Size of the identified ASD candidate genes
advertisement

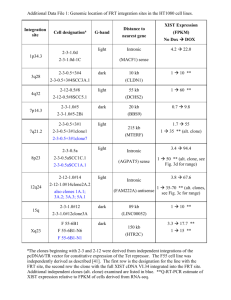
Supplementary Table 9. Top 20 single SNPs from the ASD GWASs 1-5 1-5 (Supplementary Table 1). The 15 genes encoding proteins that could be directly placed in one or more of the three networks involved in ASDs (Figures 1-3) are indicated in bold. SNP rs5918959 rs6529461 rs12392447 rs12392447 rs9932538 rs5972577 rs9822786 rs6646569 rs6646569 rs9919560 rs793094 rs7766973 rs1550976 rs6886828 rs3755827 rs3755827 rs10510837 rs892055 rs4394668 rs10774538 P value 1,22E-10 6,40E-09 5,64E-08 5,64E-08 1,94E-07 2,67E-07 2,98E-07 9,75E-07 9,75E-07 1,13E-06 1,29E-06 2,14E-06 2,30E-06 3,20E-06 3,54E-06 3,54E-06 3,56E-06 4,70E-06 4,89E-06 6,22E-06 Locus Xq12 Xq26.1 Xq28 Xq28 16p12.3 Xp21.1 3q13.2 Xq24 Xq24 11p15.3 10p11.22 6p22.3 11q25 5q33.3 3p14.2 3p14.2 3p14.2 19q13.2 1p36.22 12q24.23 Gene MSN ARHGAP36 FAM3A SLC10A3 SYT17 DMD SLC9A10 RHOXF1 RHOXF2 GALNTL4 ZNF438 JARID2 NTM SGCD CADPS FEZF2 FHIT RASGRP4 DHRS3 CCDC64 Position within gene 66 kb downstream 42 kb downstream 10 kb downstream 5 kb upstream intronic intronic intronic 1.2 kb downstream 51 kb upstream intronic 66 kb upstream intronic intronic intronic 24 kb downstream 5’ near gene intronic nonsyn, coding intronic 24 kb upstream Supplementary Table 9. Top 20 single SNPs from four published GWASs for type 1 diabetes yielding the lowest P value in any of the four GWASs is shown. SNP rs2476601 rs2292239 rs12708716 rs17696736 rs3825932 rs11755527 rs1990760 rs100446 rs6356 rs763361 rs1445898 rs10255021 rs229541 rs3764021 rs17388568 rs380421 rs6017667 rs6897932 rs6546909 rs213950 P value 2.07E-80 1.52E-20 2.57E-18 2.31E-16 3.17E-15 4.66E-12 1.77E-11 6.75E-11 2.70E-09 1.38E-08 1.45E-08 1.71E-08 1.98E-08 5.80E-08 6.35E-07 8.84E-07 1.78E-06 7.70E-06 8.53E-06 1.95E-05 Locus 1p13.2 12q13.2 16p13.13 12q24.13 15q25.1 6q15 2q24.2 11p15.5 11p15.5 18q22.2 5p13.2 7q21.3 22q12.3 12p13.31 4q27 20q13.12 20q13.12 5p13.2 2p13.1 7q31.2 Gene PTPN22 ERBB3 CLEC16A C12orf30 CTSH BACH2 IFIH1 INS TH CD226 CAPSL COL1A2 C1QTNF6 CLEC2D ADA1 SPINT2 SPINT4 IL7R DQX1 CFTR Position within gene nonsyn, coding intronic intronic intronic intronic intronic nonsyn, coding intronic nonsyn, coding nonsyn, coding nonsyn, coding intronic intronic nonsyn, coding intronic nonsyn, coding nonsyn, coding nonsyn, coding syn, coding nonsyn, coding GWAS reference (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (2) (1) (1) (2) (1) (3) (4) (3) (1) (1) (4) (4) (2) (1) 6-9 . For each gene, the SNP GWAS reference (7) (7) (7) (7) (9) (9) (7) (8) (8) (7) (7) (8) (9) (6) (6) (7) (7) (7) (6) (7) Supplementary Table 9 - continued. Top 20 single SNPs from four published GWASs for Crohn’s disease gene, the SNP yielding the lowest p value in any of the four GWASs is shown. SNP rs11465804 rs3828309 rs2076756 rs2301436 rs3197999 rs744166 rs4263839 rs11175593 rs6908425 rs2274910 rs4807569 rs3763313 rs2476601 rs780094 rs12529198 rs9858542 rs1131095 rs17309827 rs1925411 rs13003464 P value 6.66E-63 2.36E-32 7.01E-14 1.04E-12 1.15E-12 6.82E-12 2.60E-10 3.08E-10 8.96E-10 1.46E-09 2.12E-09 5.20E-09 1.46E-08 3.14E-07 6.96E-07 7.70E-07 1.21E-06 2.08E-06 3.58E-06 4.60E-06 Locus 