8 Cognitive Template- Leiter-R
advertisement
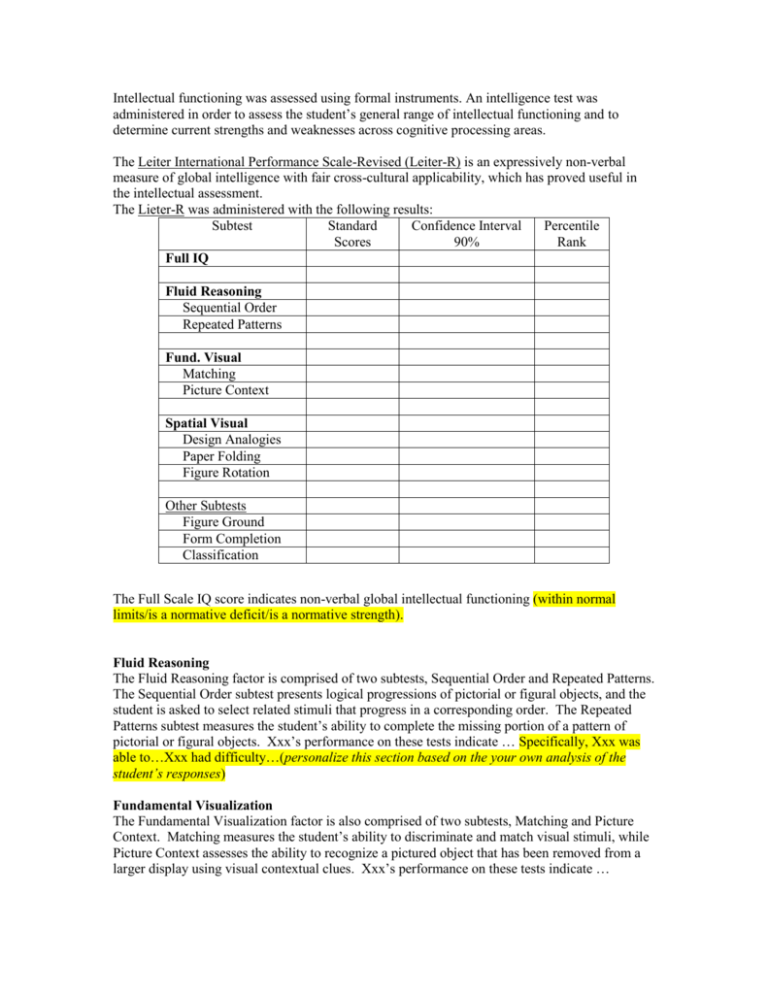
Intellectual functioning was assessed using formal instruments. An intelligence test was administered in order to assess the student’s general range of intellectual functioning and to determine current strengths and weaknesses across cognitive processing areas. The Leiter International Performance Scale-Revised (Leiter-R) is an expressively non-verbal measure of global intelligence with fair cross-cultural applicability, which has proved useful in the intellectual assessment. The Lieter-R was administered with the following results: Subtest Standard Confidence Interval Percentile Scores 90% Rank Full IQ Fluid Reasoning Sequential Order Repeated Patterns Fund. Visual Matching Picture Context Spatial Visual Design Analogies Paper Folding Figure Rotation Other Subtests Figure Ground Form Completion Classification The Full Scale IQ score indicates non-verbal global intellectual functioning (within normal limits/is a normative deficit/is a normative strength). Fluid Reasoning The Fluid Reasoning factor is comprised of two subtests, Sequential Order and Repeated Patterns. The Sequential Order subtest presents logical progressions of pictorial or figural objects, and the student is asked to select related stimuli that progress in a corresponding order. The Repeated Patterns subtest measures the student’s ability to complete the missing portion of a pattern of pictorial or figural objects. Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) Fundamental Visualization The Fundamental Visualization factor is also comprised of two subtests, Matching and Picture Context. Matching measures the student’s ability to discriminate and match visual stimuli, while Picture Context assesses the ability to recognize a pictured object that has been removed from a larger display using visual contextual clues. Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) Spatial Visual The Spatial Visual factor is comprised of Design Analogies, Paper Folding, and Figure Rotation. Design Analogies measures a student’s ability to solve matrix analogies and mentally rotate figures. Paper Folding measures a student’s ability to mentally “fold” a 2-D object and match it to a target. Figure Rotation assesses a student’s ability to mentally rotate objects and geometric figures. Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) Other Subtests There are three other subtests of the Leiter-R that are administered to children Xxx’s age. The Figure Ground subtest measures the child’s ability to identify embedded figures or designs within a complex stimulus or visual field. Form Completion measures the child’s facility in recognizing a whole object from a randomly-displayed array of its fragmented parts. Finally, Classification assesses the child’s ability to categorize objects or geometric designs. Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) OR—if using a CHC model to interpret IQ, use the table and text below. Also note that if using the CHC model, you can only use below average (84 and below), average (85-115), and above average (above 115) for descriptive ranges. Please note that you must also administer subtests from other batteries to obtain cluster scores for Gc, Ga, and Gsm and one additional subtest for Gs. The Lieter-R was administered with the following results (the CHC processing area cluster scores are based on calculations from the Essentials of Cross Battery Assessment, Second