Miguel Yus
advertisement
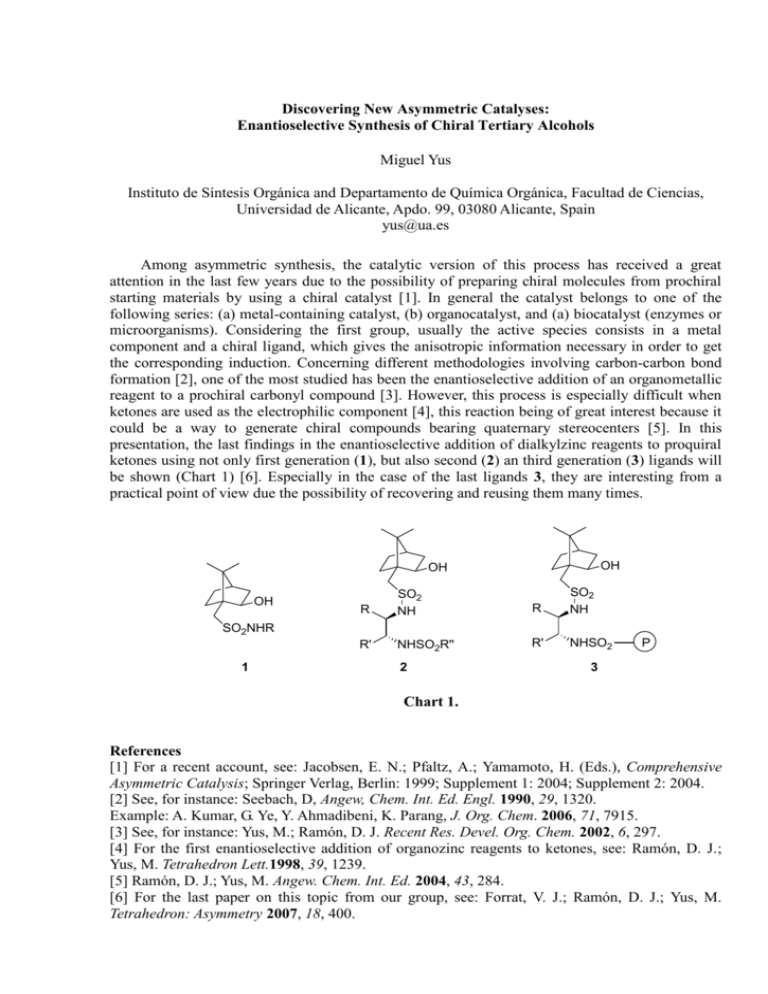
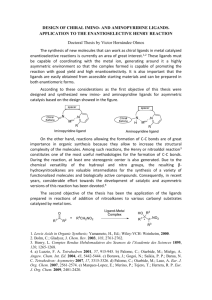
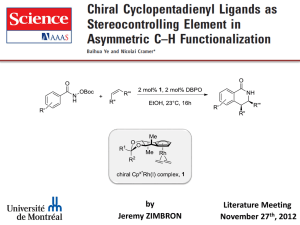
Discovering New Asymmetric Catalyses: Enantioselective Synthesis of Chiral Tertiary Alcohols Miguel Yus Instituto de Síntesis Orgánica and Departamento de Química Orgánica, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Alicante, Apdo. 99, 03080 Alicante, Spain yus@ua.es Among asymmetric synthesis, the catalytic version of this process has received a great attention in the last few years due to the possibility of preparing chiral molecules from prochiral starting materials by using a chiral catalyst [1]. In general the catalyst belongs to one of the following series: (a) metal-containing catalyst, (b) organocatalyst, and (a) biocatalyst (enzymes or microorganisms). Considering the first group, usually the active species consists in a metal component and a chiral ligand, which gives the anisotropic information necessary in order to get the corresponding induction. Concerning different methodologies involving carbon-carbon bond formation [2], one of the most studied has been the enantioselective addition of an organometallic reagent to a prochiral carbonyl compound [3]. However, this process is especially difficult when ketones are used as the electrophilic component [4], this reaction being of great interest because it could be a way to generate chiral compounds bearing quaternary stereocenters [5]. In this presentation, the last findings in the enantioselective addition of dialkylzinc reagents to proquiral ketones using not only first generation (1), but also second (2) an third generation (3) ligands will be shown (Chart 1) [6]. Especially in the case of the last ligands 3, they are interesting from a practical point of view due the possibility of recovering and reusing them many times. OH OH OH R SO2 NH R SO2 NH R' NHSO2R'' R' NHSO2 SO2NHR 1 2 P 3 Chart 1. References [1] For a recent account, see: Jacobsen, E. N.; Pfaltz, A.; Yamamoto, H. (Eds.), Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis; Springer Verlag, Berlin: 1999; Supplement 1: 2004; Supplement 2: 2004. [2] See, for instance: Seebach, D, Angew, Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1990, 29, 1320. Example: A. Kumar, G. Ye, Y. Ahmadibeni, K. Parang, J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 7915. [3] See, for instance: Yus, M.; Ramón, D. J. Recent Res. Devel. Org. Chem. 2002, 6, 297. [4] For the first enantioselective addition of organozinc reagents to ketones, see: Ramón, D. J.; Yus, M. Tetrahedron Lett.1998, 39, 1239. [5] Ramón, D. J.; Yus, M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 284. [6] For the last paper on this topic from our group, see: Forrat, V. J.; Ramón, D. J.; Yus, M. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2007, 18, 400.
![N,N′-(1S)-[1,1′-Binaphthalene]-2,2′-diylbis](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007446422_1-b88a6aa00cc2e35e8f40398da5675ef7-300x300.png)