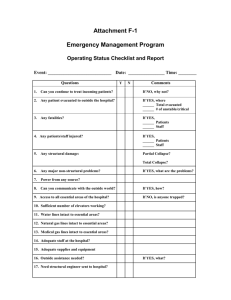
FOLDS
advertisement
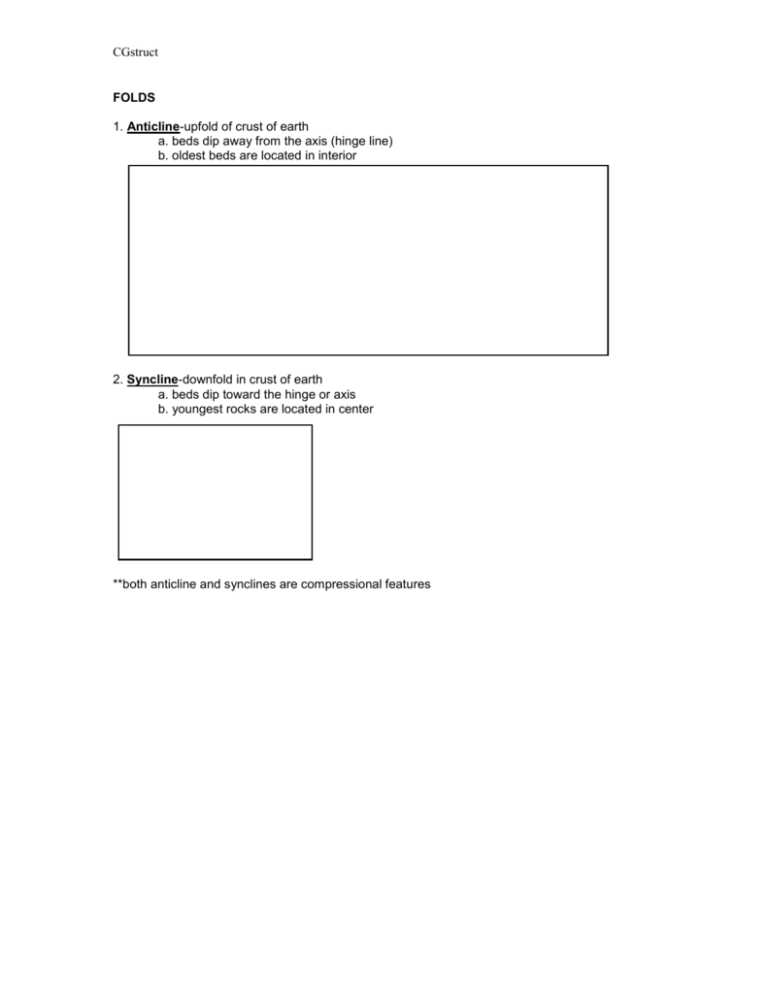
CGstruct FOLDS 1. Anticline-upfold of crust of earth a. beds dip away from the axis (hinge line) b. oldest beds are located in interior 2. Syncline-downfold in crust of earth a. beds dip toward the hinge or axis b. youngest rocks are located in center **both anticline and synclines are compressional features CGstruct 3. Shapes of Folds a. Symmetrical -hinge vertical beds dip away (toward) at same angle b. Asymmetrical -hinge inclined beds dip away (toward) at different angles (1) overturned fold--one limb overturned (2) Recumbent (lying down) -hinge horizontal one limb overturned CGstruct STRUCTURAL FEATURE INTERPRETATIONS I. Compressional a. Folding b. Thrusting or reverse faulting c. Trenching d. Thickening CGstruct II. Tensional a. Rifting b. Downdropping or Normal Faults e.g. East African Rift Gulf of California c. Crustal Thinning Death Valley CGstruct III. Shearing (sliding past one another) Before Left lateral strike slip motion Right lateral strike slip motion SPECIAL TYPE OF STRIKE SLIP FAULT Called Transform Fault Mid Ocean Ridge Transform fault (one type ) defined as: *That section located between ridge segments where the offset of ridge is opposite to spreading direction CGstruct UNCONFORMITITES are breaks or gaps in the geologic record; a time period that is missing in the rock record 1. ANGULAR UNCONFORMITY: beds above and below the unconformity meet at an angle a. 1 through 5 deposited horizontally b. Tilted (implies uplift, tectonics) c. Erosion leaves undulatory surface d. Beds 6-8 deposited horizontally 2. NONCONFORMITY: when sedimentary rocks are in unconformable contact with Igneous or metamorphic rocks 3. DISCONFORMITY: series of parallel beds with an unconformable surface between side view