Learning Targets: Date: Date: I can describe how DNA molecules
advertisement

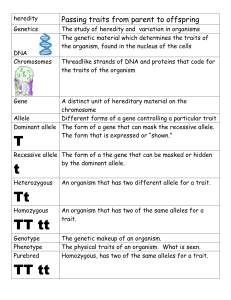
LEARNING TARGETS: Date: Date: I can describe how DNA molecules are long chains linking four subunits (smaller molecules) whose sequence encodes genetic information. 2. I can illustrate the process by which gene sequences are copied to produce proteins. 3. I can explain that regulation of cell functions can occur by changing the activity of proteins within cells. 4. I can explain that regulation of cell functions can occur by changing whether and how much a particular gene is expressed. 1. Vocabulary Large molecules inside the nucleus of living cells that carry genetic information. Fundamental concept of heredity that each organism has characteristics that are encoded in its genes and passed on from one generation to the next. The passing of traits to offspring. This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. A segment of inheritance information that, taken as a whole, specifies a trait. In common language the term “gene” sometimes refers to the scientific concept of an allele. Change in the nucleotide sequence of the genetic material of an organism. Inherited or affected by genes. A set of instructions coded in DNA molecules that specifies the traits of an organism. A measure of the tendency of individual genotypes in a population to vary from one to another. The process whereby a copy of a DNA molecule is made and the genetic information it contains is duplicated. The property of a gene (or allele) when it suppresses the expression, or dominates the effects, of the recessive gene (or allele). a gene (or allele) whose phenotypic expression is masked by a dominant gene (or allele). A set of three adjacent nucleotides that specify the type and sequence of amino acids for protein synthesis. Having two identical alleles that code for the same trait. An individual (or a condition in a cell or an organism) containing two different alleles for a particular trait. The entire set of genes in an organism. The expression of a particular trait, for example, skin color, height, behavior, etc., according to the individual’s genetic makeup and environment. QUESTIONS: Discussion Question: Answers: DNA Mendelian genetics Heredity Gene Mutation Genetic Genetic information (DNA sequence) Genetic variation DNA replication Dominant trait Recessive trait Codon Homozygous Heterozygous Genotype Phenotype Large molecules inside the nucleus of living cells that carry genetic information. Fundamental concept of heredity that each organism has characteristics that are encoded in its genes and passed on from one generation to the next. The passing of traits to offspring. This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. A segment of inheritance information that, taken as a whole, specifies a trait. In common language the term “gene” sometimes refers to the scientific concept of an allele. Change in the nucleotide sequence of the genetic material of an organism. Inherited or affected by genes. A set of instructions coded in DNA molecules that specifies the traits of an organism. A measure of the tendency of individual genotypes in a population to vary from one to another. The process whereby a copy of a DNA molecule is made and the genetic information it contains is duplicated. The property of a gene (or allele) when it suppresses the expression, or dominates the effects, of the recessive gene (or allele). a gene (or allele) whose phenotypic expression is masked by a dominant gene (or allele). A set of three adjacent nucleotides that specify the type and sequence of amino acids for protein synthesis. Having two identical alleles that code for the same trait. An individual (or a condition in a cell or an organism) containing two different alleles for a particular trait. The entire set of genes in an organism. The expression of a particular trait, for example, skin color, height, behavior, etc., according to the individual’s genetic makeup and environment.