Edition): Subtest/Cluster* Standard Confidence Percentile Scores Interval Rank 90% Full IQ Fluid Intelligence (Gf) Classification Design Analogies Picture Context Repeated Patterns Sequential Order Visual Coding Long-Term Retrieval (Glr) Associated Pairs Delayed Pairs Delayed Recognition Visual Processing (Gv) Figure Ground Figure Rotation Form Completion Forward Memory Immediate Recognition Matching Paper Folding Processing Speed (Gs) Attention Sustained The Full Scale IQ score indicates non-verbal global intellectual functioning to be within the *average range. Fluid Intelligence (Gf) Fluid intelligence is the ability to use and engage in various mental operations when faced with a relatively novel task that cannot be performed automatically. This cluster is composed of Classification, Design Analogies, Repeated Patterns, and Sequential Order (measures of Induction, which is the ability to discover the underlying characteristic that governs a problem or set of materials) and Picture Context and Visual Coding (measures of general sequential reasoning, which is the ability to start with stated rules, premises, or conditions and to engage in one or more steps to reach a solution to a problem). Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) Long-Term Retrieval (Glr) Long-term retrieval is the ability to store information (e.g., concepts, ideas, items, or names) in long-term memory and to retrieve it later fluently through association. This cluster is composed of Associated Pairs, Delayed Pairs, and Delayed Recognition (measures of associative memory, which is the ability to recall one part of a previously learned but unrelated pair of items when the other part is presented). Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) Visual Processing (Gv) Visual processing is the ability to generate, perceive, analyze, synthesize, manipulate, transform, and think with visual patterns and stimuli. This cluster is composed of Figure Ground (measure of flexibility of closure, which is the ability to identify a visual figure or pattern embedded in a complex visual array, when knowing in advance what the pattern is), Figure Rotation (measure of spatial relations, which is the ability to perceive and manipulate visual patterns rapidly or to maintain orientation with respect to objects in space), Form Completion, Matching, and Paper Folding (measures of Visualization, which is the ability to manipulate objects or visual patterns and to “see” how they would appear under altered conditions) and Forward Memory and Immediate Recognition (measures of Visual Memory, which is the ability to form and store a mental representation or image of a visual stimulus and then recognize or recall it later). Xxx’s performance on these tests indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses) Processing Speed (Gs) Processing speed is the ability to perform cognitive tasks fluently and automatically, especially when under pressure to maintain focused attention and concentration. Processing Speed is measured by the subtest Attention Sustained (measures Perceptual Speed, the ability to search and compare visual symbols rapidly when presented side-by-side or separated in a visual field, and Rate-of-Test-Taking, the ability to perform tests that are relatively easy or that require very simple decisions rapidly). Xxx’s performance on this test indicate … Specifically, Xxx was able to…Xxx had difficulty…(personalize this section based on the your own analysis of the student’s responses)