student misunderstanding. Teacher‘s questions are of uniformly high quality and help the teacher assess student learning. All students are engaged in active learning. Instructional groups are productive. The lesson’s structure is designed to give students the opportunity to meet and/or exceed the learning goal. Pacing of the lesson is appropriate. Feedback is consistently of high quality and provided in a timely manner. Professional Responsibilities Component Specific Indicators Instruction effectiveness Reflecting on Meeting student learning Teaching goals Improvement on instruction 1 2 3 4 Teacher does not know if his/her instruction was effective or achieved its goals, or profoundly misjudges the success of his/her instruction. Teacher has no suggestions for how instruction may be improved. Teacher has an accurate impression of his/her instructional effectiveness and the extent to which student learning goals were met. Teacher has ideas for how instruction may be improved, but does not implement these ideas into daily practice. Teacher participates in some of the school’s required activities for communication, and responds to stakeholder concerns. Teacher has an accurate impression of his/her instructional effectiveness and the extent to which student learning goals were met. Teacher has ideas for how instruction may be improved, and implements these ideas into daily practice. Teacher participates in the school’s required activities for communication, and responds to stakeholder concerns on a timely basis. Teacher communicates both success and concerns. Teacher has an accurate impression of his/her instructional effectiveness and the extent to which student learning goals were met. Teacher actively shares their analysis and reflection with colleagues. Communicating with Stakeholders Participation in communication activities Timely response to stakeholder concerns Communicates successes and concerns about students Teacher does not participate in the school’s required activities for communication, and does not respond to stakeholder concerns. Teacher participates beyond the school’s required activities for communication and teacher responds to stakeholder concerns on a timely basis. Teacher creates and executes additional lines of communication. Teacher creates and executes a professional learning plan which includes a capstone or significant event. Teacher can reflect on how the professional learning plan has enhanced student learning. Growing and Developing Professionally Creating and executing a professional learning plan Professional learning plan is related to student learning Teacher does not create a plan for professional learning that is either aligned with school goals or approved by the supervisor or the teacher creates a professional learning plan but does not execute the plan. Teacher creates and executes a professional learning plan. Teacher can not reflect on how the professional learning plan has enhanced student learning. Teacher creates and executes a plan for professional learning that is either aligned with the school goals or approved by the supervisor. Teacher can reflect on how the professional learning plan has enhanced student learning. Collaboration with Colleagues Positive interactions with colleagues Participates in collegial activities Teacher collaborates in collegial activities that are designed to enhance their student’s learning. Teacher does not interact in a positive and productive manner with colleagues. Teacher interactions with colleagues are positive and productive. Teacher collaborates in collegial activities that are designed to enhance their student’s learning. Teacher interactions with colleagues are positive and productive. Teacher collaborates in collegial activities that are designed to enhance school or district student learning. Advocacy Advocacy for student success Teacher does not collaborate in collegial activities that are designed to enhance their student’s learning. Teacher does not interact in a positive and productive manner with colleagues. Teacher does not know students and does not advocate for their future success. Teacher knows students but can only address and relate to a specific group of students, and advocates for their future success. Teacher knows and relates to students and can advocate for their future success. Teacher knows and relates to students and does advocate for their future success.