DEPOSITIONAL ENVIRONMENTS
advertisement
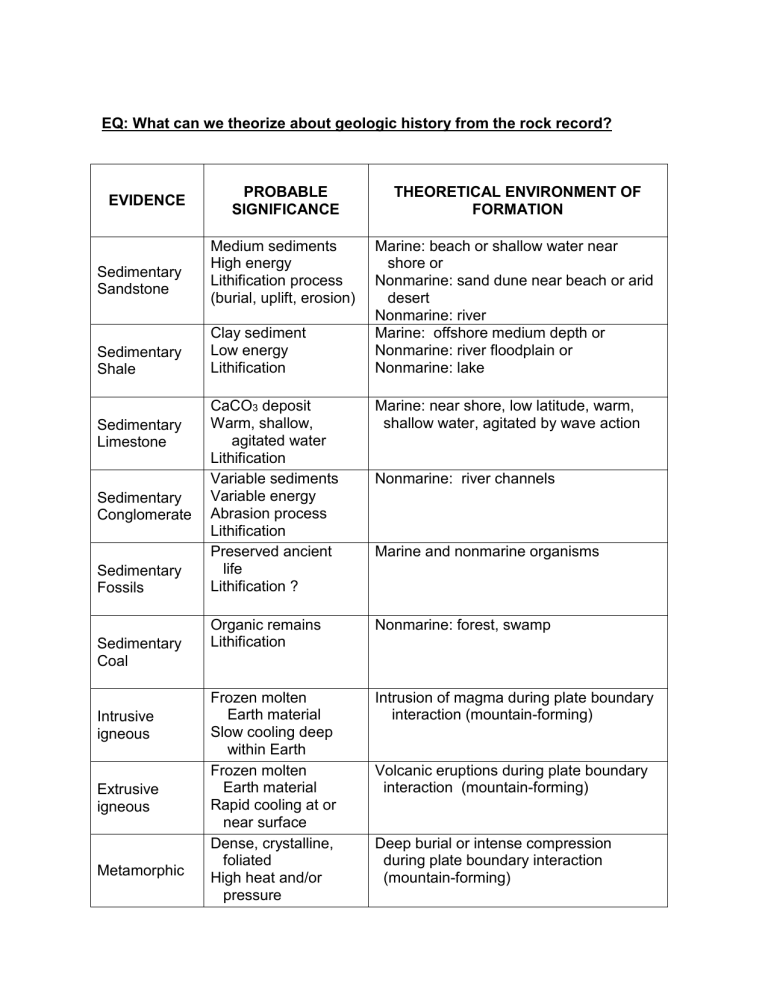
EQ: What can we theorize about geologic history from the rock record? EVIDENCE Sedimentary Sandstone Sedimentary Shale Sedimentary Limestone Sedimentary Conglomerate Sedimentary Fossils Sedimentary Coal Intrusive igneous Extrusive igneous Metamorphic PROBABLE SIGNIFICANCE THEORETICAL ENVIRONMENT OF FORMATION Medium sediments High energy Lithification process (burial, uplift, erosion) Marine: beach or shallow water near shore or Nonmarine: sand dune near beach or arid desert Nonmarine: river Marine: offshore medium depth or Nonmarine: river floodplain or Nonmarine: lake Clay sediment Low energy Lithification CaCO3 deposit Warm, shallow, agitated water Lithification Variable sediments Variable energy Abrasion process Lithification Preserved ancient life Lithification ? Marine: near shore, low latitude, warm, shallow water, agitated by wave action Organic remains Lithification Nonmarine: forest, swamp Frozen molten Earth material Slow cooling deep within Earth Frozen molten Earth material Rapid cooling at or near surface Dense, crystalline, foliated High heat and/or pressure Intrusion of magma during plate boundary interaction (mountain-forming) Nonmarine: river channels Marine and nonmarine organisms Volcanic eruptions during plate boundary interaction (mountain-forming) Deep burial or intense compression during plate boundary interaction (mountain-forming)