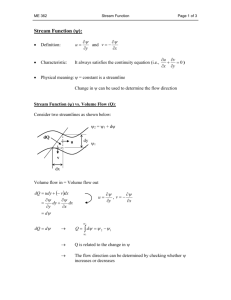
chap11 - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
advertisement

Elemental Geosystems, 5e (Christopherson) Chapter 11 River Systems and Landforms 1) At any one moment, approximately ________ of fresh water flows through Earth's rivers and streams. A) 1,250 km3 (300 mi3) B) 13,000 km3 (3,100 mi3) C) 104,000 km3 (25,000 mi3) D) 22 percent (an amount equal to that in groundwater) Answer: A 2) Of the world's largest rivers, which has the greatest discharge? A) Zaire (Congo) River B) Amazon River C) Missouri-Ohio-Mississippi river system D) Chang Chiang (Yangtze) of Asia Answer: B 3) Stream-related processes are termed A) hydrological. B) geomorphological. C) fluvial. D) erosion. Answer: C 4) Which of the following lists of processes are in the correct sequence as to their occurrence in nature? A) deposition, erosion, transport, weathering B) weathering, erosion, deposition, transport C) weathering, deposition, erosion, transport D) weathering, erosion, transport, deposition Answer: D 5) The general term for clay, silt, and sand deposited by running water is A) alluvium. B) dirt. C) soil. D) mud. Answer: A 6) John Wesley Powell put forward the idea of base level, which refers to A) an imagined surface that extends inland from sea level, and is inclined gently upward. B) a level below which a stream cannot erode its valley C) an evolutionary cycle of landscape development. D) flat plateaus. E) Both A and B are correct. Answer: E 7) The ultimate base level is A) an interior basin. B) a dam. C) sea level. D) all of these Answer: C 8) Which of the following may act as a base level? A) a lake that a river flows into B) sea level C) the upper surface of a waterfall D) all of these E) a lake that a river flows into and sea level only Answer: E 9) The degradation of a landscape by weathering, erosion, and transportation has an ultimate "goal" of reducing the landscape down to A) base level, namely sea level. B) continental shelf. C) the mountain tops. D) valley level. Answer: A 10) In response to the occurrence of a local base level, A) a stream continues to operate to reduce its landscape to sea level the ultimate base level. B) sediments accumulate upstream in response to the loss of flow velocity. C) sea level changes. D) This situation never occurs in nature. Answer: B 11) Watersheds are defined by A) continental divides. B) drainage divides. C) stream orders. D) fluvial units. Answer: B 12) Which of the following is incorrectly matched? A) rills small-scale indentations in the land surface B) drainage divides ridges that control drainage C) Allegheny and Missouri rivers form the Monongahela at Pittsburgh D) Delaware River basin composed of parts of five states Answer: C 13) Rivers east of the continental divide in the Rockies drain into the A) Pacific drainage. B) Hudson Bay/Arctic drainage. C) Gulf/Atlantic drainage. D) interior West drainage. Answer: C 14) Most of Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Ontario are in which major drainage basin? A) Hudson Bay B) Arctic C) Missouri D) Upper Mississippi Answer: A 15) Stream drainage patterns are determined by which of the following? A) slope B) differing rock resistance C) climatic and hydrologic variability D) all of these Answer: D 16) Which of the following landforms is incorrectly matched with a drainage pattern? A) volcano radial B) folded mountain belt trellis C) eroded dome annular D) topographically disrupted areas parallel Answer: D 17) The lengths of the individual channels in a dendritic drainage pattern are ________ and this increases energy ________. A) minimized; efficiency B) minimized; inefficiency C) maximized; efficiency D) maximized; inefficiency Answer: A 18) Rectangular drainage patterns form as a result of ________. A) differential resistance to erosion B) domal uplift C) flow through anticlinal and synclinal topography D) flow through a faulted landscape Answer: D 19) Which of the following stream channel types is likely to develop on gently sloping surfaces composed of rocks or sediments with approximately the same resistance to erosion? (Also assume that there are no structural controls on the pattern's development.) A) radial B) annular C) deranged D) dendritic Answer: D 20) Which drainage pattern is controlled by rock structures of variable resistance and folded strata? A) radial B) dendritic C) deranged D) trellis Answer: D 21) Steep slopes and some relief generally produce which drainage pattern? A) dendritic B) deranged C) parallel D) annular Answer: C 22) A central peak, or a dome of a volcanic mountain, generally produces ________ drainage patterns. A) radial B) trellis C) parallel D) annular Answer: A 23) The glaciated shield regions of Canada and northern Europe have disrupted surface drainage patterns that are called ________ patterns. A) trellis B) parallel C) annular D) deranged Answer: D 24) Stream capture refers to A) the legal process by which a state secures rights to the waters of a river basin. B) the merging of two streams flowing in the same valley. C) the process by which one channel erodes through a drainage divide and captures the headwater regions of another stream. D) the illegal withdrawal of water from a river. Answer: C 25) As the discharge of a stream increases, which of the following also happens? A) Stream channels narrow, become shallower, and lose velocity. B) The rate of flow decreases. C) Channel width increases but channel depth decreases. D) Width, depth, and velocity all increase. Answer: D 26) Consider the equation Q = wdv. According to the equation, if Q (discharge) remains constant, but w and d decrease (as when a channel becomes more narrow and shallow), the velocity will