Weather & Erosion Study Guide
advertisement

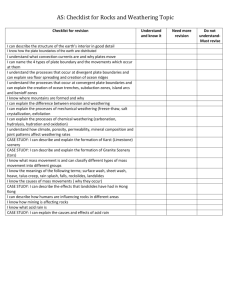
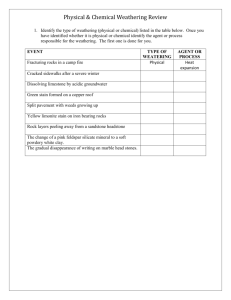
Weather & Erosion Study Guide Test Date: Tuesday, October 12th Vocabulary 1. weathering – the wearing away or break down of rocks caused by wind, water, ice or plant roots 2. erosion – carrying away of sediments 3. deposition – the dropping of sediment in a new place 4. freeze and thaw weathering – water in rock’s crack freezes and expands making more weathering 5. moraine – rocks and sediment deposited by melting glacier 6. landslide – usually soil loosened by rain or ice melting and pulled down by gravity 7. dune – hill of sand built up by wind 8. delta – large, flat land at mouth of river formed by deposited sediment 9. sediment – bits of soil, sand and rocks * Study all of your notes in your science journal. * Review all worksheets/handouts in your science folder. * Reread science textbook pages: B43, B54-55 C42, C48 D30-31, D34-37, D40-41 * Know the definition of weathering tools and be able to describe how they are used to measure weather: anemometer – instrument that measures wind speed barometer – instrument that measures air pressure rain gauge – instrument that measures rain thermometer – instrument that measures temperature wind vane – instrument that shows the direction of the wind * Know the stages and definitions of the water cycle: water cycle – water circulates through Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and streams evaporation – the process by which water turns into a gas condensation – the process by which water vapor turns into a liquid precipitation – sleet, snow, hail, rain * Know the description of clouds: cirrus – wispy, thin clouds that are usually found high in the troposphere cumulonimbus – tall clouds that often produces thunder, lightning and brings precipitation cumulous – fluffy, white clouds that you might see on a fair-weather day stratus – low, gray clouds that have flat or layered shape * Know how wind, water and ice shape and reshape Earth’s land surface by eroding rocks and soil in some areas and depositing them in other areas producing characteristic landforms (dunes, deltas, moraines). * Know how freezing, thawing and plant growth reshape the land surface by causing the weathering of rock. How wind, water and ice break down rocks. * Know changes and evidence of changes on Earth’s surface in terms of slow processes (erosion, weathering, mountain building, deposition, dunes, deltas, moraines) and rapid processes (volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, landslides).