SampleExam2 - California State University, Sacramento
advertisement

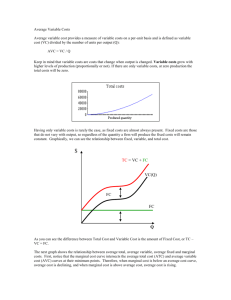
Sample Exam #2, Econ 100B 1) As the price of a good rises, the consumer will experience A) a desire to consume a different bundle. B) a decrease in utility. C) a southwesterly movement on the indifference map. D) All of the above. 2) Suppose the quantity of x is measured on the horizontal axis. If the price consumption curve is vertical when the price of x changes, then the demand for x is A) perfectly elastic. B) perfectly inelastic. C) unit elastic. D) There is not enough information to determine the price elasticity of demand for x. Figure 5.3 3) When John's income was low, he could not afford to dine out and would respond to a pay raise by purchasing more frozen dinners. Now that his income is high, a pay raise causes him to dine out more often and buy fewer frozen dinners. Which graph in Figure 5.3 best represents John's Engel curve for frozen dinners? A) Graph A B) Graph B C) Graph C D) Graph D 4) Even though Mary's income is very low, she makes sure that she purchases enough milk for her family to drink. As her income rises, she does buy more milk. Which graph in Figure 5.3 best represents Mary's Engel curve for milk? A) Graph A B) Graph B C) Graph C D) Graph D 5) When John was in college and his income was low, he drank "Red Ribbon" beer. As his income increased, he purchased better-quality beer and less "Red Ribbon." Which graph in Figure 5.3 best represents John's Engel curve for "Red Ribbon" beer? A) Graph A B) Graph B C) Graph C D) Graph D 6) Employing a fixed-weight index like the Consumer Price Index to adjust a person's salary in response to inflation will overcompensate this person because doing so will allow this person to A) buy the same bundle of goods as he did before the inflation. B) achieve a higher level of utility than he did before the inflation. C) achieve the same level of utility as before the inflation. D) buy more of all goods. 7) If a person supplies more hours of labor in response to a wage increase, then A) the substitution effect is greater than the income effect. B) the income effect is greater than the substitution effect. C) the income effect equals the substitution effect. D) the person is not maximizing utility. 8) In response to an increase in the wage rate, the income effect will cause a person to A) supply fewer hours of labor. B) supply more hours of labor. C) supply the same hours of labor. D) have a horizontal labor supply curve. 9) If the marginal productivity of labor is constant for all levels of output, then the average productivity of labor A) is constant. B) equals the marginal productivity of labor. C) Both A and B above. D) Either A or B above but not both. 10) Which situation is most likely to exhibit diminishing marginal returns to labor? A) a factory that obtains a new machine for every new worker hired B) a factory that hires more workers and never increases the amount of machinery C) a factory that increases the amount of machinery and holds the number of worker constant D) None of these situations will result in diminishing marginal returns to labor 11) To say that isoquants are convex is to say that A) the marginal rate of technical substitution falls as labor increases. B) capital and labor are perfect substitutes. C) labor, but not capital, is subject to the law of diminishing marginal returns. D) there are constant returns to scale. 12) The slope of an isoquant tells us A) how much output increases when both inputs are increased. B) the increase in MPL when capital increases. C) the decrease in capital necessary to keep output constant when labor increases by one unit. D) the decrease in capital necessary to keep MPL constant when labor increases by one unit. Figure 6.4 13) Figure 6.4 shows the isoquants for producing steel. Decreasing returns to scale are A) present when producing more than 10,000 tons. B) present when producing more than 20,000 tons. C) present when producing more than 30,000 tons. D) never present. E) 14) The returns to scale of the production function Q = 50 L.4K.2 are A) 50. B) .6. C) .8. D) 50.6. 15) The Nifty Gum Co. has purchased a large parcel of land for $1 million. The company recently discovered that the land is contaminated and is worthless to all possible buyers. The opportunity cost of the land is A) $0. B) $1 million. C) some amount greater than $0 but less than $1 million. D)equal to the cost of the factory that was planned to be built there. 16) Suppose the total cost of producing T-shirts can be represented as TC = 50 + 2q. The marginal cost of the 5th T-shirt is A) 2. B) 10. C) 12. D) 60. 