M.PHIL. BIO -INFORMATICS CURRICULUM Sl.No Papers Max
advertisement
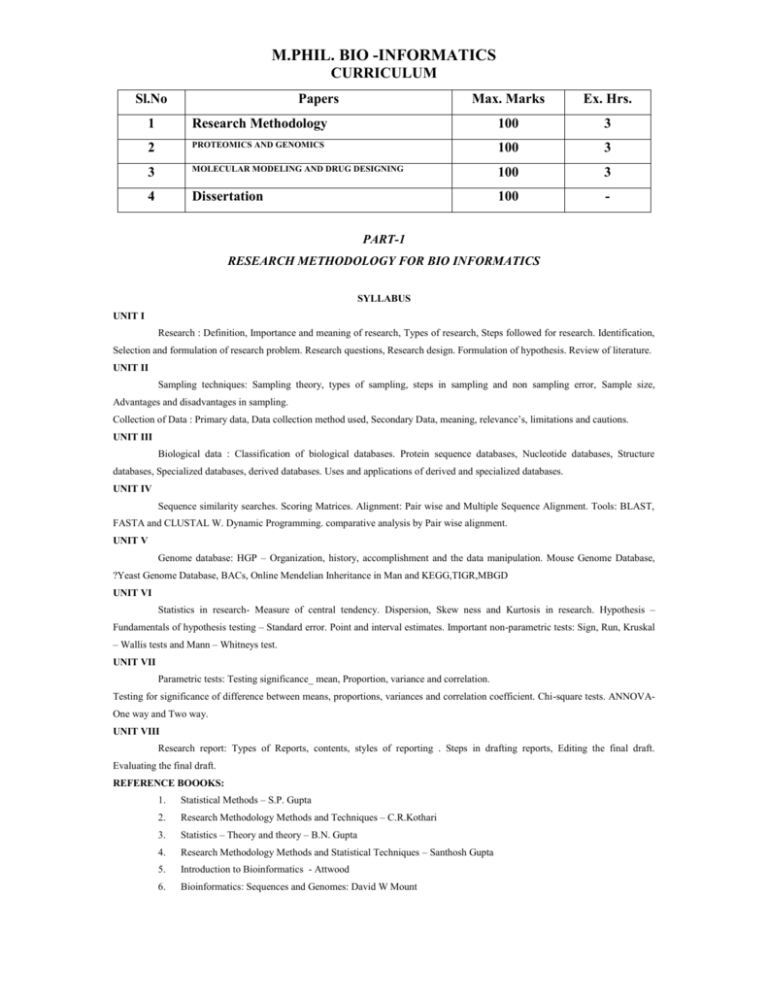
M.PHIL. BIO -INFORMATICS CURRICULUM Sl.No Papers Max. Marks Ex. Hrs. 1 Research Methodology 100 3 2 PROTEOMICS AND GENOMICS 100 3 3 MOLECULAR MODELING AND DRUG DESIGNING 100 3 4 Dissertation 100 - PART-1 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY FOR BIO INFORMATICS SYLLABUS UNIT I Research : Definition, Importance and meaning of research, Types of research, Steps followed for research. Identification, Selection and formulation of research problem. Research questions, Research design. Formulation of hypothesis. Review of literature. UNIT II Sampling techniques: Sampling theory, types of sampling, steps in sampling and non sampling error, Sample size, Advantages and disadvantages in sampling. Collection of Data : Primary data, Data collection method used, Secondary Data, meaning, relevance’s, limitations and cautions. UNIT III Biological data : Classification of biological databases. Protein sequence databases, Nucleotide databases, Structure databases, Specialized databases, derived databases. Uses and applications of derived and specialized databases. UNIT IV Sequence similarity searches. Scoring Matrices. Alignment: Pair wise and Multiple Sequence Alignment. Tools: BLAST, FASTA and CLUSTAL W. Dynamic Programming. comparative analysis by Pair wise alignment. UNIT V Genome database: HGP – Organization, history, accomplishment and the data manipulation. Mouse Genome Database, ?Yeast Genome Database, BACs, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man and KEGG,TIGR,MBGD UNIT VI Statistics in research- Measure of central tendency. Dispersion, Skew ness and Kurtosis in research. Hypothesis – Fundamentals of hypothesis testing – Standard error. Point and interval estimates. Important non-parametric tests: Sign, Run, Kruskal – Wallis tests and Mann – Whitneys test. UNIT VII Parametric tests: Testing significance_ mean, Proportion, variance and correlation. Testing for significance of difference between means, proportions, variances and correlation coefficient. Chi-square tests. ANNOVAOne way and Two way. UNIT VIII Research report: Types of Reports, contents, styles of reporting . Steps in drafting reports, Editing the final draft. Evaluating the final draft. REFERENCE BOOOKS: 1. Statistical Methods – S.P. Gupta 2. Research Methodology Methods and Techniques – C.R.Kothari 3. Statistics – Theory and theory – B.N. Gupta 4. Research Methodology Methods and Statistical Techniques – Santhosh Gupta 5. Introduction to Bioinformatics - Attwood 6. Bioinformatics: Sequences and Genomes: David W Mount PAPER II PROTEOMICS AND GENOMICS UNIT I Chemical foundation of cell – molecular weight, mass and their correct units – genetic foundations – evolutionary foundations. Amino acids – absorption of light by molecules – peptides and proteins - working with proteins – covalent structure of proteins – investigating protein with Mass Spectroscopy – Protein sequencing and evolution. UNIT II 3D structure of protein: Overview – Protein secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure – protein denaturation – protein folding – reverse turns. Protein interaction modulated by chemical energy: actin, myosin and molecular motor. Protein metabolism: genetic code – protein synthesis – determination of size of proteins. UNIT III Gene organization and expression: General principle of gene organization and replication – Common features of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic gene expression – characteristics of gene expression – transcription – splicing – chromosome structure. UNIT IV Ribonomic – Genomes and Genomics – Pattern of genome organization – nenome packaging – Genome stability – Genome Instability – Genome flexibility UNIT V Genome evolution – Genome and their mapping – Paattening genetically engineered organisms UNIT VI Sequencing of proteins – N and C terminal sequencing – Protein chip – Expasy proteomics – Current trends in expression proteomicsUNIT VII Application Proteomics: To drug development and toxicology, Mixing Proteome, Protein expression profile, UNIT VIII Application of Human genetic research – gene modifications and food uses – genetically manipulated organization to the environment – stem cells – therapeutic and regenerative medicine. TEXT BOOKS: 1. Proteomics: from protein sequence to function. Edited by S.R. Pennington & M.J. Dunn. Published by viva books (2002). 