Vocabulary - California State University, Sacramento
advertisement

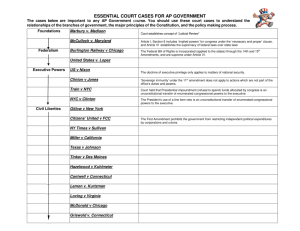
GOVT. 1: Essentials of Government Fall 2007 Final Exam Study Guide Sections Multiple-Choice (50) – To be chosen from the multiple-choice questions given in the weekly quizzes throughout the semester. Vocabulary (25) – To be taken from the terms listed below. Short Essay (5 questions) - Write one paragraph and include as much substance as necessary to impart your full knowledge of the concepts and issues surrounding the question. Essay Examples - Describe democracy in America and the American political culture. (List and describe key elements of democracy in America such as individual freedom, liberty, majority rule, protection of minority rights, limited government, separation of powers, checks and balances, Bill of Rights, due process of law, habeas corpus, etc.) - What are some of the factors that might help to determine whether democratic politics can take root in a country that has not previously experienced democracy? Is it appropriate for America to try to shape the governments and political arrangements of other countries? - Describe the essential elements of Federalism in American and reference the US Constitution as the legal “blueprint” for our federal form of government. From Article I of the Constitution, describe the structure and power of Congress as delegated and implied. Also, include a description of the power of the states as “denied” and “reserved”. - Describe the role of the US Supreme Court in our federal system of government with respect to separation of powers, jurisdiction, federal law, state law, etc. Also, describe the essence and importance of the landmark Supreme Court case, Marbury v Madison. - How do we elect a president in the United States? More specifically, describe process of a presidential election beginning with the campaign, primary, general election, and the final selection by the Electoral College. - Who participates in our political system, and how do “they” (people and groups) participate? Also, discuss the several factors that explain political participation considering political parties, interest groups, and social movements. - Discuss the California Initiative Process in terms of its history and effect. Also, consider the process itself in terms of the qualifying requirements as well as the benefits and flaws of the initiative process in California today. Is the initiative process an essential part of American Democracy? - Imagine yourself as wrongly accused of a crime. What rights and legal protections would you expect and demand as a person accused of a crime? Why are these legal protections necessary if you are innocent of a particular crime? Why is the 14th Amendment important to a person accused of committing a crime in a particular state? - Discuss the issue of immigration in California and the United States. From articles you have read in the Sacramento Bee or from other mainstream media sources, focus on the central issues and suggested political solutions. - Compare and contrast the California State Legislature and Congress in terms of their source of Constitutional power, makeup of legislators (numbers by chamber, terms, term limits, partisanship, etc.) - What do we mean when we say “the United States is a Federal Democratic Republic”? Vocabulary 1. apportionment 2. “clear and present danger” test 3. “separate but equal” rule 4. 1st Amendment 5. 10th Amendment 6. 14th Amendment 7. affirmative action 8. appropriations 9. authoritarian government 10. autocracy 11. bicameral 12. Bill of Rights 13. Brown v. Board of Education 14. capitalism 15. checks and balances 16. civil liberties 17. civil rights 18. Commander-in-Chief 19. commerce clause 20. concurrent powers 21. conservative 22. constituent 23. criminal law 24. de jure 25. delegate 26. Democrat 27. discrimination 28. double jeopardy 29. due process of law 30. egalitarian 31. electoral college 32. eminent domain 33. equal protection clause 34. exclusionary rule 35. fascism 36. line-item veto 37. executive order 38. federalism 39. Federalist Papers 40. “fighting words” 41. freedom 42. gender gap 43. gerrymandering 44. grand jury 45. guest worker program 46. habeas corpus 47. impeachment 48. implied powers 49. incumbent 50. initiative (CA) 51. Judiciary Act of 1789 52. judicial review 53. laissez-faire 54. liberal 55. liberty 56. limited government 57. line item veto 58. litigation 59. lobbying 60. majority rule 61. majority leader 62. Marbury v Madison 63. Marxism 64. Miranda rule 65. New Deal 66. opinion 67. original jurisdiction 68. oversight 69. platform 70. political action committee 71. political participation 72. poll tax 73. pork barrel 74. primary election 75. prior restraint 76. progressive/regressive taxation 77. protection of minority rights 78. recall 79. redistricting 80. republic 81. Republican 82. Roe v. Wade 83. due process of law 84. limited government 85. reserved powers 86. segregation 87. selective incorporation 88. separation of powers 89. single-member district 90. socialism 91. soft money 92. stare decisis 93. suffrage 94. socialism 95. socioeconomic status 96. secular 97. sectarian 98. term limits 99. unitary 100. War Powers Resolution