17) If a particular production process is subject to diminishing marginal returns to labor at every level of output, then at every level of output A) AC is upward sloping. B) MC exceeds AVC. C) AFC is constant. D) All of the above. 18) When the isocost line is tangent to the isoquant, then A) MRTS = w/r. B) the firm is producing that level of output at minimum cost. C) the last dollar spent on capital yields as much extra output as the last dollar spent on labor. D) All of the above. 19) If a firm makes zero economic profit, then the firm A) has total revenues greater than its costs. B) must shut down. C) can be earning positive business profit. D) must have no fixed costs. Figure 8.1 20) Figure 8.1 shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the firm is to earn economic profit, price must exceed A) $0. B) $5. C) $10. D) $11. 21) Figure 8.1 shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the firm is to operate in the short run, price must exceed A) $0. B) $5. C) $10. D) $11. 22) Figure 8.1 shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the market price is $15 per unit, the firm will earn profits of A) $0. B) $4. C) $40. D) $160. 23) A firm will shut down in the short run if A) total fixed costs are too high. B) total revenue from operating would not cover all costs. C) total revenue from operating would not cover variable costs. D)total revenue from operating would not cover fixed costs. 24) If a competitive firm maximizes short-run profits by producing some quantity of output, which of the following must be true at that level of output? A) p > MC. B) MR > MC. C) p > AVC. E) All of the above. 25) If a profit-maximizing firm finds that, at its current level of production, MR > MC, it will A) earn greater profits than if MR = MC. B) increase output. C) decrease output. D) shut down. 26) If a firm is a price taker, then its marginal revenue will always equal A) price. B) total cost. C) zero. D) one. 27) If a firm is a price taker, then its marginal revenue will always equal A) price. B) total cost. C) zero. D) one. 28) If a competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium, then A) profits equal zero. B) it will not operate at a loss. C) an increase in its fixed cost will have no effect on profit. D) an increase in its fixed cost will have no effect on output. II. Short Answer/Problem 1. Distinguish the income and substitution effects of a decrease in price of good X. Units of Good Y AB C AC Total effect Units of Good X AB Substitutioin effect Note: the blue line parallels the green line. The black budget line reflectsthe original higher price price of X, holding the price of Y unchanged.. Hold the individual’s satisfaction constant, but change the price ratio between X and Y to that implied by the green line. Because X is cheaper than Y, substitution of AB creates a new bundle of X and Y at the original level of satisfaction. A lower price of X enables the individual to buy more of both X and Y, but the increased Purchasing power effect, the income effect, is BC See figure 5.5 on page 118. 2. Complete the table below given the following information: Wage rate = $100/day. Unit price of capital = $1500. Price of the product = $50. Units of K Units of L 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Q=total product 0 10 40 55 65 70 72 73 73 Fixed cost $3,000 Variable Cost -----$100 Marginal Cost -----$10 Price of Product $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 Variable cost = units of L times wage rate Marginal cost = change in variable cost divided by change in units of Q. Since each additional unit of labor ‘costs’ the daily wage, $100 is the change in variable cost and each value of Q comes from one day increments in units of labor. Create a marginal product column and use marginal product as the divisor in this equation: $100/mp=marginal cost. Moving from one to two units of labor causes production to increase from 10 to 40 units. So the $100 spent for the second unit of labor added 30 units to output. Marginal cost of the second day of labor becomes $100/30= $33.33. The goal is to find the profit maximizing level of production. This occurs where price of the product equals the marginal cost of production, subject to the condition that price at least covers average variable cost. AVC=Variable cost/Q. Calculate profits: Total revenue = price per unit times Q Total cost = fixed cost + variable cost Profit = total revenue – total cost. If total profit = $0, then this firm can continue in perpetuity at the output (Q) where p = MC. MC= $50 when q increases from 70 to 72. [$100/2=$50] Total cost = 3000 + ($100*6) Total revenue = $50 * 72 Profit = $0 3. Find the marginal revenue product, marginal resource cost and profit maximizing level of hiring labor with the information given in problem 2. Do this on your own. I’ll answer requests for answers by e mail.