ICU Case Study
advertisement

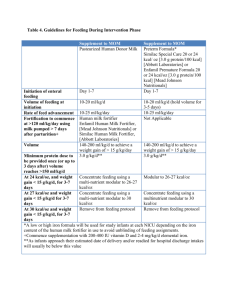
ICU Case Study Mrs GK (54 years old) was admitted to hospital with fever and leg cellulitis. Previous Medical History includes: Diabetes – type 2, on insulin, IHD, CABG x 3 in 1995, AMI 2002, HT, CCF, hypercholesterolaemia, OSA. Social Hx – lives with husband, enjoys watching TV. Not very active. 5 days later she is admitted to ICU with respiratory failure, sepsis and hypotension. Anthropometry Weight 115 kg Height 160 cm Weight history – Gradual weight gain over past few years. Biochemistry Na 138 mmol/L (N 134 – 145) K 4.1 mmol/L (N 3.5 – 5) Urea 9.2 mmol/L (N 3.0 – 8.0) Creatinine 0.11 mmol/L (N 0.05 – 0.09) Albumin 28 g/L (N 40 - 50) WCC 12.4 (N 4 – 10) Clinical Intubated and ventilated Temperature 38.5 C NGT insitu Hypotensive Requiring inotropic support – Noradrenaline infusion Nutrition History Unable to take diet history due to communication limitations but patient indicates usual good appetite and oral intake You are referred to see the patient for nutritional assessment and appropriate nutritional support. What do you think of her nutritional status? Calculate her estimated energy and protein requirements Would you use enteral or parenteral nutrition? Select the appropriate formula and determine your feeding regime. The nursing staff are checking her NG aspirates every 4 hours. They report that her most recent NG aspirate was > 200 ml. What would you do? Check previous and subsequent aspirates Check other indicators of intolerance to feeding Decrease rate and see whether aspirates improve. If ongoing high aspirates: Discuss with medical team regarding: Prokinetics SB feeding TPN to supplement EN 5 days later: Temperature 38.4 °C Oliguric Hypotensive –increased noradrenaline requirements Pulmonary oedema Biochemistry: Na 135, K 5.6, Urea 19.1, Creatinine 0.389 She is commenced on CVVHD. Would you make any changes to your feeding regime? (Would another formula be more appropriate?) Issues to consider: Fluid overload due to oliguria High K levels CVVHD able to remove fluid continuously and remove K, so unlikely to require fluid or K restriction. CVVHD also very catabolic. If she were commenced on intermittent haemodialysis (as opposed to CVVHD), how might you change her feeding regime? Issues to consider: Fluid overloaded due to oliguria K high Need to restrict K and fluid Choose Nepro Nepro @ 50 ml/hr over 24 hr/day (1200 ml) Provides 2160 kcal, 97g protein, 32 mmol K. Calculation of Energy and Protein Requirements: Weight = 115kg Adjusted Body Weight = 64 + 0.5 x (115 – 64) = 90 kg Energy 21 kcal / kg ABW / day 21 x 115 = 2415 kcal / day Schofield equation: Using adjusted body weight: BMR = 34 x 90 + 3538 = 6598 kJ = 1570 kcal EER= 1570 x 1.3 (IF) x 1.0 (AF) = 2040 kcal (8580 kJ) Using actual body weight: EER = 9680 KJ = 2300 kcal Harris Benedict Equation Using adjusted body weight: BEE = 2741 + (40.0 x 90) + (7.7 x 160) – (19.6 x 54) = 6514 kJ = 1550 kcal EER = 1550 x 1.3 x 1.0 = 2016 kcal Using actual body weight: EER = 9769 kJ = 2326 kcal Ireton Jones Equation EEE(v) = 1784 – (11 x 54) + (5 x 115) + (244 x 0) = 1765 kcal Protein Moderate stress 1 – 1.5 g / kg BW / day Using adjusted Body weight: 95 - 145 g protein / day Enteral Feeding Regime Estimated Energy Requirements: ~ 2000 kcal /day Estimated Protein Requirements: ~ 95 – 145 g / day Isosource HN 1.2 kcal / ml 53 g protein / L Therefore, Need 1666 ml to meet energy requirements (2000 / 1.2) If fed continuously over 24hrs Rate = 1666 / 24 = 69 ml / hr Isosource HN @ 70 ml /hr over 24 hrs /day (1680 ml) Provides 2016 kcal, 89 g protein