Cell Webquest
advertisement

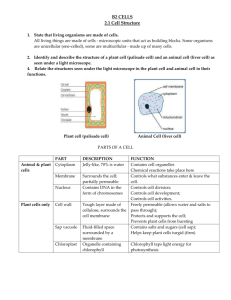
Name __________________________________ Cell Webquest Begin at the following site: http://www.wisconline.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP1101 1. The cell membrane is mainly composed of ________________ & ________________. 2. The framework consists of a double layer of _________________________________. 3. Water-soluble substances, such as glucose, amino acids, ions, and water need the help of various ______________________________ for transport through the cell membrane. 4. The phospholipid bilayer has hydrophilic ___________________ that form the surface and interior of the membrane, and hydrophobic ____________________ that face each other. 5. Draw a simple diagram or the phospholipid bilayer and label the polar heads and the nonpolar tails. 6. Fibrous _______________________ may span the length of the membrane and serve as receptors for the cell. 7. One type of globular proteins form _______________ (which are holes) that allow water to pass through the cell membrane. 8. Other integral __________________serve as channels and selectively transport ions for the cell. 9. ______________________ proteins, found on the surface of the cell, may be enzymes or glycoproteins that identify the cell. 10. ___________________________ molecules are embedded in animal cell membranes, but not plant cell membranes. 11. ___________________________ helps to stabilize the membrane. 12. Complete the activity to match pictures of the cell membrane parts with the correct label. You must drag the name over the picture. If you are correct, a blue box will appear to let you know you made a match. After you matched them all, click “Next”. 13. Draw a simple picture of the part that forms the basic frame of the cell membrane. 14. Go to the following site: http://cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm. Then click on the green words “Take me to the ANIMATION” & Choose Animal Cell 15. The nucleolus is found in the _____________________ and produces _______________________. 16. The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any______________________________ cell. Within the nucleus is ___________, which provide genetic information. 17. The rough ER appears “pebbled” because of _______________________. These ribosomes synthesize, or produce, _________________________. The endoplasmic reticulum then provides ___________________________ throughout the cell for these proteins. 18. The Golgi apparatus is a stack of membrane-bound vesicles that are important for ___________________________ macromolecules for transport throughout the cell. 19. The centrosome is an area where __________________________ are produced. The centrosome is actually a pair of small organelles called ___________________________. The centrioles are important for animal cell ________________________. 20. Microtubules and microfilaments are part of the ___________________________, which helps maintain cell shape. The primary importance of the cytoskeleton is cell _______________________, which means movement. 21. Lysosomes are common in _______________________ cells. They contain enzymes for intracellular __________________________. Uncontrolled release of lysosome contents into the cytoplasm can also cause cell necrosis, which means ________________. 22. Mitochondria produce the ___________________ a cell needs to move, divide, produce products, and contract. Within cristae of the mitochondria, sugar is combined with oxygen to produce __________, which is the primary energy source for a cell. 23. The cytosol is the “_____________” of the cell. __________________________ is a collective term for the cytosol plus the organelles suspended in the cytosol. 24. Now click on the Plant Cell. 25. Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of ______________________________. In higher plants this polysaccharide is usually _____________________________. Fluid that collects in a plant cell’s vacuole can push on the cell wall and create a pressure that is responsible for the crispness in fresh___________________________. 26. Chloroplasts are found only in ____________________ cells. They contain ___________________, which is responsible for the plant’s green color. Within the chloroplasts are membrane structures called thylakoids, which appear in stacks called _____________________. 27. In _____________________ cells the vacuoles are generally small. 28. The vacuoles in plant cells tend to be _______________________. In the plant cell the vacuole is responsible for ________________________ nutrients and waste products, increasing cell size during _____________________, and even acting like the ________________________ of animal cells. A plant’s vacuole also regulates __________________ pressure. If a plant does not have enough water, this pressure will drop and the plant ____________________. Use your notes to answer the following questions. 29. Which zoologist observed that the tissues of animal had cells? __________________ 30. Which botanist first observed that plants contained cells? ______________________ 31. Who was the first person to see cells while looking at cork cells? ________________ 32. Who was the first to observe living cells in pond water and called them “animalcules”? ___________________________________ 33. Which 3 scientists came up with the basic components of the cell theory? _______________________________________________________________________ 34. List the 3 parts of the cell theory. 1. ________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________ 35. Which type of cells do NOT contain a membrane bound nucleus? ________________ 36. Plant and animal cells are __________________________ cells, which are more advanced cells. 37. What are the 4 main parts of a eukaryotic cell? 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ 4. _________________________________ 38. A __________________________ is a long, whip-like structure (tail) of a cell that aids in movement. ______________________ are tiny, hair-like projections that cover a cell and aid in movement.