2. Introduction to Proteomics: Tools for the new biology by Daniel C. Liebler published by Humana Press. (2002). 3. Biochemistry, Wilson and Walker. 4. Genomes, T.A. Brown 5. Genetic Engineering, J. williams, A. cecceralli and A.wallace, 2 nd edition, bios publishers, 2001. 6. Genomics and cloning technology and application, HD Kumar, East West Press. REFERENCES: 1. Wilkins M.R., Williams K.L., Appel D.F., Hochstrasser (eds) 1997. Proteome Research: New Frontiers in Functional Genomics Springer – Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 2. Bentley D.R., in Genomics (eds Dixon G.K., Coppin L.G and Living Stone D), Bios Scientifics, 3. Bauw, G. and Monatgu, M.V., in Differentially expressed genes in plant: A bench manual (eds Hanse, E and harper G) , Taylor and Francis, 4. T.A. Brown, Genomes, 2nd edition, BIOS Scientific Publishers, Ltd., Oxford. 5. David W. Mount, Bioinformatics – Sequence and Genome analysis, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press 6. Eugene V. Koonin and Michael Y. Galperin, Sequence, Evolution Function, Computational Approaches in Comparative Genomics, Kulwer Academic Press. Paper-III MOLECULAR MODELING AND DRUG DESIGNING SYLLABUS UNIT I Atomic structure, molecular theory for polyatomic molecules; valence states and hybridization; Computer Simulation Methods. Time averages and ensemble averages; molecular dynamics method the basic elements of the Monte Carlo method. Calculation of simple thermodynamic properties; Monte Carlo simulation Methods. Calculating properties by integration; implementation of the Metropolis Monte Carlo method; UNIT II Quantum Mechanical Method; ab initio and semi-empitical approaches. Molecular Mechanics. Molecular mechanics force field; features calculating thermodynamic properties using a force field. UNIT III Molecular dynamics Simulation Method. Molecular dynamics using simple methods; conformational changes form molecular dynamics simulations; basic principles of protein structure; the hydrophobic effect first principles methods for predicting protein structure; lattice models for investigating protein structure; Rule based approaches; homology and comparative modeling methods. UNIT IV Drug discovery: Overview of the drug discovery process,, Modern methods of drug discovery, Various phases- Drug discovery pipeline, Economics of drug discover, Stages and strategies of drug discbvoery6, Rational approach in Drug design, Computer aided drug design, success stores. Scenarios: Combinatorial chemistry, 3D pharmacophore hypothesis, Structure based drug design, De-novo design techniques. UNIT V Structure based drug design; Molecular targets and pathways relevant to disease processes; Receptors, channels, transporters and enzymes as drug targets; Role of protein 3D structures in the drug discovery process, Techniques for protein structure prediction- Comparative modeling, structural genomics. Design of combinatorial libraries, selection of subsets for HTS and hit validation, Lead optimization and candidate selection. UNIT VI QSAR: 2D-QUAR; 3D-QSAR, Examples CoMFA and CoMSIA. Physiochemical concepts in drug design; Physiochemical and biopharmaceutical properties; Experimental approaches, solubility, Liphophilicity, absorption models; Computational approaches. UNIT VII Success stores of protein structure based drug design- X-Ray structure based drug design, Homology model based drug design. Application of protein structure information in the drug discovery process. UNIT VIII Applications of modeling in the SBDD, Substrate binding sites, Applications in combinatorial libraries and 2D and 3D database searching; TEXTBOOKS 1. Molecular Modeling, Principles & Applications, Andrew R.Leach, 2. Addison Wesley Longman, Singapore, 1996 3. ‘Modern Methods of Drug Discovery’ by Gerhard Edwin Seibold, Alexander Hillisch, Rolf Hilgenfeld Publisher 4. “Advanced Drug Design and Development” Kourounakis Taylor and Francis. References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Basic Inorganic Chemistry, F.A. Cotton & G. Wilkinson, Wiley Eastern, New Delhi (for unit I) “Drug Design: Cutting Edge Approaches”. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, Vol.42, “Biopharmaceutical Drug Design and Development”. Susanna Wu-Pong and Yongyut Rojanasakul, “Pharmacokinetics & Metabolism in Drug Design”. D.A. Smith, H.van de Waterbeemd & D.K. Walker (Eds). John Wiley & Sons, Notes on Molecular Orbital Calculations, J.D. Roberts, Benjamin.