10.3 NEUTRALIZATION REACTIONS
advertisement
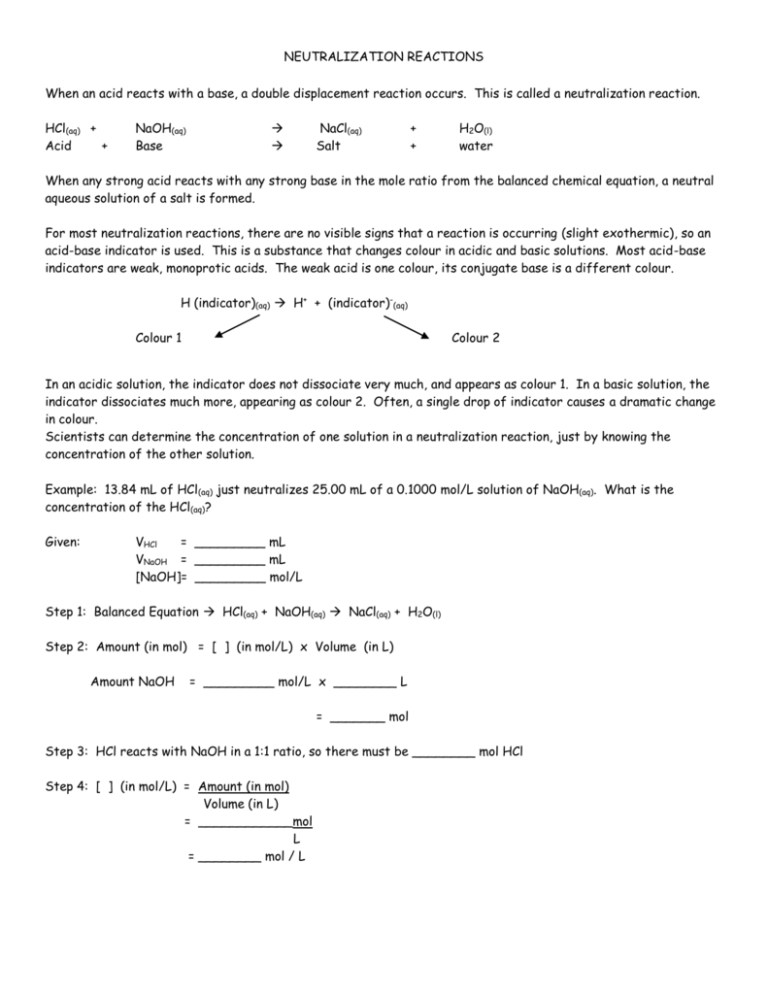
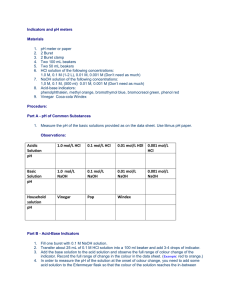
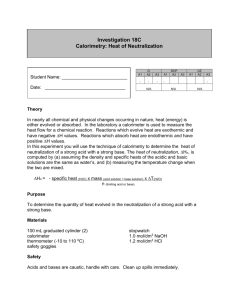
NEUTRALIZATION REACTIONS When an acid reacts with a base, a double displacement reaction occurs. This is called a neutralization reaction. HCl(aq) + Acid + NaOH(aq) Base NaCl(aq) Salt + + H2O(l) water When any strong acid reacts with any strong base in the mole ratio from the balanced chemical equation, a neutral aqueous solution of a salt is formed. For most neutralization reactions, there are no visible signs that a reaction is occurring (slight exothermic), so an acid-base indicator is used. This is a substance that changes colour in acidic and basic solutions. Most acid-base indicators are weak, monoprotic acids. The weak acid is one colour, its conjugate base is a different colour. H (indicator)(aq) H+ + (indicator)-(aq) Colour 1 Colour 2 In an acidic solution, the indicator does not dissociate very much, and appears as colour 1. In a basic solution, the indicator dissociates much more, appearing as colour 2. Often, a single drop of indicator causes a dramatic change in colour. Scientists can determine the concentration of one solution in a neutralization reaction, just by knowing the concentration of the other solution. Example: 13.84 mL of HCl(aq) just neutralizes 25.00 mL of a 0.1000 mol/L solution of NaOH(aq). What is the concentration of the HCl(aq)? Given: VHCl = _________ mL VNaOH = _________ mL [NaOH]= _________ mol/L Step 1: Balanced Equation HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Step 2: Amount (in mol) = [ ] (in mol/L) x Volume (in L) Amount NaOH = _________ mol/L x ________ L = _______ mol Step 3: HCl reacts with NaOH in a 1:1 ratio, so there must be ________ mol HCl Step 4: [ ] (in mol/L) = Amount (in mol) Volume (in L) = ____________mol L = ________ mol / L