Database Management Introduction: Concepts & SQL Examples
advertisement

Intro-Part 1
Introduction to Database Management:
Ch 1 & 2
Important Points
Databases are everywhere
Data independence and abstraction
Three Schema Architecture
DBMS characteristics and Features
Databases are everywhere
What is a database?
What is a database management system
(DBMS)?
Examples?
Example: University Database
How would you do this without a database?
What types of challenges would you face?
Registration
Grade
Recording
Entities:
students, f aculty , courses,
of f erings, enrollments
Relationships
:
f aculty teach of f erings,
students enroll in
of f erings, of f erings made
of courses, ...
Unive rsity Databas e
Faculty
Assignment
Course
Scheduling
File-Based System
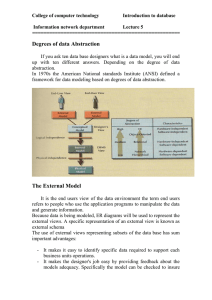
Data Independence and Abstraction
The major problem with developing applications
based on files is that the application is dependent on
the file structure.
That is, there is no program-data independence
separating the application from the data it is
manipulating.
If the data file changes, the code that accesses the file
must be changed in the application.
One of the major advantages of databases is they
provide data abstraction.
Data abstraction allows the internal definition of an
object to change without affecting programs that use
the object through an external definition.
Three Schema Architecture
View 1
External to
Conceptual
Mappings
Conceptual
to Internal
Mappings
View 2
Conceptual
Schema
Internal
Schema
View n
External
Level
Conceptual
Level
Internal
Level
DBMS
A database management system provides efficient, convenient,
and safe shared (i.e., multi-user) storage and access to massive
amounts of persistent data.
Efficient - Able to handle large data sets and complex queries
without searching all files and data items.
Convenient - Easy to write queries to retrieve data.
Safe - Protects data from system failures and hackers.
Massive - Database sizes in gigabytes and terabytes.
Persistent - Data exists after program execution completes.
Shared - More than one user can access and update data at the
same time while preserving consistency.
Interrelated – True of relational DBMS.
Common Features of a DBMS
Database Definition: The database is described to the DBMS
using a Data Definition Language (DDL). The DDL allows the
user to create data structures in the data model used by the
database.
Nonprocedural Access: Once a database has been created in a
DBMS using a DDL, the user accesses the data using a Data
Manipulation Language (DML). The standard DML is SQL.
Application Development: Graphical tools for developing forms
and reports using non-procedural access
Procedural language interface: A language that combines
nonprocedural access with procedural programming.
Transaction Processing: Perform scheduling of operations and
implements concurrency control algorithms.
Database Tuning: Tools to monitor and improve database
performance.
University Database
Relationships
Tables
s
University Database (ERD)
Student
Offering
Faculty
StdSSN
StdClass
StdMajor
StdGPA
Of f erNo
Of f Location
Of f Time
FacSSN
FacSalary
FacRank
FacHireDate
Teaches
Has
Supervises
Accepts
Course
Registers
Enrollm ent
EnrGrade
CourseNo
CrsDesc
CrsUnits
Nonprocedural Access
Query: request for data to answer a question
Indicate what parts of database to retrieve
not the procedural details
Improve productivity and improve
accessibility
SQL SELECT statement and graphical tools
Graphical Tool for Nonprocedural
Access
SQL Examples
Retrieve all products in the database:
Retrieve all products where inventory < 10:
SELECT sku, name, desc, inventory FROM
product;
SELECT name, inventory FROM product WHERE
inventory < 10;
Insert a new product into the database:
INSERT INTO product VALUES
('12345678','Soap', 'Ivory Soap',100);