Cell Chemistry

Cell Chemistry Study Guide
Life Science 7S
Focus Question 1
What are living things made of?
Relevant Vocabulary:
Atom
Molecular Formula
Element
Molecular Structure
Compound Molecule Chemical Bond
1. What elements make up 96% of living tissue? List the elements name as well as the symbol.
3. What is stored in the chemical bonds between atoms?
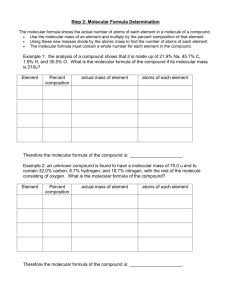
4. Compare and contrast molecular structure and molecular formula.
Molecular Structure Both Molecular Formula
5. Fill out the chart below AGAIN!!!
Name Molecular
Formula
Molecular
Structure
Water H 2 O
Carbon
Dioxide
Oxygen
Glucose
CO
2
O 2
C 6 H 12 O 6
Number
of Atoms
List the elements present
Circle ALL
that apply
Function in the human
body.
Element
Molecule
Compound
Element
Molecule
Compound
Element
Molecule
Compound
Element
Molecule
Compound
Focus Question 2
Why is water so important to living things?
Relevant Vocabulary:
Hydrogen Bonding
Density
Surface Tension
Solvent
Adhesion Cohesion
Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic
Specific Heat
Capillary Action
1. What is the most abundant molecule found in living things?
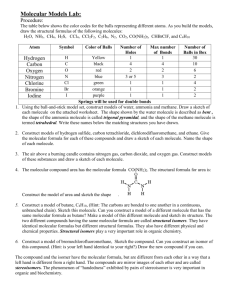
2. What is the molecular formula for the molecular structure shown below?
3. Explain what is wrong with the arrangements of the molecules below?
4. A. Sketch what the correct arrangement of water might look like (many different possibilities).
B. Use a dotted line to show the hydrogen bonds and a highlighter to show the
chemical bonds.
6. List and explain how the 6 properties of water help living things survive.
Property How it helps living things survive
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Focus Question 3
How do you determine if a solution is acidic or basic?
1.
2.
3.
Relevant Vocabulary:
Acid Base (alkaline) pH Scale Buffers
1. List three properties of both acids and bases, and give 2 examples that you tested in your lab.
Acids Bases
1.
2.
3.
2. Sketch a pH scale, label acids, bases, and neutral.
3. What does the pH vale mean? What does it tell you about what is in the solution? (hint H+)
4. What do the letters pH stand for?
5. As you go down the pH scale what happens to the concentration of hydrogen ions?
6. What is a weaker acid a pH reading, of 2 or 4?
7. What is a stronger base, a pH reading of 8 or 9?
8. How are acidic solutions turned to basic solutions?
9. T or F All living things live in the same pH range.
10. What is pollution doing to our oceans and lakes, and how do you think that affects the living things in that ecosystem?
4. Explain what buffers do in living things?
Focus Question 4
What do living things need nutrients to survive?
Relevant Vocabulary:
Organic/Inorganic
Monomer/Polymer
Unsaturated Fat
Macromolecules
Nutrient
Proteins/Amino Acids
Vitamins
Carbohydrates Lipid (fat, wax, oil)
Minerals Saturated Fat
Polymerization
Key Concepts:
1. What are nutrients? List the ones we need to survive. (W, V, M, MM)
2. Why do we need to eat?
3. Put the correct vocabulary associated in with carbohydrates.
Words: monosaccharide disaccharide
Glucose/fructose/galactose polysaccharide monomer lactose/maltose/sucrose polymer starch/fiber
Simple Carbs (one sugar) Simple Carbs (2 sugars) Complex Carbs (more than two sugars chemically bond together)
General term(s):
Examples:
General Terms(s):
Examples:
General Terms(s):
Examples:
4. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fat? Which one is the healthy option?
5. Label the image with the correct molecular structure. simple carb, complex carb, protein, and lipid (saturated and unsaturated)
6. What do calories measure?
7. Circle the organic compounds. a. CO
2 b. H
2
O c. C
6
H
12
O
6 d. NaCl
8. When you see “ose” on the end of a word, what does that mean?
9. Why do some athletes eat high-carbohydrate foods the day before a competition?
10. Fill out the chart below
Organic Compound Elements Monomer Polymer
Function in the Body
3 Healthy
Food Choices
Simple
Carbohydrate
(Sugars)
Complex
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids X