Test 1
advertisement

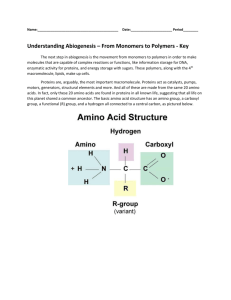
CHEM106 Section 002 Test #1 February 4, 2010 Name: ___________________________ Answer Sheet Fun! 1) ____ 11) ____ 21) ____ 2) ____ 12) ____ 22) ____ 3) ____ 13) ____ 23) ____ 4) ____ 14) ____ 24) ____ 5) ____ 15) ____ 25) ____ 6) ____ 16) ____ 26) ____ 7) ____ 17) ____ 27) ____ 8) ____ 18) ____ 28) ____ 9) ____ 19) ____ 29) ____ 10) ____ 20) ____ 30) ____ Games! 1) _____________________ 2) a) __________________ 4) a) _____________________ b) __________________ b) _____________________ 3) a) __________________ 5) _______________________ b) __________________ c) __________________ Games! (continued) 6) a) b) d) e) c) CHEM106 Section 002 Test #1 February 4, 2010 Name: ___________________________ Use the answer sheet to record your answer for all questions. The test is broken into two parts: A multiple guess part (Fun!) and a short answer part (Games!). The Fun! questions are worth 3 points a piece and the Games! Questions are worth varying amounts. If you answer all of the questions on this test correctly, you will earn 133 points, all of which will count into your grade (which counts every Test as 100 points). Write clearly, neatly and large enough for a human being to read. Make sure you box your answers on your scratch paper, carefully transfer your answers to the answer sheet. Write your name on every piece of paper you turn in. Jumbled, confusing, illogical and disorganized work will not be accepted. Relax, trust in yourself and do your best. Fun! (3 points each. Maximum Possible = 90 points) 1) Which of the following functional groups are not commonly seen in biomolecules? a) Alkyl halides b) Amides c) Carboxylic acids d) Ethers 2) Which of the following best describes the results of the Miller-Urey experiment? a) It proved that DNA is the genetic material. b) It produced proteins under conditions simulating the early Earth. c) It created living cells from non-living materials. d) It produced some simple organic compounds from a mixture of gases presumed to have existed in the early atmosphere. e) All of these results of the Miller-Urey experiment. 3) A spontaneous reaction is a) exergonic. b) endergonic. c) at equilibrium. d) none of the above. 4) The tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond is called a) polarity. b) electronegativity. c) hydrophilicity d) electrophilicity. 5) If atoms with greatly differing electronegativities form a bond, that bond will be a) polar. b) nonpolar. c) amphipathic. d) acidic. 6) Which of the following molecules is polar? a) CCl4 b) CH4 c) CO2 d) NH3 e) None of these molecules is polar. 7) A non-polar molecule cannot have any polar bonds. a) True b) False 8) Ionic compounds and polar covalent compounds tend to dissolve in water because of a) ion-dipole and dipole-dipole interactions b) dipole-induced dipole interactions c) van der Waals bonds d) hydrophobic interactions 9) How do hydrogen bonds tend to affect the melting and boiling points of substances? a) They tend to increase both melting and boiling points. b) They tend to decrease both melting and boiling points. c) They tend to increase melting points and decrease boiling points. d) They tend to decrease melting points and increase boiling points. e) They do not have any affect on either melting or boiling points. 10) Which of the following molecules will not form hydrogen bonds? a) CH4 b) NH3 c) H2O d) HF 11) How does the strength of hydrogen bonds compare with covalent bonds? a) Hydrogen bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds. b) Hydrogen bonds are much weaker than covalent bonds. c) Hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds have similar strengths. 