Regional Outline for
advertisement
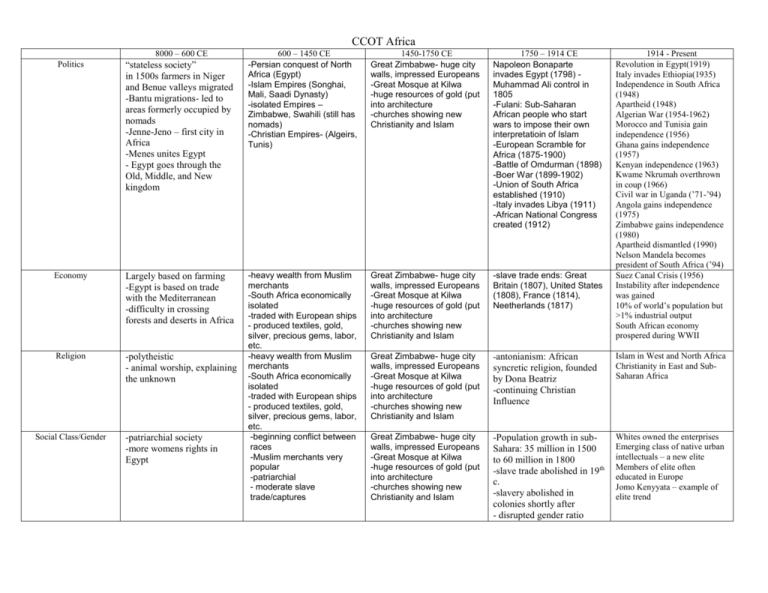
CCOT Africa 8000 – 600 CE Politics “stateless society” in 1500s farmers in Niger and Benue valleys migrated -Bantu migrations- led to areas formerly occupied by nomads -Jenne-Jeno – first city in Africa -Menes unites Egypt - Egypt goes through the Old, Middle, and New kingdom Economy Largely based on farming -Egypt is based on trade with the Mediterranean -difficulty in crossing forests and deserts in Africa Religion -polytheistic - animal worship, explaining the unknown Social Class/Gender -patriarchial society -more womens rights in Egypt 600 – 1450 CE -Persian conquest of North Africa (Egypt) -Islam Empires (Songhai, Mali, Saadi Dynasty) -isolated Empires – Zimbabwe, Swahili (still has nomads) -Christian Empires- (Algeirs, Tunis) 1450-1750 CE Great Zimbabwe- huge city walls, impressed Europeans -Great Mosque at Kilwa -huge resources of gold (put into architecture -churches showing new Christianity and Islam 1750 – 1914 CE Napoleon Bonaparte invades Egypt (1798) Muhammad Ali control in 1805 -Fulani: Sub-Saharan African people who start wars to impose their own interpretatioin of Islam -European Scramble for Africa (1875-1900) -Battle of Omdurman (1898) -Boer War (1899-1902) -Union of South Africa established (1910) -Italy invades Libya (1911) -African National Congress created (1912) -heavy wealth from Muslim merchants -South Africa economically isolated -traded with European ships - produced textiles, gold, silver, precious gems, labor, etc. -heavy wealth from Muslim merchants -South Africa economically isolated -traded with European ships - produced textiles, gold, silver, precious gems, labor, etc. -beginning conflict between races -Muslim merchants very popular -patriarchial - moderate slave trade/captures Great Zimbabwe- huge city walls, impressed Europeans -Great Mosque at Kilwa -huge resources of gold (put into architecture -churches showing new Christianity and Islam -slave trade ends: Great Britain (1807), United States (1808), France (1814), Neetherlands (1817) Great Zimbabwe- huge city walls, impressed Europeans -Great Mosque at Kilwa -huge resources of gold (put into architecture -churches showing new Christianity and Islam -antonianism: African Great Zimbabwe- huge city walls, impressed Europeans -Great Mosque at Kilwa -huge resources of gold (put into architecture -churches showing new Christianity and Islam -Population growth in subSahara: 35 million in 1500 to 60 million in 1800 -slave trade abolished in 19th c. -slavery abolished in colonies shortly after - disrupted gender ratio syncretic religion, founded by Dona Beatriz -continuing Christian Influence 1914 - Present Revolution in Egypt(1919) Italy invades Ethiopia(1935) Independence in South Africa (1948) Apartheid (1948) Algerian War (1954-1962) Morocco and Tunisia gain independence (1956) Ghana gains independence (1957) Kenyan independence (1963) Kwame Nkrumah overthrown in coup (1966) Civil war in Uganda (’71-’94) Angola gains independence (1975) Zimbabwe gains independence (1980) Apartheid dismantled (1990) Nelson Mandela becomes president of South Africa (’94) Suez Canal Crisis (1956) Instability after independence was gained 10% of world’s population but >1% industrial output South African economy prospered during WWII Islam in West and North Africa Christianity in East and SubSaharan Africa Whites owned the enterprises Emerging class of native urban intellectuals – a new elite Members of elite often educated in Europe Jomo Kenyyata – example of elite trend Science/Inventions Art/Architecture Geography -not particular cities, but rather small farming communities living close together -extensive roads to connect isolated city-states -use of materials to build churches/walls Kinship and clans remained unchanged at the local level Construction of the Suez Canal (1859-1869) Port facilities, railroads, roads, telegraph wires Great Zimbabwe- huge city walls, impressed Europeans -Great Mosque at Kilwa -huge resources of gold (put into architecture -churches showing new Christianity and Islam Great Zimbabwe- huge city walls, impressed Europeans -Great Mosque at Kilwa -huge resources of gold (put into architecture -churches showing new Christianity and Islam Timbuktu becomes intellectual center -Islamic universities -“blood” diamonds discovered -weaving -pottery -slavery creates African diaspora No information Swahili city=states of East Africa and West Africa was where Islam was very popular. Kingdom of Kongo and Kingdom of Ndongowere involved in slave trade with the Portuguese -vital part of Triangle Trade -still huge differences between North and South from separation of Saharan Desert People’s National Identity -Some based it on Geography Nations built along the borders that defined existing colonial states