A) increase. B) decrease. C) remain constant. Answer: A 27) The San Juan River near Bluff, Utah, flooded in 1941 producing A) decreased discharge. B) a deepening of the channel, followed by subsequent filling. C) a lack of equilibrium to balance discharge, velocity, and sediment load. D) a surprising lack of response in the river channel. Answer: B 28) Which of the following is incorrectly matched? A) abrasion a hydraulic squeeze-and-release action B) competence a stream's ability to move particles of a specific size C) capacity the total possible load that a stream can transport D) fine particles physically held aloft in a stream suspended load E) particles rolled and bounced along a stream bed saltation Answer: A 29) Stream transport involves all of the following except A) saltation. B) bed load. C) traction. D) sheet flow. Answer: D 30) The largest material that can be carried by a stream is carried as A) bed load. B) suspended load. C) dissolved load. D) truck load. Answer: A 31) The suspended load of a stream consists of particles that are A) rolled and bounced along the stream bed. B) held aloft in the stream flow. C) dragged along the stream bed. D) in solution. Answer: B 32) Which of the following rock types is most affected by fluvial solution? A) granite B) sandstone C) rhyolite D) limestone Answer: D 33) If you journeyed to the headwaters of the Rio Grande River in New Mexico, you would find that the material in the channel consists of large cobbles and boulders. However, if you then traveled to the mouth of the river as it enters the Gulf of Mexico, you would find that the channel bed material is composed of sand and silt. The process responsible for this type of change in sediment size is A) solution. B) abrasion. C) hydraulic action. D) suspension. Answer: B 34) The downstream portion of a river A) generally becomes more sluggish. B) generally is of higher velocity, although it is masked by reduced turbulence. C) features greater hydraulic action than do upstream portions. D) has lower discharges than do upstream portions. Answer: B 35) The total possible load a stream can transport is its ________, whereas a stream's ability to move particles of specific size is its ________. A) capacity; competence B) competence; capacity C) discharge; competence D) bed load; sediment load Answer: A 36) As a stream's carrying capacity decreases, which of the following sizes of sediments will be deposited last? A) gravel B) sand C) silt D) clay Answer: D 37) As base level is approached by a stream, the ability of a stream to erode its bed A) increases. B) decreases. C) remains constant. Answer: B 38) If the capacity of a stream is exceeded, ________ will occur. A) downcutting B) erosion of valley walls C) aggradation D) downcutting and erosion of valley walls Answer: C 39) The construction of a dam across a river is likely to cause ________ upstream and ________ downstream. A) erosion; aggradation B) erosion; erosion C) aggradation; erosion D) aggradation; aggradation Answer: C 40) Which of the following stream channel forms is likely to develop when aggradation greatly exceeds erosion? A) V-shaped valleys B) braided channels C) meandering channels D) straight, steep-walled channels Answer: B 41) Increased velocity and a rough channel can produce a A) turbulent flow. B) laminar flow. C) maximum velocity. D) decreased capacity. Answer: A 42) An increase in turbulence A) results in deposition of sediment. B) results in aggradation. C) causes terraces to form. D) increases the river's erosive power. Answer: D 43) A meandering stream is one that is A) completely stable. B) completely unstable. C) delicately balanced between equilibrium and chaos. D) closed in terms of energy and matter input. Answer: C 44) Which of the following is likely to occur if the gradient of a stream increases? (Assume that the discharge and sediment load remain unchanged.) A) The stream will begin to deposit more of its load. B) The amount of aggradation in the channel will increase. C) The amount of bed load transport will decrease. D) The stream will begin to erode its channel and/or its banks. Answer: D 45) The maximum velocity line in a stream is A) near the bottom. B) near the inside of a meander. C) at the center and near the surface, corresponding with the deepest parts of the stream channel. D) at the center and near the surface, corresponding with the shallowest parts of the stream channel. Answer: C 46) If you wanted to build a structure along a river especially one that flows through unconsolidated sediments you should build the structure ________ to maximize its lifetime. A) along the cutbank B) above the point bar C) in a delta D) Any of these is equally safe. Answer: B 47) Which of the following is incorrectly matched? A) cut bank outer portion of a stream meander B) point bar area of substantial erosion C) aggradation sediment accumulation in the stream channel D) braided stream maze of interconnected channels Answer: B 48) A cutoff on a meandering stream results in the formation of A) an oxbow lake. B) a levee. C) a point bar. D) a terrace. Answer: A 49) If a stream has just the gradient and discharge to transport its sediment load, it is said to be A) "fit." B) competent. C) graded. D) in a nonequilibrium state. Answer: C 50) Which of the following is true of the longitudinal profile of most rivers? A) It always changes at a constant rate from the headwater region to the sea. B) It is convex in shape. C) It is concave in shape. D) It is gentle upstream and steep downstream. Answer: C 51) An interruption in a stream's graded profile of equilibrium is called a A) gradation. B) longitudinal interruption. C) base level. D) nickpoint. Answer: D 52) According to classical theories