Concept Check 4.5
advertisement

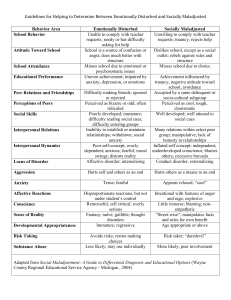
Chapter Four Concept Checks Concept Check 4.1 Complete the following statements about anxiety and its causes with the following terms: (a) comorbidity, (b) panic attack, (c) situationally bound, (d) neurotransmitter, (e) brain circuits, (f) stressful 1. A ____________ is an abrupt experience of intense fear or acute discomfort accompanied by physical symptoms, such as chest pain and shortness of breath. 2. A ____________panic attack often occurs in certain situations but not anywhere else. 3. Anxiety is associated with specific ____________ (e.g., behavioral inhibition system or fight/flight system) and ____________ systems (e.g., noradrenergic). 4. The rates of ____________ among anxiety disorders are high because they share the common features of anxiety and panic. 5. ____________ life events can trigger our biological and psychological vulnerabilities to anxiety. Concept Check 4.2 True or False? 1. ___ GAD is characterized by muscle tension, mental agitation, irritability, sleeping difficulties, and susceptibility to fatigue. 2. ___ Most studies show that the majority of cases of GAD onset early in adulthood as an immediate response to a life stressor. 3. ___ GAD is very prevalent in the elderly and in females in our society. 4. ___ GAD has no genetic basis. 5. ___ Cognitive behavioral treatment and other psychological treatments for GAD are probably better than drug therapies in the long run. Concept Check 4.3 True or False? 1. ___ Panic disorder without agoraphobia (PD) is a disorder in which an individual experiences anxiety and panic with phobic avoidance of what s/he considers an “unsafe” situation. 2. ___ About 40% of the population meets the criteria for panic disorder at some point in their lives. 3. ___ Some individuals with PD are suicidal, have nocturnal panic, and/or are agoraphobic. 4. ___ Psychological treatments like panic control treatment or CBT are highly effective for treating this disorder. Concept Check 4.4 Identify the following specific phobias: (a) blood-injection-injury, (b) acrophobia, (c) animal, (d) social, (e) natural environment, (f) other 1. Mark had no friends at school and hid in the boys’ bathroom during both lunch and recess. ____________ 2. Dennis fears and strenuously avoids storms. Not surprisingly, on his first oceangoing cruise, he found that deep water terrified him too. ____________ 3. Rita was comfortable at the zoo until the old terror gripped her at the insect display. ____________ 4. Armando would love to eat fish with his fishing buddies, but he experiences an inordinate fear of choking on a bone. ____________ 5. John had to give up his dream of becoming a surgeon because he faints at the sight of blood. ____________ 6. Rachel turned down several lucrative job offers that involved public speaking for a low-paying desk job. ____________ 7. Farrah can’t visit her rural friends because of her fear of snakes. ____________ Concept Check 4.5 Match the correct preliminary diagnosis with the following cases: (a) acute posttraumatic stress disorder, (b) acute stress disorder, (c) delayed onset posttraumatic stress disorder 1. Judy witnessed a horrific tornado level her farm 3 weeks ago. Since then, she’s had many flashbacks of the incident, trouble sleeping, and a fear of going outside in storms. ____________ 2. Jack was involved in a car accident 6 weeks ago in which the driver of the other car was killed. Since then, Jack has been unable to get in a car because it brings back the horrible scene he witnessed. Nightmares of the incident haunt him and interfere with his sleep. He is irritable and has lost interest in his work and hobbies. ____________ 3. Patricia was raped at the age of 17, thirty years ago. Just recently, she has been having flashbacks of the event, difficulty sleeping, and fear of sexual contact with her husband. ____________ Concept Check 4.6 Fill in the blanks to form facts about obsessive-compulsive disorder. 1. ____________ are intrusive and nonsensical thoughts, images, or urges an individual tries to eliminate or suppress. 2. The practices of washing, counting, and hoarding to suppress obsessions and provide relief are called ____________. 3. The lifetime prevalence of OCD is approximately ____________%, or even lower. 4. ____________ is a radical treatment for OCD involving a surgical lesion to the cingulate bundle. Answers to Concept Checks 4.1 1. b 2. c 4.2 1. T 2. F (more gradual) 3. e, d 4. a 5. f 4. F 5. T 4.3 1. F (with agoraphobia) 2. F (3.5%) 3. T 4.4 1. d 2. e 3. c 5. a 7. c 4.5 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. f 3. T 4.6 1. obsessions 2. compulsions 6. d 3. 2.6% 4. T 4. psychosurgery