Lenses Class Exercises
advertisement

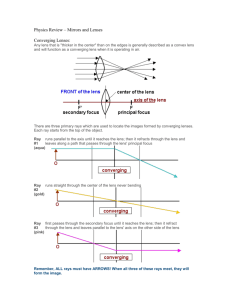
Lenses Class Exercises AP Physics 1. Lenses create images similarly to the way mirrors do. How is the way that lenses create images different from the way that mirrors create images? 2. a) Use Snell’s law to follow each of the two light rays through the typical crown glass lens shown below. b) How does the image compare to the original object? What type of image is it? 3. Lenses come in two types: converging and diverging. Identify the type of lens in each picture: a) b) c) d) e) f) All light rays coming from an object and passing through an ideal lens should be redirected so that they appear to come from the same point – the image. To follow most of these rays would require a lot of work repeatedly applying Snell’s law. There are 3 rays that obey simple rules, which are the ones that we use most often. 4. How do ray diagrams for lenses act differently from ray diagrams for mirrors? What is different about the way that lenses affect light? 5. Consider the object in front of the converging lens shown below: a) What does a ray parallel to the axis do after it passes through a converging lens? b) What does a ray through the near side focal point do after it passes through a converging lens? c) What does a ray pass through the center of the lens do after it passes through a converging lens? 6. a) Now combine all three rays to locate the image. b) What are the characteristics of the image? 7. How does the image change if I move the object to different points in front of the lens? For each of the following pictures, draw two of the three useful rays to locate the image, characterize the image and compare it to the actual object. a) b) c) What type of mirror is the converging lens most like? How is it similar? How is it different? 8. Consider the object in front of the diverging lens shown below: a) What does a ray parallel to the axis after it passes through a diverging lens? b) What does a ray through the far side focal point do after it passes through a converging lens? c) What does a ray pass through the center of the lens do after it passes through a diverging lens? 9. Now put them all together and locate the image produced by the diverging lens 10. How does the image change if I move the object closer to the lens? For each of the following pictures, draw two of the three useful rays to locate the image, characterize the image and compare it to the actual object. 11. Which type of mirror is a diverging lens most like? Why? What is similar? What is different? 12. What equations describe the images formed by lenses? 13. a) A 1 cm tall hat (for use as a game piece) stands 20 cm away from a converging lens with a focal length of 12 cm. What are the characteristics of the image produced by the lens? b) What if the hat is moved so that it is 6 cm away from the lens? What will the characteristics of the images produced by the lens be? 14. a) A 10 cm tall candle stands 24 cm away from a diverging lens with a focal length of 8 cm. What are the characteristics of the image of the candle that the lens produces? b) How does the image change if the candle is moved to be 6 cm away from the lens? What are the characteristics of the image now? 15. While the equations for mirrors and lenses are the same, the interpretations of the results can be different. What is different for lens calculations compared to mirror calculations?