12) The pH of a solution of 0.04 M HCl is: a) 4 b) 1.4 c) 0.4 d) 0.04 e) The pH cannot be determined 13) An HCl solution has a pH = 3. If you dilute 10 mL of the solution to 1000mL, the final pH will be: a) 1.0 b) 2.0 c) The pH does not change. d) 4.0 e) 5.0 14) A solution at pH 7 contains a weak acid, HA. The pKa of the acid is 6.5. What is the ratio of [A-]:[HA]? a) 1:3 b) 1:1 c) 3:1 d) 10:1 - 15) The pH of a solution where the A to HA ratio is 1 has a pH = pK . a a) True b) False 16) Which amino acid has the one-letter symbol E? a) lysine b) phenylalanine c) histidine d) glutamic acid 17) Which amino acid has the three-letter symbol Asn? a) aspartic acid b) asparagine c) alanine d) arginine 18) Which amino acid has a phenol group? a) Glutamic Acid b) Histidine c) Isoleucine d) Serine e) Tyrosine 19) Which amino acid is classified as polar? a) L b) H c) P d) I 20) Which group consists only of amino acids with polar side chains? a) serine, threonine, and leucine b) serine, threonine, and cysteine c) serine, threonine, and valine d) serine, threonine, and isoleucine 21) Which group consists only of amino acids with basic side chains? a) leucine and lysine b) arginine and leucine c) lysine and arginine d) arginine and isoleucine 22) Which amino acids contain sulfur? a) cysteine and lysine b) cysteine and methionine c) arginine and methionine d) cysteine and isoleucine 23) Which amino acid takes on a negative charge when the R-group loses a proton? a) Glutamic Acid b) Histidine c) Glutamine d) Tyrosine e) Glutamic Acid and Tyrosine 24) Which amino acid takes on a positive charge when the R-group gains a proton? a) Glutamic Acid b) Histidine c) Glutamine d) Tyrosine e) Glycine Figure 1 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 25) Referring to Figure 1: Which points on the graph represent pK’s? a) 1 and 7 b) 2, 4 and 6 c) 3 and 5 d) 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 e) The pKs cannot be determined without more information . 26) Referring to Figure 1: Which point most likely represents the pK for the carboxyl group? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 27) Referring to Figure 1: At which point would the amino acid have its maximum negative charge? a) 1 b) 2 c) 4 d) 6 e) 7 28) Referring to Figure 1: At which point would the isoelectric point be found? a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 e) 6 29) Which of the following can produce esters? a) a primary alcohol plus K2Cr2O7(aq), H2SO4 b) an alcohol plus an aldehyde c) an aldehyde plus KMnO4(aq) in acidic solution d) an acid plus an alcohol e) an acid plus an aldehyde 30) The formation of an amide from a primary amine and a carboxylic acid is: a) a substitution reaction. b) an oxidation reaction. c) an addition reaction. d) an elimination reaction. e) a condensation reaction. Games! And now the adventure begins… 1) (5 points) For the titration of 45.0 mL of 0.020 M aqueous whattheheckic acid (a monoprotic acid) with 0.020 M KOH(aq), calculate the pH after the addition of 36.0 mL of KOH(aq). The pKa of whattheheckic acid is 2.97. 2) (6 points) Answer the following questions about dilutions. a) What volume of 0.778 M Na2CO3 (aq) should be diluted to 150.0 mL with water to reduce its concentration to 0.1022 M Na2CO3 (aq)? b) An experiment requires the use of 20.0 mL of 0.50 M NaOH (aq). The stockroom assistant can only find a bottle of 3.0 M NaOH (aq). How can the 0.50 M NaOH be prepared? 3) (6 points) Name the following compounds: a) b) c) (Your answer MUST INCLUDE relevant stereochemical information) 4) This question has 2 parts (10 points) a) The typical amino acid, NH2CHRCOOH, has pKa1 and pKa2 of 2.4 and 9.8, respectively. What is(are) the major species in an aqueous solution whose pH is 10? b) Draw the Lewis structure of 3 of the possible amino acids that the amino acid in part (a) could be. 5) (6 points) Which of the following would be attacked by a nucleophilic reagent? 6) (10 points) Write the name, give the one letter symbol and draw the Lewis Structure of: a) b) c) d) e) A polar, uncharged amino acid A polar, charged amino acid An acidic amino acid A hydrophobic amino acid A basic amino acid