Ch 1 - Introduction to Database Processing
advertisement

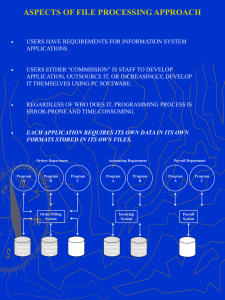
Ch 1 - Introduction to Database Processing In-Class Quiz - name five databases you have interacted with this week Confidence level - discuss - redo you answer - confidence level What is a database? A collection of Integrated Records Organized Business Data - Telephone books; UW Registration System Business Transactions - Blockbuster tracks checkout / returns / payments; Accounting What types of databases have you been exposed to? Transaction or Organized Data Think about the purposed of the database; Goal of the System What are the complicated issues in designing each system? Transaction systems require multiple postings to different accounts UW Registration has concurrency issues; two people trying to get the same class In-Class Quiz - data vs. information and Database Management System vs. Database All databases deal with two major issues - 1) Acceptance of data and 2) manipulation of data into information. Data comes into the system without meaning; Information is data output of the system in a meaningful format. What is Data? Raw Facts What is Information? Meaningful Form Database Management System Collects, stores and manipulates data (data input screens; Edit/Deletion of data screen) and disseminates information (executes queries and creates reports) Database - the structure data is stored in; contains Meta Data and the Data Dictionary Microsoft Access is a Database Management System that contains a Database Visual Basic can be used as a Database Management System but not a Database SQL Server is a Database with limited Database Management capabilities Types of Database Systems (from the textbook)… Manual System - Customer Ledger Cards; Check Book Green Ledger File-Processing System - Check Book in an Excel Spreadsheet Microcomputer DBMS - Single-User Database System Client/Server DBMS - Multiple-Users on the same LAN Internet DBMS - Multiple-Users from different locations using Web to share data Distributed DBMS - Multiple-Servers sharing the data processing load (bank) Object-Oriented DBMS - processing/data management of objects (new engineering) In-Class Quiz - List advantages for Manual System and Computerized Systems? (Think Accounting) What are some of the reasons for implementing a database system? Elimination of duplication of data Data sharing Centralizing file maintenance Ease of creating information Improve data consistency Improve data accessibility and responsiveness Improve Data Integrity - Number One What are some of the PROBLEMS with moving from a manual to a computerized DBMS? Special personnel Cost (New Hardware/Software) Conversion Costs (training, duplication of systems) Problems with change As Systems Analysts, you will be recommending business systems… Why would you recommend each? And what problems should you be aware of? Manual System Why? Unknown business rules or data needs; very small effort Problem? Data sharing; Accuracy of data dependent on user File-Processing System Why? Linear data; used for a single purpose Problem? Inability to create relationships with other data Microcomputer DBMS - Single-User Database System Why? Accounting data; relational data; improve data integrity Problem? Time; level of effort; some business rules can't be modeled; changing environment; New developments in third-party software Client/Server DBMS Why? Multiple-Users need to share/input data Problem? Concurrency control issues; data locking Yes/No Internet DBMS Why? Users can share/input data from any terminal with Web access; no special software needed; multi-site businesses allow customers and vendors to interface directly Problem? Harder to control; other people in your data; data corruptions; not all business functions on Web; combining data for reporting Distributed DBMS - sharing the data processing load Why? Business cannot allow system downtime; banks, airlines Problem? Cost in hardware, software (requires middleware) and staff Object-Oriented DBMS Why? Intensive object processing (heat-loss photos) Problem? Difficult to use; limited supply of experts; not cost effective to move from existing system *** InClass FiredUp – small groups page 23