Unit 4: Classification of Organisms-Diversity EOCT Study
advertisement

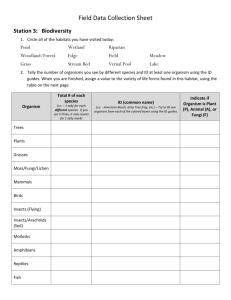
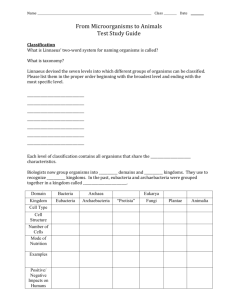
Unit 4: Classification of Organisms-Diversity EOCT Study Guide 1. Which two kingdoms in the kingdom system include all the prokaryotes? a. Fungi b. Animalia c. Protista d. Eubacteria e. Archeabacteria 2. The scientific name of the live oak tree is Quercus virginiana. In this example, Quercus is the a. Order b. Family c. Phylum d. Species e. Genus 3. Which kingdom or domain or organisms is the most numerous on Earth? a. Plantae b. Fungi c. Archea d. Bacteria e. Protista 4. Imagine that a meteorite has fallen to Earth and scientists have found life inside it. They have extracted an organism that is unicellular, lacks cilia or flagella, possesses a nucleus, performs photosynthesis, and has cells walls made of silica. Which of these Earth organisms most closely fits this description? a. Diatom b. Dinoflagellate c. Slime mold d. Apicomplexan protozoan e. Spirochete bacterium 5. What adaptation, to cut down on water loss, would you expect to find on a desert plant, such as a plant? a. Numerous leaves b. Thick roots c. Reduced amounts of lignin d. Large number of stomata e. Thick cuticle 6. Jellyfish and coral are both in the phylum a. Nematoda b. Annelida c. Cnidaria d. Porifera e. Mollusca 7. Which part of the flower is male and produces pollen? a. b. c. d. e. Sepals Petals Carpels Anthers Ovary 8. The following pictures show some stages during asexual reproduction of a hydra. Which picture shows the first step? 9. Which of these could be successfully treated with antibiotics? a. HIV b. Influenza c. Strep Throat d. Common cold 10. In plants, gymnosperms have cones and angiosperms have flowers. Both of these plant structures are specialized for a. Photosynthesis b. Food production c. Sexual reproduction d. Water absorption 11. A dog is a member of the Kingdom a. Animalia b. Eubacteria c. Protista d. Archeabacteria e. Plantea 12. Which of these is a type of prokaryotic cell a. Worm cell b. Human cell c. Bacterial cell d. Mushroom cell e. Plant cell 13. The one-celled eukaryotic organisms below are often found in freshwater ponds. What is one characteristic they all have in common? a. b. c. d. Nucleus Cilia Pseudopodia Flagellum 14. Which of the following require a host cell because they are not able to make proteins on their own. a. blue-green algae b. bacteria c. protozoans d. viruses 14. Chordates all share these key features in the embryo or in the adult stage except a. Dorsal nerve cord b. Notochord c. Pharyngeal slits d. Post-anal tail e. Hard backbone 15. Which mollusk listed below does not have a hard shell? a. Snail b. Oyster c. Squid d. Octopus e. Clam 16. Earthworms and Leeches are both examples of a. Nematode b. Annelida c. Mollusca d. Arthropoda e. Cnidaria 17. Which of these organisms is not a producer? a. Phytoplankton b. Insect c. Algae d. Autotrophic bacterium e. Plant 18. The exoskeleton of an insect provides all the following except a. Protection from predators b. Flexibility around the joints c. The ability to get larger as the body grows d. Reduction in water loss from the surface of the body 19. Reproduction in a pine tree, and other gymnosperms, involves a. Sperm that swim through water to insects b. Sperm that swim through water to the female cone c. Insects that carry pollen from flower to flower d. Pollen that blows onto the female cone e. Sperm the swim through water to fertilize the egg 20. Which of the following best describes nutrition in fungi? a. Fungi are photosynthetic b. Fungi are autotrophic, like land plants c. Fungi absorb food that has been digested by animals d. Fungi secrete enzymes to digest food outside their body e. Fungi digest food in their stomach, like humans 21. Which two groups of organisms are the main decomposers in an ecosystem? a. Fungi and animals b. Animals and bacteria c. Land plants and animals d. Bacteria and fungi 22. Flowering plants can use any of these techniques or structures to attract pollinators except a. Special markings on the flower b. Flower color c. Fragrance d. Sound e. Nectar 23. An animal the crawls forward on the ground would most likely have a. Radial symmetry, and no brain at all b. Bilateral symmetry, and a brain at the hind end c. Radial symmetry, and a brain at the front end d. Radial symmetry and a brain at the hind end e. Bilateral symmetry and a brain a the front end 24. Experimental Observations 1. Nucleus is present. 