Egypt
advertisement
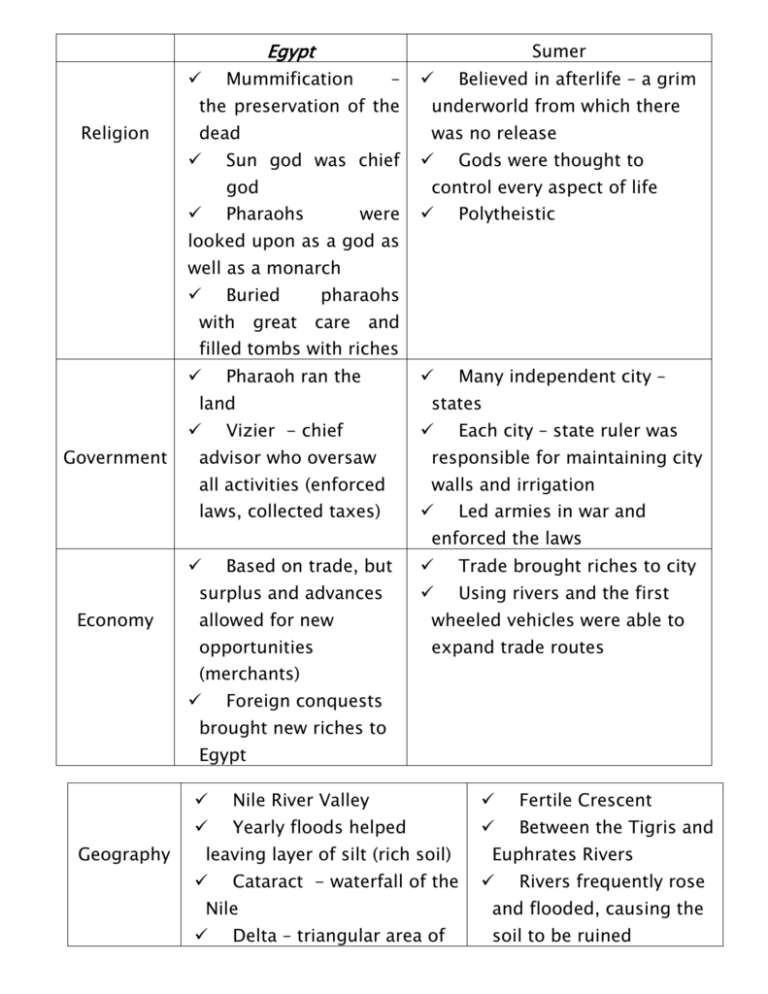
Egypt Mummification Religion Sumer – Believed in afterlife – a grim the preservation of the underworld from which there dead was no release Sun god was chief god Gods were thought to control every aspect of life Pharaohs were Polytheistic Many independent city – looked upon as a god as well as a monarch Buried with great pharaohs care and filled tombs with riches Pharaoh ran the land Vizier - chief Government states Each city – state ruler was advisor who oversaw responsible for maintaining city all activities (enforced walls and irrigation laws, collected taxes) Led armies in war and enforced the laws Based on trade, but surplus and advances Economy Trade brought riches to city Using rivers and the first allowed for new wheeled vehicles were able to opportunities expand trade routes (merchants) Foreign conquests brought new riches to Egypt Geography Nile River Valley Fertile Crescent Yearly floods helped Between the Tigris and leaving layer of silt (rich soil) Cataract - waterfall of the Nile Delta – triangular area of Euphrates Rivers Rivers frequently rose and flooded, causing the soil to be ruined marshland formed by deposits of silt at the mouth of some rivers Pharaoh – top of social Social hierarchy order Ruling family, high Social High priests/priestesses priests, leading Structure Nobles(fought the officials (highest class) pharaohs wars) Merchants (developed lesser priests, scribes from surplus of food), (small middle class) scribes, artisans (small class) Merchants, artisans, Peasant farmers (largest Peasant farmers (largest class) Slaves (lowest class) class) Slaves Accomplish Building of pyramids First wheeled vehicles ments Advancement in medicine, 1st writing system astronomy, and (cuneiform) mathematics used iron Developed form of picture development of writing (hieroglyphics) Developed simpler form of writing (demotic) Irrigation projects Developed new military technology geometry and algebra built ziggurats