for the evolution of a landscape, the stage of maturity exists when a stream has A) cut a "V"-shaped canyon in a bluff. B) developed a rough, abrupt profile. C) begun to cut laterally (side-to-side) into the banks, beginning a floodplain. D) begun to cut downward. Answer: C 53) Which of the following is not a feature of a rejuvenated landscape? A) entrenched meanders B) the San Juan River near Mexican Hat, Utah C) a broad, nearly level floodplain D) the Colorado River through the Colorado Plateau Answer: C 54) Which of the following is incorrect regarding floodplains? A) They are formed by recurrent flooding in the area adjacent to the stream. B) Natural levees on either side of a stream are formed during times when the stream is at flood stage and overflows the bank. C) They are generally low-lying areas. D) They are characterized by rapids and low waterfalls. Answer: D 55) Natural levees are created during A) floods. B) normal flow conditions. C) low flow conditions. D) None of the above all levees are manmade. Answer: A 56) The average size of sediment in a natural levee is ________ that found in the surrounding floodplain. A) larger than B) smaller than C) the same size as Answer: A 57) A tributary that is physically unable to join the main channel on a floodplain is called a/n A) alluvial stream. B) yazoo tributary. C) levee tributary. D) meandering tributary. Answer: B 58) The primary cause of terrace formation is A) an increase in channel load. B) a decrease in flood frequency. C) an increase in a river's velocity. D) flow through loose sediment. Answer: C 59) Terraces can form as a result of A) erosion. B) rejuvenation. C) uplift. D) all of these E) none of these Answer: D 60) When a river reaches a base level, its forward velocity rapidly decelerates as it enters a larger body of standing water and ________ is formed. A) an estuary B) an alluvial terrace C) a delta D) a stream terrace Answer: C 61) Which of the following is true of the Mississippi River and New Orleans? A) The possibility of a sudden, major shift in the river's course now exists. B) New Orleans could become a "city without a river." C) Accumulation of sediments in the Mississippi Delta has caused portions of New Orleans to sink below sea level. D) All of the above are true. E) A and B are true. Answer: D 62) Which of the following is used to measure streamflow? A) stilling well and staff gauge B) barometer and sling psychrometer C) statistical methods of probability D) reservoirs Answer: A 63) The effect of urbanization on a typical stream hydrograph is to A) create a base flow. B) increase lag time between storm peak and peak stream discharge. C) decrease runoff. D) decrease lag time between storm peak and peak stream discharge. Answer: D 64) If you live in an area that was flooded by the 100-year flood last year, you can conclude that A) the next 100-year flood will occur in exactly 100 years. B) the next 100-year flood will occur in exactly 99 years. C) you could be flooded by the 100-year flood again this year. D) you do not have to worry about another flood of that size during your lifetime. Answer: C 65) The Nile delta is shrinking because A) manmade distributaries have been added for farming purposes. B) sediment loads are deposited before reaching the coast. C) ocean currents have increased along the coastline. D) the Mediterranean Basin is subsiding, thereby steepening the coastal margin. E) both A and B Answer: E 66) Which of the following is true of the Mississippi River? A) It is in danger of jumping channels into the Atchafalaya River. B) Human development in coastal wetlands have increased hurricane damage protection for the interior lands. C) The disastrous flooding of New Orleans in 2005 was completely unpredicted. D) Within Bayou Laforche, houses built on stilts were protected from Hurricane Katrina. Answer: A 67) Because rivers constitute such a small percentage of the earth's total water supply, they play a small role in landform change. Answer: True False 68) A floodplain consists of alluvium. Answer: True False 69) A major drainage basin consists of a single watershed. Answer: True False 70) Stream width, depth, and velocity are all responsive to discharge rates. Answer: True False 71) The suspended load of a stream's transportation refers to those coarser materials that are dragged along the stream bed. Answer: True False 72) The increased velocity downstream in the Mississippi River is masked by its reduced turbulence. Answer: True False 73) Erosion of the valley walls of a channel normally occurs on the outside curve of a meander. Answer: True False 74) When a stream is graded (at grade), it has attained its lowest possible gradient and slowest flow velocity. Answer: True False 75) Nickpoints migrate downstream. Answer: True False 76) Aggradation of a stream channel produces scouring and alluvial terraces. Answer: True False 77) Terraces form when a river's energy increases. Answer: True False 78) Flood control often produces conditions of worse flooding in subsequent high-water events. Answer: True False 79) Deforestation in the headwater regions of a river can cause the river to flood more frequently in downstream areas. Answer: True False 80) A flood recurrence interval of 100 years means that floods of that size will occur only once every 100 years. Answer: True False 81) Historically, zoning laws regarding floodplain use have been strictly adhered to, thereby diminishing the amount of damage done during floods. Answer: True False 82) The construction of levees can actually increase the risk of a catastrophic flood. Answer: True False 83) Rivers make excellent political boundaries since they are clearly defined landform features. Answer: True False