milestone 5 – process modeling
advertisement

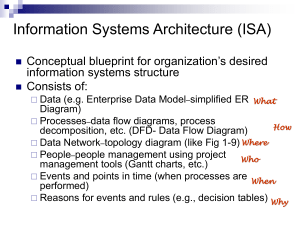
SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-1 MILESTONE 5 – PROCESS MODELING Synopsis rocess modeling is a technique for organizing and documenting the structure and flow of data through a system’s processes and/or the logic, policies, and procedures to be implemented by a system’s processes. In this milestone, you focus on using and constructing data flow diagrams (DFDs) and decomposition diagrams to perform process modeling. P Data flow diagrams are tools that depict the flow of data through a system and the work or processing performed by that system. A decomposition diagram is a DFD planning tool that shows the top-down functional decomposition and structure of a system. During this milestone, you will first construct a context diagram to establish project scope and boundaries. Second, you will draw a functional decomposition diagram to partition the system into logical subsystems and/or functions. Third, you will draw event decomposition diagrams to model individual processes. Finally, you will construct a system data flow diagram that shows the big picture of the system, and a primitive data flow diagram for a single event process. Objectives After completing this milestone, you should be able to: Construct a context diagram to illustrate a system’s interfaces with its environment. Identify external and temporal business events for a system. Logically group events to create a functional decomposition diagram. Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001 SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-2 Create event diagrams. Merge event diagrams into a system data flow diagram. Draw appropriate primitive data flow diagrams. Prerequisites 1. Process modeling – Chapter 8 2. Optional: Milestone 3 or 4 solution Assignment As a systems analyst or knowledgeable end-user, you must learn how to draw decomposition and data flow diagrams to model business process requirements. The preliminary investigation and problem analysis phases of the methodology have been completed, and you understand the current system’s strengths, weaknesses, limitations, problems, opportunities, and constraints. As part of a requirements analysis phase, you have already built the data model (Milestones 3 and 4) to document business data requirements for the new system. You now need to build the corresponding process models. Activities 1. Draw a Context Diagram using the accompanying narrative. 2. Given the accompanying use-case (event/response) matrix, draw the Functional Decomposition Diagram. 3. Given your decomposition diagram from above and the use-case matrix, draw Event Decomposition Diagrams. Your instructor will tell you which ones to draw. Use your data model from milestones 3 and 4 as an attribute reference. Also, state any assumptions you make. 4. Merge your event diagrams from #3 above into a System Diagram. 5. For all transaction processes described in the accompanying narratives, draw the Primitive Data Flow Diagram. Deliverable format and software to be used are according to your instructor’s specifications. Deliverables should be neatly packaged in a binder, separated with a tab divider labeled “Milestone 5.” Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001 SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-3 References: Completed Data Model Solution from Milestone 4 Context Diagram Narrative Exhibit 5.1 Completed Use-Case (or Event-Response) List Exhibit 5.2 Primitive Diagram Narrative(s) Exhibit 5.3 Deliverables: Context Diagram: Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ Functional Decomposition Diagram: Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ Event Decomposition Diagrams: Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ System Diagram: Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ Primitive Diagram(s): Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001 SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-4 ALTERNATIVE OPTION Exhibit 5.2 is a partial Use-Case list. Add all maintenance and report UseCases necessary to match the system narrative in Exhibit 5.1. Then draw the Event Decomposition Diagrams and the System Diagram based on the complete list. Use-cases: Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ Activity diagrams and state models: Due: __/__/__ Time:_______ Milestone’s Point Value: Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman _______ Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001 SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-5 Exhibit 5.1 Use the following narrative to construct the Context Diagram for the IT Tracker system The purpose of the IT Tracker system is to provide a single central repository of all information about information technology equipment, including its purchase information, history of installed components, service requests, and responses to those requests. Users will submit service requests to the system whenever they have a problem with their equipment. Users will also be able to check on the status of their service requests at any time. In response to a submitted service request, the IT director will assign each request to a technician. The technicians will be able to view a list of their assignments at any time. As they respond to and fix problems, technicians will enter service information. If they replace parts or entire machines, they will also enter new equipment and component change information. To help technicians do their jobs, they will be able to view reports of the service and component installation history of any machine. The IT director will be able to view various management reports such as the service and component installation history of any machine, service requests and responses for any period of time, a list of machines by department, and the work history for any technician. The IT director will also be able to view a “digital dashboard” of key statistics and trends. Purchase Order information is created and updated in a separate system located on a mainframe computer. However, that information will be available to IT Tracker on a read-only basis to help in tracking warranty information. IT Tracker will allow technicians and the IT director to view the complete information on any purchase order and for technicians to reference a specific purchase order number when entering component installation information. Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001 SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-6 Exhibit 5.2 Below is a Use-Case list for the major processes of the system. To keep the assignment simple, most “maintenance” events, such as adding new technicians and departments and edit/delete options have been ignored along with some of the reports. Actor Event (or Use Case) Trigger Responses Tech Add equipment New equipment is installed Create new Equipment in database Tech Add component to a computer New component is installed Create new Installed Component in database Tech Remove component from a computer Old component is removed Update Installed Component information in database Technology User Add service request User finds problem Create new Service Request in database Send e-mail to IT Director IT Director View open requests for service Upon request Generate Open Requests report IT Director Assign service request to a technician Decision by IT Director Update Service Request information in database Tech or IT Director View list of service assignments for a technician Upon request Generate Tech Assignment report Tech or IT Director View service and component history for a machine Upon request Generate Machine History report Tech Add service record Tech performs service work Create new Service Response in database (Time) Import purchase order info Nightly Update Purchase Order info in database Technology User or IT Director View service request status Upon request Generate Service Request Status report IT Director Report Digital Dashboard of service response times, total cost of ownership, technician utilization Upon request Generate Digital Dashboard Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001 SADM 5/ed – CASE STUDY 4 – Milestone 5: Process Modeling Page: 5-7 Exhibit 5.3 Use the following narrative to construct the Primitive Diagram for the Add Service Request event. The User enters the Equipment ID, Problem Description, the User’s name, and the User’s telephone extension. The system will verify the Equipment ID by checking it against the list of Equipment IDs in the system. If it is not valid, send an error response to the User. If it is valid, set the Report Date to the current date and add the service request to the ServiceRequest data store. Generate e-mail to IT Director. Prepared by Gary B. Randolph for Systems Analysis & Design Methods 5ed by J. L. Whitten, L. D. Bentley, & K. C. Dittman Copyright Irwin/McGraw-Hill 2001