1p31.3 2q37.1 16q12.1 6q27 3p21.31 17q21.2 9q32 12q12 6p22.3 1q23.3 19p13.3 6p21.32 1p13.2 2p23.3 6p25.1 3p21.31 3p21.31 6p25.2 1p31.3 2p16.1 Gene IL23R ATG16L1 NOD2 FGFR1OP MST1 STAT3 TNFSF15 LRRK2 CDKAL1 ITLN1 SBNO2 BTNL2 PTPN22 GCKR LYRM4 BSN APEH SLC22A23 WDR78 PUS10 Position within gene intronic intronic intronic intronic nonsyn, coding intronic intronic intronic intronic intronic intronic intronic nonsyn, coding intronic intronic syn, coding syn, coding intronic intronic intronic 6,10-12 For each GWAS reference (12) (12) (10) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (12) (6) (11) (12) (11) (12) Abbreviations: ASD(s), autism spectrum disorder(s); GWAS, genome-wide association study; GWASs, genome-wide association studies; nonsyn, nonsynonymous; SNP(s), single nucleotide polymorphism(s) * The size of each gene in kilobase (kb) was derived from its exact start and end positions according to the Ensembl Human Genome Browse (http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/). References 1. Wang K, Zhang H, Ma D, Bucan M, Glessner JT, Abrahams BS et al. Common genetic variants on 5p14.1 associate with autism spectrum disorders. Nature 2009; 459: 528-533. 2. Ma D, Salyakina D, Jaworski JM, Konidari I, Whitehead PL, Andersen AN et al. A genome-wide association study of autism reveals a common novel risk locus at 5p14.1. Ann Hum Genet 2009; 73: 263273. 3. Weiss LA, Arking DE, Brune CW, West K, O'Connor A, Hilton G. et al. A genome-wide linkage and association scan reveals novel loci for autism. Nature 2009; 461: 802-808. 4. Salyakina D, Ma DQ, Jaworski JM, Konidari I, Whitehead PL, Henson R et al. Variants in several genomic regions associated with asperger disorder. Autism Res 2010; 3: 303-310. 5. Hussman JP, Chung RH, Griswold AJ, Jaworski JM, Salyakina D, Ma D et al. A noise-reduction GWAS analysis implicates altered regulation of neurite outgrowth and guidance in autism. Mol Autism 2011; 2: 1. 6. Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661-678. 7. Todd JA, Walker NM, Cooper JD, Smyth DJ, Downes K, Plagnol V et al. Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 857-864. 8. Hakonarson H, Grant SF, Bradfield JP, Marchand L, Kim CE, Glessner JT et al. A genome-wide association study identifies KIAA0350 as a type 1 diabetes gene. Nature 2007; 448: 591-594. 9. Cooper JD, Smyth DJ, Smiles AM, Plagnol V, Walker NM, Allen JE et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association study data identifies additional type 1 diabetes risk loci. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1399-1401. 10. Rioux JD, Xavier RJ, Taylor KD, Silverberg MS, Goyette P, Huett A et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 596-604. 11. Raelson JV, Little RD, Ruether A, Fournier H, Paquin B, Van Eerdewegh P et al. Genome-wide association study for Crohn's disease in the Quebec Founder Population identifies multiple validated disease loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci. USA 2007; 104: 14747-14752. 12. Barrett JC, Hansoul S, Nicolae DL, Cho JH, Duerr RH, Rioux JD et al. Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn's disease. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 955-962.