climates around the world
advertisement

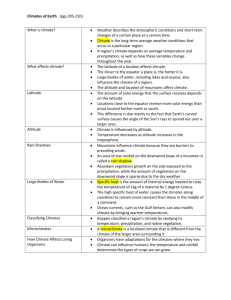
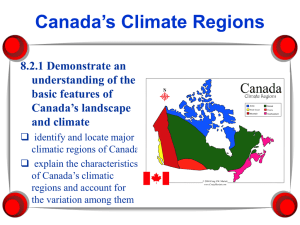
LESSON PLAN: Climates Around the World LEVEL: Advanced CLIMATES AROUND THE WORLD Related topics: latitude OVERVIEW This lesson helps students identify major climates around the world and understand how climate is related to latitude. MATERIALS NEEDED • • World Climate Map (Home >> World >> Maps for the World>>World Climate Map - Advanced) • World Outline Map (Home >> World >> Maps for the World>> World Outline Map with Countries) Climate Graphs [Note: Climate graphs are located in the "Climate Graphs for the World Climate Map" section that follows Activity 1.] ACTIVITIES Activity 1 helps students identify major climates and compare climates in different parts of the world. Activity 2 helps students understand how climate is related to latitude. OBJECTIVES Students will use the World Climate Map and its accompanying climate graphs to identify places in the world that have similar climates. Students will create a map from memory (mental map) to show how climates are related to latitude. NATIONAL GEOGRAPHY STANDARDS • • • How to use maps and other geographic representations, tools, and technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective How to use mental maps to organize information about people, places, and environments in a spatial context The physical and human characteristics of places BACKGROUND INFORMATION Climate is the average kind of weather a place has over a period of years. It can be described in terms of temperature, wind velocity, and precipitation. Other characteristics of climate include humidity, sunshine and cloudiness, air pressure, and seasonal variations. Climates are generally classified in thirteen major categories, which are shown on the World Climate Map used for this lesson. Climate is related to latitude. In simplest terms, places in the low latitudes (nearest the Equator) have the warmest climates because they receive the direct rays of the sun year round. Places in the high latitudes (nearest the poles) have the coldest climates because they receive less intense sunlight. Places in the middle latitudes (between the Arctic Circle and the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere and between the Antarctic Circle and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere) have climates that vary with the seasons. Climate is also affected by location and by elevation. Places near a coast are generally warmer in winter and cooler in summer than places inland. Places at high elevations are generally cooler than places at low elevations. . www.randmcnallyclassroom.com 1 LESSON PLAN: Climates Around the World LEVEL: Advanced ACTIVITY 1 Review the map legend on the World Climate Map. Then review the climate graphs from the "Climate Graphs for the World Climate Map" section following this activity. Explain to them what each graph shows. [Curved lines show average monthly temperatures; vertical bars show average monthly precipitation. Each graph is correlated with a type of climate and a place that has that climate.] Ask students to match cities on different continents with similar climates. (Examples include Houston and Buenos Aires, Johannesburg and Paris, Bangkok and Darwin.) Have students complete the worksheet titled “Comparing Climates.” [Note: Students will need the climate graphs from the "Climate Graphs for the World Climate Map" section to complete the worksheet. To provide students with copies of the climate graphs, download this lesson plan and adjust your printer settings to print only page 3.] www.randmcnallyclassroom.com 2 LESSON PLAN: Climates Around the World LEVEL: Advanced CLIMATE GRAPHS FOR THE WORLD CLIMATE MAP www.randmcnallyclassroom.com 3 LESSON PLAN: Climates Around the World LEVEL: Advanced ACTIVITY 2 Based on the comparison of climates in Activity 1, students should begin to see that climates are related to latitude. Ask them to match the following kinds of climates to the latitudes in which they are generally found. [Note: Climate #2 has two correct answers (b & d)] _____ 1. Tropical a. north of the Arctic Circle (66ºN) and south of the Antarctic Circle (66ºS) _____ 2. Moderate (Rainy Winter) b. between the Tropic of Cancer (23ºN) and the Arctic Circle (66ºN) _____ 3. Continental (Snowy Winter) c. between the Tropic of Capricorn (23ºS) and the Tropic of Cancer (23ºN) _____ 4. Polar d. between the Tropic Capricorn (23ºS) and the Antarctic Circle (66ºS) (1. c, 2. d, b 3. b, 4. a) Emphasize that these are generalizations and that climates also vary because of location and elevation. CONCLUDING AND ASSESSMENT Provide students with the World Outline Map. Without referring to a map, have students label the following latitudes: Arctic Circle, Tropic of Cancer, Equator, Tropic of Capricorn, and Antarctic Circle. Have them color their maps to indicate the following climate zones: a. Places that are always cold b. Places that have cool/cold winters and warm/hot summers c. Places that are warm all year INTERNET CONNECTIONS Students can access www.worldclimate.com to find out what the weather is usually like in thousands of places worldwide. CROSS-CURRICULAR CONNECTIONS Science Have students work in groups to prepare a demonstration showing why places that are near the Equator generally have warmer climates than places that are far from the Equator. ANSWERS FOR STUDENT WORKSHEET 1. Jakarta: 80º, 13” for the month, rain Stockholm: 28º, less than 2” for the month, snow 2. a. about 38ºF b. slightly less than 2” for the month c. rain 3. Students' answers will vary. Check to make sure they are correct. 4. a. much less rainfall www.randmcnallyclassroom.com 4 LESSON PLAN: Climates Around the World LEVEL: Advanced b. much warmer, more precipitation, rain instead of snow c. much warmer, no precipitation www.randmcnallyclassroom.com 5 Name: _______________________________________________________ Date: ___________________ COMPARING CLIMATES Use the World Climate Map and the climate graphs to help you answer the following questions. 1. It is January, and you are flying from Jakarta, Indonesia, to Stockholm, Sweden. What climatic differences will you find between the two places? January Climate Jakarta Stockholm Average temperature (Fahrenheit) Average precipitation (inches) Form of precipitation (rain or snow) 2. You continue your trip by flying to Tehran, Iran. What climatic conditions are you likely to find? a. Temperature ________________________ b. Precipitation ________________________ c. Form of precipitation ______________________ 3. Before returning to the United States, you decide to fly to Darwin, Australia. Name another city shown on the map that has the same climate as Darwin. ______________________________________________________________________ 4. If you made a similar trip in July, how would climatic conditions be different in: a. Jakarta? _____________________________________________________ b. Stockholm? ___________________________________________________ c. Tehran? _____________________________________________________ 6