TABLE S3 - Figshare
advertisement

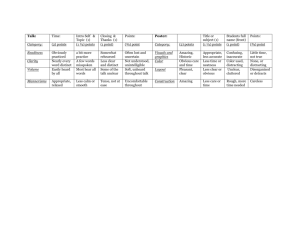
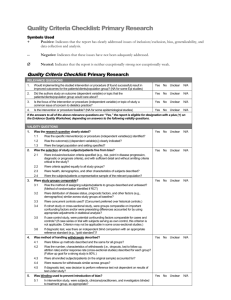
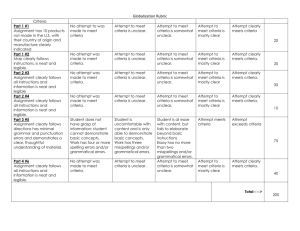
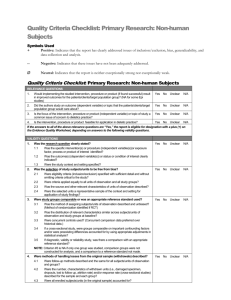
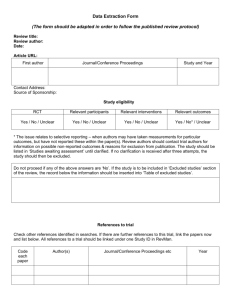
Table S3. Assessment of bias risk of randomized & controlled clinical trials a Study Sequence Allocation generation concealment Blinding of Incomplete outcome data Free of participants, and withdrawals personnel, and Other sources of Overall selective bias and assessment reporting? commentaries High/ outcome assessors moderate/ low risk of bias Deb 1976 No No Unclear No No Unclear No conflict of Assigned by “Persons in the Clinical strict placebo group also outcomes interest was alternation received 6 doses of not multivitamins to included match the dosage schedule of tetracycline”. reported. High Echevarria Yes Yes Yes Unclear 1995 Random Household contacts The study drug was 250 were randomized; of (Main author table with enrolled in the study provided in a sachet these, 213 fulfilled all the Unclear Unclear The study was partially financed was contacted fixed blocks were given sequential labeled only with the inclusion criteria by Bayer's Latin and provided containing American Affairs, further 50 numbers was not possible for Information provided and 17 from the study numbers. It study number. Unclear (20 from the placebo group Bayer-México. information on either the team by the author: ciprofloxacin group were Conflict of methods) members or the Personnel and excluded). Two additional interests not household contacts patients were blind; household contacts were declared. to identify the study the medication and excluded from the efficacy Informed Consent, drugs. Information placebo had similar analysis (one voluntarily protocol approved provided by the appearance. Codes withdrew and one was by Ethical IRB of author: codes were were open once the excluded because she Universidad assigned centrally. trial was terminated. received other treatment). Peruana Cholera samples were Cayetano taken only the 3rd and 7th Heredia. days of follow-up. Joint ICMR- Unclear GWB-WHO 1971 Unclear Unclear No No Unclear Probably not Probably not done “In order to avoid No clinical outcomes were Clinical done bias, the study was collected. No adverse outcomes interests not designed as a events reported. No not doubled-blind baseline characteristics included Trial” reported. Conflict of declared. High Khan 1982 No No No No No Unclear Assigned by Half of control group was No conflict of strict not re-visit at 10-12 days interest was alternation Contact participants were reported. High not tested for V. Cholera Lapeyssonnie Yes Unclear Unclear No 1971 Random Probably not done “Double blind”. It is Only data from contacts No conflict of (Preliminary Table unclear who was that were positive to V. interest was report. Unclear blind. No information Cholera the first day was authorship relating to whether No Unclear High reported. included; data on 30% of the intended blinding them was not reported. No No was effective. adverse events. No Unclear McCormack No 1968 Assigned by Data from 556 data of 655 Clinical strict contacts was reported. No outcomes treatment alternation information on difference of not because the to one of 4 losses according to groups. included RAMADAN groups More families in the groups dosage schedule given placebo or one single was modified. dose of tetracycline No conflict of hydrochloride had at least I interest was member (other than the reported. index patient) infected No Unclear Differential High Sen Gupta No No 1978 Unclear Unclear. No Unclear. Although the term Of the expected total of Clinical No conflict of “placebo” was used, 2760 samples from 276 outcomes interest was there is no contacts, 2672 (96.8 %) not reported. The description that the were collected. included Vibramycin brand trial was “blind”. High of doxycycline used in the present trial was supplied by the Pfizer Chemical Co. a According to the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook: Sequence generation: Was the allocation sequence adequately generated? Allocation concealment: Was allocation adequately concealed? Blinding of participants, personnel, and outcome assessors: Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study? Incomplete outcome data and withdrawals: Were intention-to-treat analyses performed? Had participants withdrawn from the study? Free of selective reporting? Other sources of bias and commentaries: Was sample size calculated? Were inclusion and exclusion criteria and baseline characteristics defined? Were conflicts of interests reported? b Yes = low risk of bias. c No = high risk of bias.