Persuasive text - Bundarra Central School
advertisement

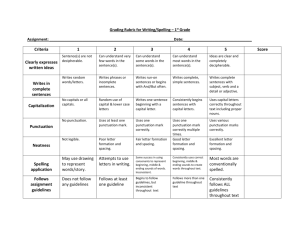
Persuasive Text Rubric – All Stages Feature Score 0 Score 1 Score 2 Score 3 Score 4 Score 5 Score 6 Text Structure - introduction -arguments -conclusion Scribes a basic orientation that identifies the issue and the writers opinion about it Writes a simple introduction that identifies the issue and argues by expressing the writer’s opinions about the issue Writes a statement of position that identifies the issue and provides: writer’s overall opinion, 3 supporting arguments, and rounds off the text in some way Writes a statement of position, at least three arguments and rounds off with a simple restatement of position. Includes a strong statement of position, a preview of the points being presented and at least three arguments. The reinforcement of position strongly concludes the text. Includes a forceful statement of position that previews the points being presented, developed arguments and a reinforcement of position that is emphatic. Has a forceful statement of position, a succinct preview of points, well-developed arguments and a reinforcement of position that is emphatic. Effective technical language and a range of persuasive devices are use effectively throughout the text. Arguments are developed with reasons that persuade Draws a picture and scribes or writes 1-2 sentences that gives an opinion about an issue with a supporting reason Writes a short text of at least 3-4 sentences that includes simple supporting arguments or opinion, briefly presents reason/s Writes a short persuasive text that provides arguments with at least one with 2 or 3 reason/s with some elaboration Writes a persuasive text in which most arguments contain a relevant point and a separate sentence that elaborates a reason or consequence Writes a detailed persuasive text, all arguments contain a relevant point and an elaboration of 1-2 sentences outlining the reasons or consequences Arguments successfully persuade. Most are elaborated and sustained across several sentences and are supported by evidence: researched information or statistics, reported viewpoints or quoted speech of experts or interested parties. Arguments effectively persuade. Elaborated arguments are sustained across several sentences and supported by evidence: researched information or statistics, reported viewpoints or quoted speech of experts or interested parties. Sentence Structure Can correctly structure some simple and/or compound sentences and copy models Most (50%) simple and compound sentences are correctly structured and attempts some (12) complex Nearly all simple and compound sentences are correctly structured and some (1-2) complex are correct (limited types) Nearly all simple and compound sentences correct and experiments with different types of complex with some success Nearly all simple and compound correct and demonstrates mostly correct complex structures, eg begins sentences with a dependent clause Simple and compound correct and demonstrates nearly all correct complex sentences throughout text with more variety and including non-finite clauses Variety of correctly structured sentences including many different complex structures throughout the text Vocabulary - precise words - persuasive language Uses only basic words including single simple adjectives and adverbial phrases to tell when and where. Uses basic nouns and verbs and some everyday adjectives to create noun groups. Uses everyday nouns, adjectives and verbs and adverbial phrases and may include 1-2 more precise words or words used to persuade. Uses everyday nouns, noun groups, verbs and verb groups with at least 3-4 precise words. Some persuasive words/phrases are demonstrated. Mostly uses everyday vocabulary but demonstrates at least 5 precise words or phrases including some persuasive language used effectively. Appropriate technical and evaluative language is use effectively across the text. A variety of persuasive devices demonstrated. Uses a range of deliberate word choices across the text including; examples of precise words, complex noun groups, literal comparisons, effective similes and personification Cohesion -pronouns -conjunctions -connectives Few or no cohesive devises except and and simple pronouns Limited cohesion within texts (either absent or some errors) may use common link words such as and, then Uses only some basic conjunctions and/or basic time connectives Uses pronouns and a few simple conjunctions to join ideas within texts; 1-2 more specific time connectives Uses pronouns, some different conjunctions and 3 or more temporal and causal connectives to join ideas within texts Correctly uses pronouns, varies conjunctions and uses a range of connectives to join ideas across a text Correctly uses pronouns, varies conjunctions and controls the use of a wider range of connectives to link meanings across a text Punctuation Some evidence of sentence punctuation Uses some sentence punctuation, eg full stops, capitals and question marks but is inconsistent Mostly uses correct sentence punctuation and some other correct punctuation eg speech marks, name capitals and commas in lists Most sentence punctuation correct and evidence of other correct punctuation, eg proper noun capitals & contraction apostrophes Nearly all correct sentence punctuation and other punctuation mostly correct, inverted commas, possessive apostrophes (there may be some omissions) Correct punctuation includes sentence markers, proper noun capitals, apostrophes, clause commas and most punctuation within speech marks Correct punctuation throughout a longer text including punctuation within speech marks and some other complex punctuation with few errors or omissions Handout 46 Handout 46