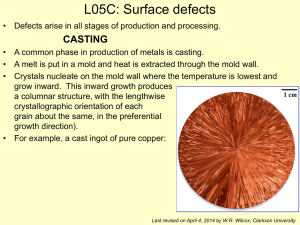
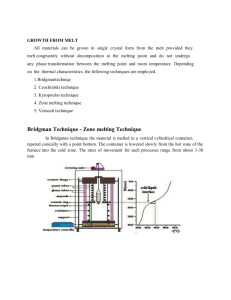
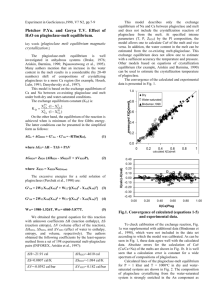
Homework 03 Ch 3 b
advertisement

ES 4901 Petrology Homework 3 Chapter 3 Igneous Textures and Petrography A. Memorization for Match the Terms later Abbreviations Tx = texture T = Temperature, xtals = crystals rxn = reaction M = melting 1. Surface Energy excess energy at the surface of a material 2. Instability separation of clusters of compatible ions due to high surface charge. 3. Nucleation forming a critical-sized embryonic crystal 4. Undercooling cooling of a melt below the crystallization T of some mineral 5. Crystal Growth addition of ions to an existing crystal 6. Diffusion the spread of something more widely 7. Euhedral Crystal well-formed, sharp, easily recognized faces. Opposite: Anhedral 8. Epitaxis preferred nucleation of one mineral on another pre-existing mineral 9. Porphyritic having distinctly different crystal sizes (Igneous term) 10. Phenocrysts the large xtals in a porphyry 11. Poikilitic phenocrysts contain inclusion of minerals they surrounded 12. Interstitial filling the spaces between 13. Ophitic Tx clinopyroxenes (Augite, etc.) surround Plagioclase laths 14. Granophyric Tx angular intergrowth, ex. K-spar and Quartz form simul. low H2O melt 15. Graphic Tx coarse Granophyric Tx, looks like square writing 16. Resorption dissolution of a mineral back into the melt. 17. Decompression M a decrease in pressure. *(see below) 18. Dewatering raises melting point; forming minerals now more undercooled 19. Trachytic Tx microphenocrysts aligned due to flow 20. Felty (pilotaxitic) Tx microphenocrysts randomly oriented 21. Intergranular Tx Pyroxene and Plagioclase xtals similar in size * Pressure affects melting points. Most substances expand as they melt. An increase of pressure retards the melting of these substances. A decrease in pressure allows expansion and melting. 22. Orthocumulate melt between settled crystals isolated, remains, forms interstitial xtals 23. Adcumulate melt between settled crystals not isolated, squashed out 24. Polysynthetic twins multiple twins aligned in parallel; loosely “Albite twins” 25. Carlsbad twin two crystals, one rotates parallel c-axis (perpendicular to a-axis) 26. Sericite a fine grain potassium mica, can be an alteration product of K-spars 27. Myrmekitic an intergrowth of quartz in a single crystal of Plagioclase B. Mixed Format Abbreviations s = slide 1. Name two hydrous minerals 2. What does glass (no crystals) look like under crossed polars? 3. Explain the role of water in the formation of large crystal in a Pegmatite s9 lower viscosity, easier diffusion, better growth 4. Explain why a melt at some constant temperature can produce different minerals that nucleate and grow at different rates. s10 5. Explain the consequences of rapid dewatering of a magma. s12 Loss water, raise melting po int, currently forming undercooled, to n ucl, aphanitics 6. Which grows faster s13 & 14 a. a plane with a high density of lattice points, smaller interplanar distance, and low surface energy, and a larger pocket of undepleted melt b. a plane with a low density of lattice points, larger interplanar distance, and high surface energy, and a smaller pocket of undepleted melt 7. For a growing crystal, which area usually has a greater volume of undepleted melt from which it can obtain components? s14 a. an edge between two planar sides b. a planar side 8. In Bowen’s Reaction Series, which Plagioclase end member forms at a higher temperature? Choose [ Anorthite CaAl (AlSi2O8 ) OR Albite NaSi (AlSi2O8 ) ] 9. Igneous Plagioclase crystals may show a CaAl - rich composition in the center, and a NaSi - rich composition on the outside. Slide 18. The reason is Plagioclase does not reequilibrate with the melt when the cooling melt changes composition, which would require substitution of Al for Si in one position. This is difficult because: a. Al-O and Si-O bonds are very strong b. Al+3 is a very slow diffuser c. both of the above 10. Oscillatory Zoning. Electron Microprobe scans of compositionally zoned Plagioclase crystals from center to rim show zones of decreasing Anorthite CaAl (AlSi2O8 ) , followed by a sharp increase in Anorthite. Slide 19. Give one possible explanation for this.