2. Cell wall is present. 3. Chloroplasts and mitochondria are both present. The eukaryotic organism described above should be classified asa. a fungus b. a plant c. a bacterium d. an animal 25. Organisms may be classified as consumers or producers. Which of these is classified as a producer? a. An insect b. A bird c. A tree d. A mouse 26. What is the purpose of the flagellum? a. b. c. d. circulation catching prey movement attachment 27. Based on the method used by which they get food, organisms are classified as autotrophs or heterotrophs. Which organism listed below is correctly paired with its metabolism? a. Grass-heterotroph b. Human-heterotroph c. Mushroom-autotroph d. Fish-autotroph 28. What structure is common to all 6 kingdoms of living organisms? a. Cell wall b. Nucleus c. DNA e. Lysosomes 29. Which skull belongs to an herbivore? 30. The colorful petals of a flower benefit the plant by a. absorbing radiant energy b. attracting insect pollinators c. protecting it from predators d. catching windblown pollen 31. Which kingdom contains organisms that are multicellular, autotrophic eukaryotes? a. Animalia b. Plantae c. Fungi d. Archeabacteria 32. Which characteristic supports the hypothesis that this organism spends a great deal of time burrowing through the soil? a. The shape of its body b. The position of its nose c. The length of the tail d. The size of the claws 33. According to the key below, to what family does the plant above belong? a. Viper’s bugloss (Echium vulgare) b. Virginia bluebell (Mertensia virginica) c. Grey beardtongue (Penstemon canescens) e. Lyre-leaved sage (salvia lyrata) 34. The kingdom of prokaryotes that live in extreme environments a. Protists b. Archeabacteria c. Fungi d. Eubacteria e. Animalia f. Plantae 35. In order to maintain homeostasis, it is most important for an animal to be able to— a. Respond to its environment _ b. Hide from its predators c. Change its habitat d. Increase its prey population 36. Most are unicellular. They are eukaryotic. They are both autotrophic and heterotrophic. They have a very large variety of members. They area. Animalia b. Archeabacteria c. Fungi d. Protista 37. Which of these processes is carried out in the same way in both plants and animals? a. Cellular respiration b. Asexual reproduction c. Circulation of body fluids e. Excretion of metabolic wastes 38. Which of these could be successfully treated with antibiotics? a. Common cold b. Influenza c. Strep throat d. HIV 39. Which of the following would most likely change the current classification of two closely related flower species to a single species? a. An analysis of photosynthesis for each species b. The discovery of a new, related species c. An analysis of the DNA sequence of each species d. The collection of seeds from each species 40. During a trip to a rain forest, a scientist discovered a new organism, living near some rotting logs. The scientist observed that the organism had moist skin, no hair, and an internal skeleton and that it laid its eggs under the logs. This organism was probably a new species ofa. Invertebrate b. Amphibian c. Mammal d. Reptile 41. Which of these hypotheses is best supported by observations of this animal? a. This animal spends much of its time digging. _ b. This animal usually hunts for food at night. c. This animal is herbivorous. e. This animal has poor hearing. 42. This organism is most closely related to animals in the Phylum Arthropoda, the phylum that contains beetles, because it has — legs b. antennae c. jointed appendages d. an elongated body a.