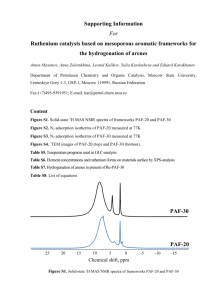
Characterization of Ru-containing Zeolites by XAS
advertisement

Characterization of Ru-containing Zeolites by XAS Angelia Sulaiman Lo (羅嘉雁)1, Pang-hung Liu (劉邦弘)1, Kuei-jung Chao (趙桂蓉)1, Stefan Altwasser2, Roger Gläser2, and Jens Weitkamp2 1 2 Department of Chemistry, Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan Institute of Chemical Technology, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany Ruthenium oxide particles were introduced into ZSM-5 (MFI type) by aqueous ion exchange and hydrothermal zeolite synthesis methods in the presence or absence of tetrapropyl ammonium ions as organic template. The local structure of ruthenium has been studied by XAS, PXRD, and TEM characterization methods. The aqueous ion exchange method leads to anhydrous ruthenium oxide with average particle size of ~1.0 nm, while small hydrous ruthenium oxide particles with diameter ~0.6 nm are obtained by template-free synthesis. Similar template-free method was applied to introduce ruthenium oxide particles into FAU pores, which leads to hydrous ruthenium oxide with diameter ~1.3 nm. In the presence of organic template (TPA), hydrous ruthenium oxide particles were introduced, but after subsequent calcination, large anhydrous ruthenium oxide particles were obtained.