Biology Standard 7 – Plants
advertisement

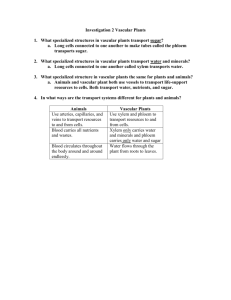
Biology Standard 7 – Plants I. Introduction to Plants a. Key Terms Alternation of Generations - The fluctuation between the diploid (sporophyte) and haploid (gametophyte) life stages that occurs in plants. Angiosperm - A vascular flowering plant in which seeds are enclosed inside of protective ovaries. Autotroph - An organism that synthesizes its own organic nutrients and does not rely on other organisms for food. Bryophyte - A lower terrestrial plant (often a moss or liverwort) that lacks a vascular system and is dependent on environmental moisture for reproductive and nutritive functions. Dicot - An flowering plant (angiosperm) that possesses two cotyledons during embryonic development. Monocot - A flowering plant (angiosperm) that possesses one cotyledon during embryonic development. Ovary - In plants, the protective structure that holds the ovules and surrounds the angiosperm seed; after fertilization, develops into a fruit. Ovule - Structure that contains the female gametophyte and gametes; after fertilization, develops into a seed. Phloem - Vascular tissue composed of cells that are living at maturity; transports the products of photosynthesis throughout Pollen Grain - The male gametophyte of gymnosperms and angiosperms. Root - The part of a plant beneath the soil; responsible for collecting water and minerals from the soil, storing nutrients, and securing the plant to the ground. Shoot - The part of the plant above the soil, including all aerial structures such as stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits; gathers carbon dioxide and light energy for photosynthesis, provides surfaces for gas exchange, and contains the plant's reproductive organs. Sporophyte - A diploid plant or plant structure that produces haploid spores through meiosis. Stoma - A very small epidermal pore, surrounded by two guard cells, through which gases diffuse in and out of a leaf. Vascular System - Mechanism of internal water and nutrient transport, made up of the vascular tissues xylem and phloem, that is characteristic of tracheophytes. Vascular Tissue - A conductive component (either xylem or phloem) of the system that transports food and nutrients throughout the plant body. Xylem - Vascular tissue composed of cells that are dead at maturity; transports water and dissolved minerals upwards from the roots to the shoot. II. b. Plant Characteristics 1. underground root 2. above ground shoot 3. waxy cuticle to keep from dessicating 4. stoma to allow for exchange of gases 5. autotrophic 6. alternation of generation c. Plant Classification 1. Bryophytes: (mosses and liverworts) contain no vascular system 2. Tracheophytes: (gymnosperms and angiosperms) contain vascular system Plant Structures a. Key Terms Anther - Pollen-producing structure at the top of the stamen, the male reproductive organ of flowers. Calyx - The outermost flower whorl, containing the sepals. Carpel - One of the modified leaves of the flower that encloses the ovules; this term sometimes refers to the entire female reproductive organ, otherwise known as the pistil. Cotyledon - An embryonic leaf characteristic of angiosperms; monocot embryos have one, and dicot embryos have two. Guard cell - One of the two epidermal cells that surround the stoma of the leaf and regulate gas exchange by opening and closing the stoma. Ovary - In plants, the protective structure that holds the ovules and surrounds the angiosperm seed; composed of carpels and found at the base of the pistil. Ovule - Structure that contains the female gametophyte and gametes; after fertilization, develops into a seed. Palisade Layer - A layer of the mesophyll. The palisade layer is made up chloroplasts arranged in columns and located just below the epidermis of plant cells. In most plants, the palisade layer exists only on the top of the life, where the leaf receives sunlight. In some plants, in which leaves hang down and both sides of the leaves receive sunlight, the palisade layer is on both sides of the leaf. Petal - Modified leaf, usually brightly colored, that attracts insects and other pollen- carrying animals to the flower. Phloem - Vascular tissue composed of conductile cells that are living at maturity; transports the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant body. Pistil - The female reproductive organ of the flower, composed of a stigma, style, and ovary; sometimes called the carpel. Pith - Plant tissue located at the center of the stem; functions partly in nutrient storage. Pollen Grain - The male gametophyte of gymnosperms and angiosperms. Spongy Layer - A layer of the mesophyll. The spongy layer consists of chloroplasts and parenchyma cells, and relatively large intercellular spaces. It is far less ordered than the palisade layer, and the intercellular spaces are important in gas exchange and transpiration. Stamen - The male reproductive organ of the flower, comprised of an anther and filament. Stigma - The top part of the pistil, where pollen grains are received. Stoma - A very small epidermal pore, surrounded by two guard cells, through which gases diffuse in and out of a leaf. Style - The shaft of the pistil that leads from the stigma down into the ovary. Triploid - Having three sets of chromosomes. Vascular Bundle - Vascular passageways comprised of xylem and phloem "bundled" together. Vascular Cambium - Tissue that produces new vascular cells; lies between the xylem and phloem in dicot stems. Vascular System - Mechanism of internal water and nutrient transport, made up of the vascular tissues xylem and phloem, that is characteristic of tracheophytes. Vascular Tissue - A conductile component (either xylem or phloem) of the system that transports food and nutrients throughout the plant body. Xylem - Vascular tissue composed of conductile cells that are dead at maturity; transports water and dissolved minerals upwards from the roots to the shoot. b. c. d. e. III. Seed 1. 2. Gymnosperms – the ovule develops into the seed Angiosperms- ovule which becomes the seed is encased in a protective covering (ovaries) 1. 2. Taproot: single dominant root in which other roots extend Fibrous root: many small roots combined 1. 2. 3. contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis stomata: exchange of gases palisade layer: choloroplast 1. 2. reproductive structures of the angiosperms pistil (female) and the stamen (male) reproductive structures of the plant Roots Leaf Flower Life Cycle of the Pant a. Key Terms Stigma - The top part of the pistil, where pollen grains are received. Sporangium - The part of a plant where spores are produced. Spore - Haploid cell from which a gametophyte is produced. Sporophyte - A diploid plant or plant structure that produces haploid spores through meiosis. Pollen Grain - The male gametophyte of gymnosperms and angiosperms. Pollen Tube - The outgrowth of a pollen grain that creates a path through the female sex organ in order to penetrate to the egg cells. Ovary - In plants, the protective structure that holds the ovules and surrounds the angiosperm seed; after fertilization, develops into a fruit. Ovule - Structure that contains the female gametophyte and gametes; after fertilization, develops into a seed. Pistil - The female reproductive organ of the flower, composed of a stigma, style, and ovary; sometimes called the carpel. Gametophyte - A haploid plant or plant structure that produces haploid gametes through mitosis. Double Fertilization - The mechanism of angiosperm fertilization that involves the joining of haploid gametes to create a diploid zygote, and the simultaneous joining of a second sperm cell with a fusion nucleus to create a triploid nucleus (which becomes endosperm). Cross-pollination - The process, occurring in most angiosperms, by which the male gametes of one plant (carried by pollen grains) fertilize the eggs of another. Alternation of Generations - The fluctuation between the diploid (sporophyte) and haploid (gametophyte) life stages that occurs in plants. Angiosperm - A vascular flowering plant in which seeds are enclosed inside of protective ovaries. Archegonium - The female sex organ of terrestrial plants; where egg cells are produced. b. Alternation of Generations The multicellular diploid plant structure is called the sporophyte, which produces spores through meiotic (asexual) division. The multicellular haploid plant structure is called the gametophyte, which is formed from the spore and give rise to the haploid gametes.