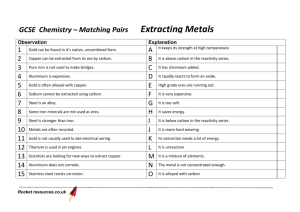
Are Organic foods better for us
advertisement

2011 Ideas in context – Additional Science Copper – not just in mobile phones Relevant textbook sections Higher- Section G and I 1. Where do all metals come from - which sphere? All metals come from the lithosphere and most are too reactive to exist on their own in the ground, instead they exist combined with other elements as compounds. The Earth’s lithosphere is the rigid outer layer that is made up of the crust and the part of the mantle just below it. 2. What is the RAM of 4g of copper? Regardless of how many grams you have, the atomic mass should still be 63.546 (as shown in the periodic table). 3. Give two properties of lithium Lithium is an alkali metal and is soft, low density, low melting point 4. What is the proton number of aluminium? Proton number is the same as the atomic number, which is 13. This means that aluminium has 13 protons and 13 electrons. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons because atoms are neutral (have no overall charge). 5. What type of energy is in a battery? Chemical energy 6. What types of metals are iron and zinc? Transition metals 7. What is meant by the word components? Parts e.g. like parts of the mobile phone 8. What is meant by the word extracted? Means the action of taking out something, often using effort or force. Metals are extracted from ores. 9. What is an ore? An ore is a type of rock that contains useful minerals. The valuable minerals are often the oxides or sulfides of metals. The ores are extracted through mining and then valuable element is extracted from the ore. E.g. Al from Bauxite Al2O3 10. What percentage of copper ore is pure copper mineral? Most copper ores contain only a small percentage of copper metal bound up within valuable ore minerals, with the remainder of the ore being unwanted rock. The ore in an open pit mine may contain as little as 0.4% copper and the 99.6% of the rock dug up from the ground is becomes waste. 11. Which issues have to be considered before metals can be extracted from ores? Costs of extraction, effects on the environment, the amount of waste produced. 12. Why is carbon used to extract metals from ores? Carbon is used as a reducing agent to extract metals because at high temperatures carbon has a strong tendency to react with oxygen. Another benefit to using carbon is that the carbon monoxide formed after it has removed the oxygen from the air is a gas so does not left behind to make the metal that was being extracted impure. The source of carbon for this reduction is coke, obtained by heating coal in the absence of oxygen. 13. What is electrolysis and how does it work? Electrolysis is the extraction method used when the metal being extracted is more reactive than carbon. E.g. Aluminium is a reactive metal and holds on oxygen very strongly. Aluminium ore is called bauxite, aluminium oxide, from which aluminium can be extracted. But first the aluminium oxide must be made molten because for electrolysis to work, the ions must be free to move. When an ionic compound is dissolved in water, or melts, the ions break free from the ionic 2011 Ideas in context – Additional Science lattice. These ions are then free to move. The solution or molten ionic compound is called an electrolyte. The negative electrode is called the cathode, while the positive electrode is called the anode. This is what happens during electrolysis: Positively charged ions (e.g. in this case Cu2+) move to the negative electrode. Metal ions are positively charged, so metals are produced at the negative electrode (cathode). Negatively charged ions move to the positive electrode. Non-metal ions, such as oxide ions and chloride ions, are negatively charged, so gases such as oxygen or chlorine are produced at the positive electrode (anode). 14. Why has the price of copper “rocketed up”? Because copper is being extracted from ores that have lower and lower percentages of copper because the ores with the higher copper content are running out. 15. How much did copper cost in 2003? Four times less than it did in 2008. 16. What do you think might be a problem with mining ores with lower percentages of copper in them? Because a lot of the rock that has been dug will be wasted. Lots of waste, very little metal. 17. What is an open cast mine? Open-cast mining refers to a method of extracting rock or minerals from the earth by their removal from an open pit or borrow. The other type of mining involves e tunneling into the earth. Open-cast mines are used when commercially useful minerals or rock are found near the surface. 18. Apart from noise, dust and traffic problems, what other problems does copper mining produce? Mining produces large volumes of waste rock and can leave large holes in the ground. 18. How do mining companies try to address peoples’ concerns 19. What other environmental problems do you think mining can cause? Mining produces large volumes of waste rock and can leave large holes in the ground. 20. What is the same about both methods of processing copper? Both methods require large amounts of energy. 21. How is this an environmental problem? Energy comes the burning of fossil fuels, which are a non renewable source of energy and releases CO2 into the atmosphere. 22. What does the word blister mean? Bubbles of trapped gas (sulphur dioxide)on the copper 23. What is the RFM of copper pyrites? Cu (63.5) + Fe (56) + 2S (32.1 x2) = 183.7 24. What are the disadvantages of the blister process? The copper made using this process is not very pure. 25. What is meant by the words waste iron slag? It is Iron mixed with silicon 26. What does the word oxidised mean? Oxidation is gain of oxygen. Oxidation needs a oxidising agent which will add the oxygen. 27. What does the word reduction mean? Reduction is loss of oxygen. Reduction needs a reducing agent to remove the oxygen. 28. What is the RFM of malachite? Cu (63.5) + C (12) + 3O (3 x16) = 123.5 29. What does the word purified mean? It means that all the impurities (anything that will contaminate the metal) have been removed. 30. Why is copper used in mobile phone? Pure copper is an excellent electricity conductor. 31. What does malleability mean? 2011 Ideas in context – Additional Science It is a word used to describe metals and if a metal is malleable it means it can be hammered into shape without cracking 32. What property do you think makes copper good for making jewellery? Copper is very malleable 33. Page 139 – questions 4,5,6,7,8 (questions and answers are below, use a periodic table to look up relative atomic masses. 4. Q-What is the relative formula mass of carbon dioxide (CO2)? A- 12 + (2 16) = 44 5. Q- What mass of Aluminium could be made from 1 tonne of Al2O3? A-53 tonne 6. Q-What mass of Na could made from 2 tonnes NaCl? A- 0.79 tonne 7. Q-The main ore of chromium is FeCr2O4. What is the mass percentage of Cr in FeCr2O4? A-46% 8. Q- 1000 tonnes of copper are dug out of the ground. Only 1% of this is pure mineral, CuFeS2. What mass of the Cu could be made from a 1000 tonnes of the ore? A-3.5 tonne 34. page 141 – questions 9 and 10 9. Q- Draw a diagram to electron arrangements in an aluminium atom and an alumium ion. A- 10 Q- Sodium is extracted by extracted by electrolysis of molten sodium chloride. a) what are the two products of the process? b) Use words and symbols to describe the changes at the electrodes during this process A- a) Sodium and chlorine b) At the negative electrode: sodium ion + electron sodium atom Na+ + e– Na At the positive electrode: chloride ion – electron chlorine atom Cl– – e– Cl chlorine atom + chlorine atom chlorine molecule Cl + Cl Cl2