kb fragments
advertisement

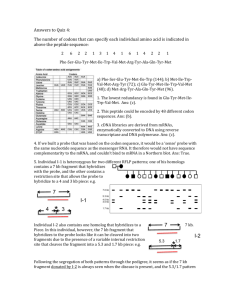
1. False. Bacterial plasmids used for propagation of recombinant DNA in E. coli do not integrate into the genome. They replicate from their own origins of replication and are often found at much higher numbers of copies than the bacterial chromosome. 2. The recognition sequence is PuAATTPy. For positions 2,3,4 and 5 in this sequence only 1 base out of four will lead to cutting. For positions 1 and 6 in the sequence, two bases out of 4 will lead to cutting. Therefore, the odds of having this exact sequence in a random DNA molecule will be: 1/4 x1/2 x 1/4 x 1/4 x 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/1024; or it will cut once every 1024 base pairs. Ans: 1024 bp (c) 3. The cut sites for the three enzymes are: 5’...GGATC C...3’ 3’...C CTAGG...5’ 5’...TCTAG A...3’ 3’...A GATCT...5’ 5’...AGATC T...3’ 3’...T CTAGA...5’ The results of separating the two strands of DNA will leave a 4 base overhang…this 4 base overhang happens to be THE SAME for the enzymes BamHI and BglII: 5’...G GATCC...3’ 3’...CCTAG G...5’ 5’...T CTAGA...3’ 3’...AGATC T...5’ 5’...A GATCT...3’ 3’...TCTAG A...5’ Therefore, the single strand overhangs for these two enzymes would allow them to base pair with each other. Please note, however, that if we used these two enzymes for cloning, we would not reconstitute either a BamHI or BglII site after ligation: e.g. 5’…AGATCC…3’ 3’…TCTAGG…5’ Ans: (c) 4. The restriction patterns seen for the first six individuals on the Southern blot represent the locations of 5 HindIII restriction sites, three of which are variable (polymorphic) in the human genome. For individuals 3, 5 and 6, a single band is visible using the radiolabeled probe, 6 kb in size for individual #3; 9 kb in size for individual #5 and 15 kb in size for individual 6. These data indicate that the size of the largest fragment bound by the probe is 15 kb. In addition, individuals 1, 2 and 4 contain a 2 kb fragment that hybridizes, and the size of the larger fragments in these individuals would add to 6, 9 and 15 kb respectively. These data indicate that a restriction site is present in some 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 individuals (vertical line with asterisk) located 2 kb internal to a fixed site. In addition, two variable sites located 4 kb, and 3 kb 15 kb 13 kb from the variable 2 kb site would explain the 6, 9 and 15 kb 9 kb 7 kb patterns. If all three variable 6 kb sites were missing (2 + 4 + 3 + 4 kb 6) the 15 kb fragment would be expected to hybridize. Since 2 kb individuals 1, 2 and 4 show two bands, the probe must extend into the 4 kb fragment. So the probe used in this experiment must span the DNA on either side of the first variable site, but can not be complementary to the 3 kb fragment. If this were so, a 3 kb band would be visible on the Southern blot. Ans: (c) 5. Individuals 7-15 represent individuals who are carrying two homolog chromosomes which differ with regard to the variable sites present- i.e. they are carry homologs with different polymorphisms. For example, individual 1 would be homozygous for two homologs that contained the first two polymorphic sites (site three can’t be determined): * 1) 2 3 4 6 Individual 5 would be homozygous for two homologs that were missing the first two sites and contained the third site: 5) 2 4 3 6 The cross between the two can therefore be represented as: 1,1 x 5,5 1,5 This heterozygote would on Southern blot analysis give the pattern seen in individual #10 above; there would be a 2 kb, 4 kb and 9 kb fragment which would hybridize with the probe. Ans: (a) only 1. 6. The 720 nt probe hybridizes to the 2 kb fragment, and to other fragments containing this sequence (2, 6 and 9 kb). If the 13 kb and 15 kb fragments hybridized, the carboxy terminal end of the coding sequence would lie to the right of the 2 kb fragment, but these fragments do not hybridize. The 720 nt probe must therefore lie within the 2 kb fragment. Ans: (true) 7. The size of the coding sequence needed to code for 1600 amino acids would need to be 1600 x 3 = 4800 nucleotides. However, the amino terminal coding sequence did NOT hybridize to the 6 kb fragment; this suggests that the coding region is not contiguous, and that there is an intron interrupting the coding sequence. Ans: True. 8. The TEMPLATE strand is the strand that is complementary and runs antiparallel to the strand being synthesized. If the strand being synthesized is: 5’-AGCTGCACGCAT-3’ Then the template strand would be: 5’-ATGCGTGCAGCT-3’. Ans: (d) 9. The A reaction must contain ALL of the dNTPs and ddATP. Ans: (e) 10. F→E→D→A→B→C→Z 3 2 1 6 4 5 The E to D conversion would be performed by enzyme 2. Ans: (b)